Abstract
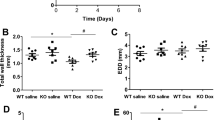
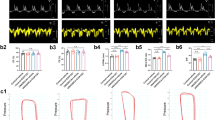
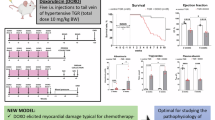
Doxorubicin (Dox) is an effective chemotherapy drug against a wide range of cancers, including both hematological and solid tumors. However, the serious cardiotoxic effect restricted its clinical application. We previously have illuminated the protective role of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling in Dox-induced cardiotoxicity. Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (sFRP1) is one of the endogenous inhibitors of both canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling. In this study, we investigated the relationship between sFRP1 and noncanonical Wnt/PCP-JNK (Wnt/planar cell polarity-c-Jun N-terminal kinase) pathway in Dox-induced cardiotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. We showed that treatment of H9c2 cardiac myoblasts with Dox (1 μM) time-dependently suppressed cell viability accompanied by significantly decreased sFRP1 protein level and increased Wnt/PCP-JNK signaling. Pretreatment with SP600125, the Wnt/PCP-JNK signaling inhibitor, attenuated Dox-induced apoptosis of H9c2 cells. Overexpression of sFRP1 protected H9c2 cells from Dox-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the Wnt/PCP-JNK pathway. After intraperitoneal injection of a cumulative dose of 15 mg/kg Dox, rats displayed significant cardiac dysfunction; their heart showed inhibited Wnt/β-catenin signaling and activated Wnt/PCP-JNK signaling. These results suggest that sFRP1 may be a novel target for Dox-induced cardiotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Razavi-Azarkhiavi K, Jaafari MR, Abnous K, Razavi BM, Jafarian AH, Hassani FV. et al. The cardiotoxic mechanism of doxorubicin (DOX) and pegylated liposomal DOX in mice bearing C-26 colon carcinoma: a study focused on microRNA role for toxicity assessment of new formulations. Pharmaol Res. 2017;34:1849–56.
Bruynzeel AM, Abou El Hassan MA, Schalkwijk C, Berkhof J, Bast A, Niessen HW, et al. Anti-inflammatory agents and monoHER protect against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity and accumulation of CML in mice. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:937–43.
Shi Y, Moon M, Dawood S, McManus B, Liu PP. Mechanisms and management of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Herz. 2011;36:296–305.
Bruynzeel AM, Vormer-Bonne S, Bast A, Niessen HW, van der Vijgh WJ. Long-term effects of 7-monohydroxyethylrutoside (monoHER) on DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2007;60:509–14.
Mohammed MK, Shao C, Wang J, Wei Q, Wang X, Collier Z, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling plays an ever-expanding role in stem cell self-renewal, tumorigenesis and cancer chemoresistance. Genes Dis. 2016;3:11–40.
Korkut C, Ataman B, Ramachandran P, Ashley J, Barria R, Gherbesi N, et al. Trans-synaptic transmission of vesicular Wnt signals through Evi/Wntless. Cell. 2009;139:393–404.
Hu Y, Guo Z, Lu J, Wang P, Sun S, Zhang Y, et al. sFRP1 has a biphasic effect on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in a cellular location-dependent manner in NRCMs and Rats. Arch Toxicol. 2019;93:533–46.
Matsuyama M, Nomori A, Nakakuni K, Shimono A, Fukushima M. Secreted Frizzled-related protein 1 (Sfrp1) regulates the progression of renal fibrosis in a mouse model of obstructive nephropathy. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:31526–33.
Asad M, Wong MK, Tan TZ, Choolani M, Low J, Mori S, et al. FZD7 drives in vitro aggressiveness in Stem-A subtype of ovarian cancer via regulation of non-canonical Wnt/PCP pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1346.
Lopez-Escobar B, Cano DA, Rojas A, de Felipe B, Palma F, Sanchez-Alcazar JA, et al. The effect of maternal diabetes on the Wnt-PCP pathway during embryogenesis as reflected in the developing mouse eye. Dis Model Mech. 2015;8:157–68.
Dufourcq P, Couffinhal T, Ezan J, Barandon L, Moreau C, Daret D, et al. FrzA, a secreted frizzled related protein, induced angiogenic response. Circulation. 2002;106:3097–103.
Jones SE, Jomary C. Secreted Frizzled-related proteins: searching for relationships and patterns. BioEssays. 2002;24:811–20.
