Abstract
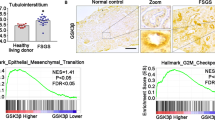
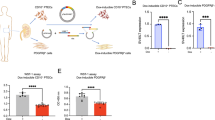
Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) is regarded as a key factor in promoting renal fibrosis during chronic kidney disease (CKD). Signaling transduction of TGF-β1 starts with binding to TGF-β type II receptor (Tgfbr2), a constitutively activated kinase that phosphorylates TGF-β type I receptor (Tgfbr1), and then activates downstream Smad2/3 or noncanonical pathways. Previous studies show that cellular senescence is associated with the progression of CKD, and accelerated tubular cell senescence is implicated in promoting renal fibrosis. In the present study we investigated the renal parenchymal cell senescence in fibrosis from the sight of posttranslational regulation and focused on Tgfbr2, the important gatekeeper for TGF-β1 downstream signaling. In mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) and folic acid (FA)-induced fibrotic kidneys, we found that Tgfbr2 was markedly elevated without obvious change in its mRNA levels. As an important member of deubiquitinating enzymes, ubiquitin-specific protease 11 (Usp11) was also significantly increased in fibrotic kidneys, and co-distributed with Tgfbr2 in tubular epithelial cells. Pretreatment with Usp11 inhibitor mitoxantrone (MTX, 30 mg · kg−1 · d−1, i.p.) twice a week, for 2 weeks significantly attenuated the elevation of Tgfbr2, activation in downstream senescence-related signaling pathway, as well as renal senescence and fibrosis. In cultured mouse tubular epithelial cells (MTECs), treatment with angiotensin II (Ang-II, 10−7, 10−6 M) dose-dependently elevated both Tgfbr2 and Usp11 levels. Inhibition or knockdown on Usp11 attenuated Ang-II-induced elevation in Tgfbr2 level, and attenuated the activation of downstream senescent-related signaling pathway and as well as cell senescence. We conducted Co-IP experiments, which revealed that Usp11 was able to interact with Tgfbr2, and inhibition of Usp11 increased the ubiquitination of Tgfbr2. Taken together, these results demonstrate that the elevation of Usp11 under pathological condition is implicated in promoting renal fibrosis. Usp11 promotes the development of renal fibrosis by deubiquitinating Tgfbr2, reducing Tgfbr2 ubiquitination degradation, and then facilitating the activation of downstream senescent signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Zhang L, Long J, Jiang W, Shi Y, He X, Zhou Z, et al. Trends in chronic kidney disease in China. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:905–6.
Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, Bragg-Gresham J, Chen X, Gipson D, et al. US renal data system 2019 annual data report: epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;75:A6–a7.
Humphreys BD. Mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2018;80:309–26.
Ruiz-Ortega M, Rayego-Mateos S, Lamas S, Ortiz A, Rodrigues-Diez RR. Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16:269–88.
Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Lan HY. TGF-β: the master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12:325–38.
Vander Ark A, Cao J, Li X. TGF-β receptors: In and beyond TGF-β signaling. Cell Signal. 2018;52:112–20.
Liu S, Chen S, Zeng J. TGF‑β signaling: a complex role in tumorigenesis (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2018;17:699–704.
Gifford CC, Tang J, Costello A, Khakoo NS, Nguyen TQ, Goldschmeding R, et al. Negative regulators of TGF-β1 signaling in renal fibrosis; pathological mechanisms and novel therapeutic opportunities. Clin Sci. 2021;135:275–303.
Wang W, Zhu Y, Sun Z, Jin C, Wang X. Positive feedback regulation between USP15 and ERK2 inhibits osteoarthritis progression through TGF-β/SMAD2 signaling. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23:84.
Zhang S, Xie C, Li H, Zhang K, Li J, Wang X, et al. Ubiquitin-specific protease 11 serves as a marker of poor prognosis and promotes metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Lab Invest. 2018;98:883–94.
Tu L, Lin Z, Huang Q, Liu D. USP15 enhances the proliferation, migration, and collagen deposition of hypertrophic scar-derived fibroblasts by deubiquitinating TGF-βR1 in vitro. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148:1040–51.
Zhang L, Zhou F, Drabsch Y, Gao R, Snaar-Jagalska BE, Mickanin C, et al. USP4 is regulated by AKT phosphorylation and directly deubiquitylates TGF-β type I receptor. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14:717–26.
Bard JAM, Goodall EA, Greene ER, Jonsson E, Dong KC, Martin A. Structure and function of the 26S proteasome. Annu Rev Biochem. 2018;87:697–724.
Luza S, Opazo CM, Bousman CA, Pantelis C, Bush AI, Everall IP. The ubiquitin proteasome system and schizophrenia. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;7:528–37.
Snyder NA, Silva GM. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs): regulation, homeostasis, and oxidative stress response. J Biol Chem. 2021;297:101077.
Harrigan JA, Jacq X, Martin NM, Jackson SP. Deubiquitylating enzymes and drug discovery: emerging opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17:57–78.
Harper S, Gratton HE, Cornaciu I, Oberer M, Scott DJ, Emsley J, et al. Structure and catalytic regulatory function of ubiquitin specific protease 11 N-terminal and ubiquitin-like domains. Biochemistry. 2014;53:2966–78.
