Abstract
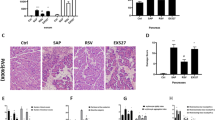
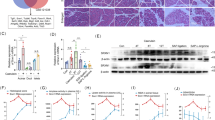
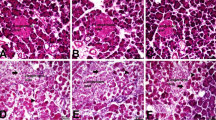
Acute pancreatitis (AP), an inflammatory disorder of the pancreas, is a complicated disease without specific drug therapy. (R)-4,6-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxy phenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-indanone [(R)-TML104] is a synthesized analog of the natural product resveratrol sesquiterpenes (±) -isopaucifloral F. This study aimed to investigate the effect and underlying mechanism of (R)-TML104 on AP. The experimental AP model was induced by caerulein hyperstimulation in BALB/c mice. (R)-TML104 markedly attenuated caerulein-induced AP, as evidenced by decreased pancreatic edema, serum amylase levels, serum lipase levels, and pancreatic myeloperoxidase activity. In addition, (R)-TML104 significantly inhibited the expression of pancreatic chemokines C–C motif chemokine ligand 2 and macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and the infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages. Mechanistically, (R)-TML104 activated AMP-activated protein kinase and induced sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) expression. (R)-TML104 treatment markedly induced the SIRT1-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) interaction and reduced acetylation of STAT3, thus inhibiting the inflammatory response mediated by the interleukin 6-STAT3 pathway. The effect of (R)-TML104 on SIRT1-STAT3 interaction was reversed by treatment with a SIRT1 inhibitor selisistat (EX527). Together, our findings indicate that (R)-TML104 alleviates experimental pancreatitis by reducing the infiltration of inflammatory cells through modulating SIRT1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Data availability
The authors declare that the main data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article. Extra data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Lankisch PG, Apte M, Banks PA. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 2015;386:85–96.
Saluja AK, Lerch MM, Phillips PA, Dudeja V. Why does pancreatic overstimulation cause pancreatitis? Annu Rev Physiol. 2007;69:249–69.
Logsdon CD, Ji B. The role of protein synthesis and digestive enzymes in acinar cell injury. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:362–70.
Frossard J-L, Steer ML, Pastor CM. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 2008;371:143–52.
Mayerle J, Sendler M, Hegyi E, Beyer G, Lerch MM, Sahin-Tóth M. Genetics, cell biology, and pathophysiology of pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1951–68.
Steinberg W, Tenner S. Acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1198–210.
Merza M, Hartman H, Rahman M, Hwaiz R, Zhang E, Renström E, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps induce trypsin activation, inflammation, and tissue damage in mice with severe acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1920–31.
Sendler M, Weiss F-U, Golchert J, Homuth G, van den Brandt C, Mahajan UM, et al. Cathepsin B-mediated activation of trypsinogen in endocytosing macrophages increases severity of pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:704–18.
Watanabe T, Kudo M, Strober W. Immunopathogenesis of pancreatitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2017;10:283–98.
Saeki K, Kanai T, Nakano M, Nakamura Y, Miyata N, Sujino T, et al. CCL2-induced migration and SOCS3-mediated activation of macrophages are involved in cerulein-induced pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:1010–20.
Han X, Li B, Ye X, Mulatibieke T, Wu J, Dai J, et al. Dopamine D receptor signalling controls inflammation in acute pancreatitis via a PP2A-dependent Akt/NF-κB signalling pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174:4751–70.
Pan X, Fang X, Wang F, Li H, Niu W, Liang W, et al. Butyrate ameliorates caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis and associated intestinal injury by tissue-specific mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol. 2019;176:4446–61.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:798–809.
Zhang H, Neuhöfer P, Song L, Rabe B, Lesina M, Kurkowski MU, et al. IL-6 trans-signaling promotes pancreatitis-associated lung injury and lethality. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:1019–31.
Lesina M, Wörmann SM, Neuhöfer P, Song L, Algül H. Interleukin-6 in inflammatory and malignant diseases of the pancreas. Semin Immunol. 2014;26:80–7.
Yuan Z-L, Guan Y-J, Chatterjee D, Chin YE. Stat3 dimerization regulated by reversible acetylation of a single lysine residue. Science. 2005;307:269–73.
Xia N, Daiber A, Förstermann U, Li H. Antioxidant effects of resveratrol in the cardiovascular system. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174:1633–46.
Rauf A, Imran M, Butt MS, Nadeem M, Peters DG, Mubarak MS. Resveratrol as an anti-cancer agent: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2018;58:1428–47.
Hubbard BP, Sinclair DA. Small molecule SIRT1 activators for the treatment of aging and age-related diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014;35:146–54.
Wang N, Zhang F, Yang L, Zou J, Wang H, Liu K, et al. Resveratrol protects against L-arginine-induced acute necrotizing pancreatitis in mice by enhancing SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of p53 and heat shock factor 1. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40:427–37.
Liu D, Song G, Ma Z, Geng X, Dai Y, Yang T, et al. Resveratrol improves the therapeutic efficacy of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106128.
Xiang H, Zhang Q, Qi B, Tao X, Xia S, Song H, et al. Chinese herbal medicines attenuate acute pancreatitis: pharmacological activities and mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:216.