Sklepkiewicz P, Shiomi T, Kaur R, Sun J, Kwon S, Mercer B, et al. Loss of secreted frizzled-related protein-1 leads to deterioration of cardiac function in mice and plays a role in human cardiomyopathy. Circ Heart Fail. 2015;8:362–72.
Matsuyama M, Aizawa S, Shimono A. Sfrp controls apicobasal polarity and oriented cell division in developing gut epithelium. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000427.
Satoh W, Matsuyama M, Takemura H, Aizawa S, Shimono A. Sfrp1, Sfrp2, and Sfrp5 regulate the Wnt/beta-catenin and the planar cell polarity pathways during early trunk formation in mouse. Genesis. 2008;46:92–103.
Guo Z, Lu J, Li J, Wang P, Li Z, Zhong Y, et al. JMJD3 inhibition protects against isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy by suppressing beta-MHC expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018;477:1–14.
Zhang Q, Liu Y, Wang H, Ma L, Xia H, Niu J, et al. The preventive effects of taurine on neural tube defects through the Wnt/PCP-Jnk-dependent pathway. Amino Acids. 2017;49:1633–40.
American Society of Clinical Oncology 2008 Clinical practice guideline update summary: use of chemotherapy and radiation therapy protectants. J Oncol Pract. 2008;4:277–9.
Malcom J, Arnold O, Howlett JG, Ducharme A, Ezekowitz JA, Gardner M, et al. Canadian Cardiovascular Society Consensus Conference guidelines on heart failure—2008 update: best practices for the transition of care of heart failure patients, and the recognition, investigation and treatment of cardiomyopathies. Can J Cardiol. 2008;24:21–40.
Shaddy RE, Olsen SL, Bristow MR, Taylor DO, Bullock EA, Tani LY, et al. Efficacy and safety of metoprolol in the treatment of doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in pediatric patients. Am Heart J. 1995;129:197–9.
Spallarossa P, Garibaldi S, Altieri P, Fabbi P, Manca V, Nasti S, et al. Carvedilol prevents doxorubicin-induced free radical release and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes in vitro. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004;37:837–46.
Sacco G, Mario B, Lopez G, Evangelista S, Manzini S, Maggi CA. ACE inhibition and protection from doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in the rat. Vasc Pharmacol. 2009;50:166–70.
Songbo M, Lang H, Xinyong C, Bin X, Ping Z, Liang S. Oxidative stress injury in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Lett. 2019;307:41–8.
Green PS, Leeuwenburgh C. Mitochondrial dysfunction is an early indicator of doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1588:94–101.
Han X, Amar S. Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (SFRP1) protects fibroblasts from ceramide-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:2832–40.
Tao J, Abudoukelimu M, Ma YT, Yang YN, Li XM, Chen BD, et al. Secreted frizzled related protein 1 protects H9C2 cells from hypoxia/re-oxygenation injury by blocking the Wnt signaling pathway. Lipids Health Dis. 2016;15:72.
Barandon L, Casassus F, Leroux L, Moreau C, Allieres C, Lamaziere JM, et al. Secreted frizzled-related protein-1 improves postinfarction scar formation through a modulation of inflammatory response. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31:e80–7.
Routledge D, Scholpp S. Mechanisms of intercellular Wnt transport. Development. 2019;146:dev176073.
Gao C, Chen YG. Dishevelled: the hub of Wnt signaling. Cell Signal. 2010;22:717–27.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81872860, 81803521, 81673433, and 81572925), Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program (2017BT01Y093), National Major Special Projects for the Creation and Manufacture of New Drugs (2019ZX09301104), Special Program for Applied Science and Technology of Guangdong Province (2015B020232009), National Engineering and Technology Research Center for New Druggability Evaluation (Seed Program of Guangdong Province, 2017B090903004), Guangzhou Science and Technology Program Project (201604020121), and YangFan Project of Guangdong Province (2014YT02S044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YHH designed and performed the research; Jie Liu, Jing Lu, and FHH wrote the paper; PXW analyzed the data; JXC and YG prepared the reagents; and JJW, WL, and PQL designed the research.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Yh., Liu, J., Lu, J. et al. sFRP1 protects H9c2 cardiac myoblasts from doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the Wnt/PCP-JNK pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41, 1150–1157 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-0364-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-0364-z
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Naringin attenuates angiotensin II induced cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting carbonic anhydrase II
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
eEF2K alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting GSK3β and improving autophagy dysfunction
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2024)
-
Vaccarin Ameliorates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Inhibition of p38 MAPK Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research (2024)
-
Regulated cell death pathways in cardiomyopathy
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2023)
-
Regulated cell death pathways in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
Cell Death & Disease (2021)