Jacko AM, Nan L, Li S, Tan J, Zhao J, Kass DJ, et al. De-ubiquitinating enzyme, USP11, promotes transforming growth factor β-1 signaling through stabilization of transforming growth factor β receptor II. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2474.
Calcinotto A, Kohli J, Zagato E, Pellegrini L, Demaria M, Alimonti A. Cellular senescence: aging, cancer, and injury. Physiol Rev. 2019;99:1047–78.
Di Micco R, Krizhanovsky V, Baker D, d’Adda di Fagagna F. Cellular senescence in ageing: from mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:75–95.
Gorgoulis V, Adams PD, Alimonti A, Bennett DC, Bischof O, Bishop C, et al. Cellular senescence: defining a path forward. Cell. 2019;179:813–27.
Hernandez-Segura A, Nehme J, Demaria M. Hallmarks of cellular senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28:436–53.
He S, Sharpless NE. Senescence in health and disease. Cell. 2017;169:1000–11.
Docherty MH, O’Sullivan ED, Bonventre JV, Ferenbach DA. Cellular senescence in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;30:726–36.
Luo C, Zhou S, Zhou Z, Liu Y, Yang L, Liu J, et al. Wnt9a promotes renal fibrosis by accelerating cellular senescence in tubular epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29:1238–56.
Miao NJ, Xie HY, Xu D, Yin JY, Wang YZ, Wang B, et al. Caspase-11 promotes renal fibrosis by stimulating IL-1β maturation via activating caspase-1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40:790–800.
Reis-Mendes A, Dores-Sousa JL, Padrão AI, Duarte-Araújo M, Duarte JA, Seabra V, et al. Inflammation as a possible trigger for mitoxantrone-induced cardiotoxicity: an in vivo study in adult and infant mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2021;14:510.
Subramaniam V, Chuang G, Xia H, Burn B, Bradley J, Maderdrut JL, et al. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) protects against mitoxantrone-induced cardiac injury in mice. Peptides. 2017;95:25–32.
Brandão SR, Reis-Mendes A, Domingues P, Duarte JA, Bastos ML, Carvalho F, et al. Exploring the aging effect of the anticancer drugs doxorubicin and mitoxantrone on cardiac mitochondrial proteome using a murine model. Toxicology. 2021;459:152852.
Chen JH, Hales CN, Ozanne SE. DNA damage, cellular senescence and organismal ageing: causal or correlative? Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:7417–28.
de Magalhães JP, Passos JF. Stress, cell senescence and organismal ageing. Mech Ageing Dev. 2018;170:2–9.
Stenvinkel P, Larsson TE. Chronic kidney disease: a clinical model of premature aging. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62:339–51.
Zhou L, Li Y, Zhou D, Tan RJ, Liu Y. Loss of Klotho contributes to kidney injury by derepression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24:771–85.
Verzola D, Gandolfo MT, Gaetani G, Ferraris A, Mangerini R, Ferrario F, et al. Accelerated senescence in the kidneys of patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2008;295:F1563–73.
Zhu K, Kakehi T, Matsumoto M, Iwata K, Ibi M, Ohshima Y, et al. NADPH oxidase NOX1 is involved in activation of protein kinase C and premature senescence in early stage diabetic kidney. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;83:21–30.
Sis B, Tasanarong A, Khoshjou F, Dadras F, Solez K, Halloran PF. Accelerated expression of senescence associated cell cycle inhibitor p16INK4A in kidneys with glomerular disease. Kidney Int. 2007;71:218–26.
Satriano J, Mansoury H, Deng A, Sharma K, Vallon V, Blantz RC, et al. Transition of kidney tubule cells to a senescent phenotype in early experimental diabetes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010;299:C374–80.
Li C, Xie N, Li Y, Liu C, Hou FF, Wang J. N-acetylcysteine ameliorates cisplatin-induced renal senescence and renal interstitial fibrosis through sirtuin1 activation and p53 deacetylation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;130:512–27.
Hafner A, Bulyk ML, Jambhekar A, Lahav G. The multiple mechanisms that regulate p53 activity and cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:199–210.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82070712, 81873603) and the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (14DZ2260200, the project of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Kidney and Blood Purification).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LML, JL, JYN participated in the design of the study. LML, JYN, and XW wrote the paper. JYN and XW performed the experiments and analyzed the results. JYN, XW, HYX, NHY, JYL, XAS, HJG, LZ, and WZ took part in the revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, Jy., Wang, X., Xie, Hy. et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme USP11 promotes renal tubular cell senescence and fibrosis via inhibiting the ubiquitin degradation of TGF-β receptor II. Acta Pharmacol Sin 44, 584–595 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00977-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00977-5
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
TUFT1 stabilizes TGF-β receptor II protein and facilitates activation of hepatic stellate cells into metastasis-promoting myofibroblasts
Cell Death & Differentiation (2026)
-
Immunoinflammation and post-translational modifications in the aging process
Journal of Translational Medicine (2025)
-
Natural products targeting ubiquitination to combat kidney fibrosis
Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (2025)
-
The emerging role of E3 ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Journal of Translational Medicine (2025)
-
MiR-106b-5p improving the progression of chronic kidney disease by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad pathway
Hereditas (2025)