Agah S, Akbari A, Sadeghi E, Morvaridzadeh M, Basharat Z, Palmowski A, et al. Resveratrol supplementation and acute pancreatitis: a comprehensive review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137:111268.
Walle T. Bioavailability of resveratrol. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1215:9–15.
Cottart CH, Nivet-Antoine V, Laguillier-Morizot C, Beaudeux JL. Resveratrol bioavailability and toxicity in humans. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010;54:7–16.
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A, Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. Br J Pharmcol. 2020;177:3617–24.
Ren Z, Li H, Zhang M, Zhao Y, Fang X, Li X, et al. A novel derivative of the natural product danshensu suppresses inflammatory responses to alleviate caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2513.
Tsang SW, Guan YF, Wang J, Bian ZX, Zhang HJ. Inhibition of pancreatic oxidative damage by stilbene derivative dihydro-resveratrol: implication for treatment of acute pancreatitis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22859.
Smith MR, Syed A, Lukacsovich T, Purcell J, Barbaro BA, Worthge SA, et al. A potent and selective Sirtuin 1 inhibitor alleviates pathology in multiple animal and cell models of Huntington’s disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:2995–3007.
Hu F, Lou N, Jiao J, Guo F, Xiang H, Shang D. Macrophages in pancreatitis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110693.
Price NL, Gomes AP, Ling AJY, Duarte FV, Martin-Montalvo A, North BJ, et al. SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab. 2012;15:675–90.
Ramnath RD, Sun J, Bhatia M. Role of calcium in substance P-induced chemokine synthesis in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2008;154:1339–48.
Nie Y, Erion DM, Yuan Z, Dietrich M, Shulman GI, Horvath TL, et al. STAT3 inhibition of gluconeogenesis is downregulated by SirT1. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:492–500.
Wang Y, Shen Y, Wang S, Shen Q, Zhou X. The role of STAT3 in leading the crosstalk between human cancers and the immune system. Cancer Lett. 2018;415:117–28.
Johnson DE, O’Keefe RA, Grandis JR. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:234–48.
Stark GR, Darnell JE. The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity. 2012;36:503–14.
Braunstein J, Brutsaert S, Olson R, Schindler C. STATs dimerize in the absence of phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:34133–40.
Ma L, Gao J-S, Guan Y, Shi X, Zhang H, Ayrapetov MK, et al. Acetylation modulates prolactin receptor dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:19314–9.
Wang R, Cherukuri P, Luo J. Activation of Stat3 sequence-specific DNA binding and transcription by p300/CREB-binding protein-mediated acetylation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:11528–34.
O’Shea JJ, Kanno Y, Chen X, Levy DE. Cell signaling. Stat acetylation–a key facet of cytokine signaling? Science. 2005;307:217–8.
Chang H-C, Guarente L. SIRT1 and other sirtuins in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014;25:138–45.
Limagne E, Thibaudin M, Euvrard R, Berger H, Chalons P, Végan F, et al. Sirtuin-1 activation controls tumor growth by impeding Th17 differentiation via STAT3 deacetylation. Cell Rep. 2017;19:746–59.
Howitz KT, Bitterman KJ, Cohen HY, Lamming DW, Lavu S, Wood JG, et al. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature. 2003;425:191–6.
Tarasiuk A, Fichna J. Effectiveness and therapeutic value of phytochemicals in acute pancreatitis: a review. Pancreatology. 2019;19:481–7.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos: 80270666, 81870439, 81973322, 91642114, 31570915, and National Youth 1000 Talents Plan), the Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Jiangsu Province (Grant no: BK20200026), Jiangsu Province Recruitment Plan for High-level, Innovative and Entrepreneurial Talents (Innovative Research Team), Wuxi Social Development Funds for International Science & Technology Cooperation (Grant no: WX0303B010518180007PB), Jiangsu Province “Six Summit Talents” program (Grant no: YY-038), Jiangsu Province Qing Lan Project, National First-class Discipline Program of Food Science and Technology (Grant no: JUFSTR20180103), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant nos: JUSRP221037, JUSRP22007), Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant no: KYCX20_1876), Collaborative Innovation Center of Food Safety and Quality Control in Jiangsu Province and Wuxi Taihu Talent Project. Shanghai Municipal Committee of Science and Technology (Grant no: 17JC1400200). Youth Project of Public Health Research Center of Jiangnan University (Grant no: JUPH201825); Translational Medicine Project of Wuxi Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (Grant no: ZM007); Wuxi City’s first “double hundred” young and middle-aged medical and health talents (Grant no: BJ2020045); Wuxi Social Development Science and Technology Demonstration Project (Grant no: N20201003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZNR, MYZ, YH, and DXS performed experiments and analyzed data. XS synthesized and provided novel resveratrol analog (R)-TML104. JS and LLP designed and interpreted experiments. JY contributed to the data acquisition and critically reviewed the manuscript. ZNR, LLP, and JS wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors disclose no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Zn., Yang, J., Zhang, My. et al. A novel resveratrol analog upregulates sirtuin 1 and inhibits inflammatory cell infiltration in acute pancreatitis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43, 1264–1273 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00744-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00744-y
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lysine acetylation and its role in the pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis
Inflammation Research (2025)