Abstract
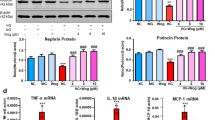
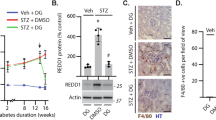
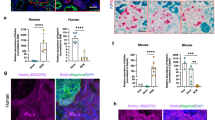
Hyperglycemia-caused podocyte injury plays a crucial role in the progress of diabetic kidney disease. Podoplanin, one of the podocyte-associated molecules, is closely related to the integrity of the glomerular filtration barrier. A number of studies demonstrate that berberine could ameliorate renal dysfunction in diabetic mice with nephropathy, but the molecular mechanisms have not been fully elucidated. In this study, we explored the relationship between the renoprotective effect of berberine and podoplanin expression in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice as well as mouse podocytes (MPC5 cells) cultured in high glucose (HG, 30 mM) medium. We found that the expression levels of podoplanin were significantly decreased both in the renal glomerulus of STZ-induced diabetic mice and HG-cultured MPC5 cells. We also demonstrated that NF-κB signaling pathway was activated in MPC5 cells under HG condition, which downregulated the expression level of podoplanin, thus leading to increased podocyte apoptosis. Administration of berberine (100, 200 mg/kg every day, ig, for 8 weeks) significantly improved hyperglycemia and the renal function of STZ-induced diabetic mice and restored the expression level of podoplanin in renal glomerulus. In high glucose-cultured MPC5 cells, treatment with berberine (30–120 μM) dose-dependently decreased the apoptosis rate, increased the expression of podoplanin, and inhibited the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway. When podoplanin expression was silenced with shRNA, berberine treatment still inhibited the NF-κB signaling pathway, but its antiapoptotic effect on podocytes almost disappeared. Our results suggest that berberine inhibits the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway, thus increasing the podoplanin expression to exert renoprotective effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Foley RN, Collins AJ. The USRDS: what you need to know about what it can and can’t tell us about ESRD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;8:845–51.
Reutens AT. Epidemiology of diabetic kidney disease. Med Clin North Am. 2013;97:1–18.
Ali IH, Brazil DP. Under the right conditions: protecting podocytes from diabetes-induced damage. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4:119.
Gnudi L, Coward RJM, Long DA. Diabetic nephropathy: perspective on novel molecular mechanisms. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016;27:820–30.
Lal MA, Patrakka J. Understanding podocyte biology to develop novel kidney therapeutics. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:409.
Dumont V, Tolvanen TA, Kuusela S, Wang H, Nyman TA, Lindfors S, et al. PACSIN2 accelerates nephrin trafficking and is up-regulated in diabetic kidney disease. FASEB J. 2017;31:3978–90.
Liu Y, Su H, Ma C, Ji D, Zheng X, Wang P, et al. IQGAP1 mediates podocyte injury in diabetic kidney disease by regulating nephrin endocytosis. Cell Signal. 2019;59:13–23.
Huang N, Zhang X, Jiang Y, Mei H, Zhang L, Zhang Q, et al. Increased levels of serum pigment epithelium-derived factor aggravate proteinuria via induction of podocyte actin rearrangement. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019;51:359–67.
Fang J, Wei H, Sun Y, Zhang X, Liu W, Chang Q, et al. Regulation of podocalyxin expression in the kidney of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats with Chinese herbs (Yishen capsule). BMC Complement Alter Med. 2013;13:76.
Breiteneder-Geleff S, Matsui K, Soleiman A, Meraner P, Poczewski H, Kalt R, et al. Podoplanin, novel 43-kd membrane protein of glomerular epithelial cells, is down-regulated in puromycin nephrosis. Am J Pathol. 1997;151:1141–52.
Matsui K, Breiteneder-Geleff S, Kerjaschki D. Epitope-specific antibodies to the 43-kD glomerular membrane protein podoplanin cause proteinuria and rapid flattening of podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:2013–26.
Zhang K, Barragan-Adjemian C, Ye L, Kotha S, Dallas M, Lu Y, et al. E11/gp38 selective expression in osteocytes: regulation by mechanical strain and role in dendrite elongation. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:4539–52.
Chen C, Yu Z, Li Y, Fichna J, Storr M. Effects of berberine in the gastrointestinal tract - a review of actions and therapeutic implications. Am J Chin Med. 2014;42:1053–70.
Xu L, Zhao W, Wang D, Ma X. Chinese medicine in the battle against obesity and metabolic diseases. Front Physiol. 2018;9:850.
Zhang X, Guan T, Yang B, Chi Z, Wan Q, Gu HF. Protective effect of berberine on high glucose and hypoxia-induced apoptosis via the modulation of HIF-1alpha in renal tubular epithelial cells. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:669–82.
Liu W, Zhang X, Liu P, Shen X, Lan T, Li W, et al. Effects of berberine on matrix accumulation and NF-kappa B signal pathway in alloxan-induced diabetic mice with renal injury. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;638:150–5.
Zhu L, Han J, Yuan R, Xue L, Pang W. Berberine ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Biol Res. 2018;51:9.
Tesch GH, Allen TJ. Rodent models of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton). 2007;12:261–6.
Mundel P, Reiser J, Zuniga Mejia Borja A, Pavenstadt H, Davidson GR, Kriz W, et al. Rearrangements of the cytoskeleton and cell contacts induce process formation during differentiation of conditionally immortalized mouse podocyte cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 1997;236:248–58.
Xavier LL, Viola GG, Ferraz AC, Da Cunha C, Deonizio JM, Netto CA, et al. A simple and fast densitometric method for the analysis of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in the substantia nigra pars compacta and in the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 2005;16:58–64.
Liu R, Zhong Y, Li X, Chen H, Jim B, Zhou MM, et al. Role of transcription factor acetylation in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes. 2014;63:2440–53.
Mora C, Navarro JF. The role of inflammation as a pathogenic factor in the development of renal disease in diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2005;5:399–401.
Yi B, Hu X, Zhang H, Huang J, Liu J, Hu J, et al. Nuclear NF-kappaB p65 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells correlates with urinary MCP-1, RANTES and the severity of type 2 diabetic nephropathy. PLoS One. 2014;9:e99633.
Kuhad A, Chopra K. Attenuation of diabetic nephropathy by tocotrienol: involvement of NFkB signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2009;84:296–301.
Zhang X, He H, Liang D, Jiang Y, Liang W, Chi ZH, et al. Protective effects of berberine on renal injury in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:1327.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the China Diabetes Young Scientific Talent Research Funding.
Author contributions
KQZ and JY contributed to the development of the project and experimental design, and JY, GNZ, and HW contributed to the performance of experiments and data analysis. All authors contributed to the paper writing and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Zong, Gn., Wu, H. et al. Podoplanin mediates the renoprotective effect of berberine on diabetic kidney disease in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40, 1544–1554 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0263-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0263-3
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The irreversible, towards fatalic neuropathy: from the genesis of diabetes
Acta Diabetologica (2024)
-
Mechanisms and efficacy of traditional Chinese herb monomers in diabetic kidney disease
International Urology and Nephrology (2023)
-
Effects of alkaloids on peripheral neuropathic pain: a review
Chinese Medicine (2020)