Abstract
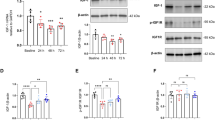
Aging is one of the main risk factors for cognitive dysfunction. During aging process, the decrease of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and the impairment of astrocyte function contribute to the cognitive impairment. Metrnl, a neurotrophic factor, promotes neural growth, migration and survival, and supports neural function. In this study, we investigated the role of Metrnl in cognitive functions. D-galactose (D-gal)-induced aging model was used to simulate the process of aging. Cognitive impairment was assessed by the Morris water maze test. We showed that Metrnl expression levels were significantly increased in the hippocampus of D-gal-induced aging mice. Metrnl knockout did not affect the cognitive functions in the baseline state, but aggravated the cognitive impairment in the D-gal-induced aging mice. Furthermore, Metrnl knockout significantly reduced hippocampal BDNF, TrkB, and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) levels in the D-gal-induced aging mice. In the D-gal-induced aging cell model in vitro, Metrnl levels in the hippocampal astrocytes were significantly increased, and Metrnl knockdown and overexpression regulated the BDNF levels in primary hippocampal astrocytes rather than in neurons. We conclude that Metrnl regulates cognitive functions and hippocampal BDNF levels during aging process. As a neurotrophic factor and an endogenous protein, Metrnl is expected to become a new candidate for the treatment or alleviation of aging-related cognitive dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
James GA, Kearney-Ramos TE, Young JA, Kilts CD, Gess JL, Fausett JS. Functional independence in resting-state connectivity facilitates higher-order cognition. Brain Cogn. 2016;105:78–87.
2021 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2021;17:327–406.
Janota C, Lemere CA, Brito MA. Dissecting the contribution of vascular alterations and aging to Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53:3793–811.
Jia L, Quan M, Fu Y, Zhao T, Li Y, Wei C, et al. Dementia in China: epidemiology, clinical management, and research advances. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:81–92.
Sahakian BJ, Bruhl AB, Cook J, Killikelly C, Savulich G, Piercy T, et al. The impact of neuroscience on society: cognitive enhancement in neuropsychiatric disorders and in healthy people. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2014.0214.
Haapasalo A, Hiltunen M. A report from the 8th Kuopio Alzheimer Symposium. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2018;8:289–99.
Li ZY, Zheng SL, Wang P, Xu TY, Guan YF, Zhang YJ, et al. Subfatin is a novel adipokine and unlike Meteorin in adipose and brain expression. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014;20:344–54.
Li ZY, Song J, Zheng SL, Fan MB, Guan YF, Qu Y, et al. Adipocyte metrnl antagonizes insulin resistance through PPAR-γ signaling. Diabetes. 2015;64:4011–22.
Li ZY, Fan MB, Zhang SL, Qu Y, Zheng SL, Song J, et al. Intestinal Metrnl released into the gut lumen acts as a local regulator for gut antimicrobial peptides. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016;37:1458–66.
Zheng SL, Li ZY, Song J, Liu JM, Miao CY. Metrnl: a secreted protein with new emerging functions. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016;37:571–9.
Qi Q, Hu WJ, Zheng SL, Zhang SL, Le YY, Li ZY, et al. Metrnl deficiency decreases blood HDL cholesterol and increases blood triglyceride. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41:1568–75.
Miao ZW, Hu WJ, Li ZY, Miao CY. Involvement of the secreted protein Metrnl in human diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41:1525–30.
Zhang SL, Li ZY, Wang DS, Xu TY, Fan MB, Cheng MH, et al. Aggravated ulcerative colitis caused by intestinal Metrnl deficiency is associated with reduced autophagy in epithelial cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41:763–70.
Surace C, Piazzolla S, Sirleto P, Digilio MC, Roberti MC, Lombardo A, et al. Mild ring 17 syndrome shares common phenotypic features irrespective of the chromosomal breakpoints location. Clin Genet. 2009;76:256–62.
Jorgensen JR, Fransson A, Fjord-Larsen L, Thompson LH, Houchins JP, Andrade N, et al. Cometin is a novel neurotrophic factor that promotes neurite outgrowth and neuroblast migration in vitro and supports survival of spiral ganglion neurons in vivo. Exp Neurol. 2012;233:172–81.
Shwe T, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC. Role of D-galactose-induced brain aging and its potential used for therapeutic interventions. Exp Gerontol. 2018;101:13–36.
Ali T, Badshah H, Kim TH, Kim MO. Melatonin attenuates D-galactose-induced memory impairment, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration via RAGE/NF-K B/JNK signaling pathway in aging mouse model. J Pineal Res. 2015;58:71–85.
Azman KF, Zakaria R. D-Galactose-induced accelerated aging model: an overview. Biogerontology. 2019;20:763–82.
Dooley TP, Miranda M, Jones NC, Depamphilis ML. Transactivation of the adenovirus EIIa promoter in the absence of adenovirus E1A protein is restricted to mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Development. 1989;107:945–56.
Vorhees CV, Williams MT. Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:848–58.
Wang SN, Xu TY, Wang X, Guan YF, Zhang SL, Wang P, et al. Neuroprotective efficacy of an aminopropyl carbazole derivative P7C3-A20 in ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016;22:782–8.
Prah J, Winters A, Chaudhari K, Hersh J, Liu R, Yang SH. A novel serum free primary astrocyte culture method that mimic quiescent astrocyte phenotype. J Neurosci Methods. 2019;320:50–63.
Chen L, Yao H, Chen X, Wang Z, Xiang Y, Xia J, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 decreases oxidative stress and down-regulates Akt/mTOR signalling to attenuate cognitive impairment in mice and senescence of neural stem cells induced by D-galactose. Neurochem Res. 2018;43:430–40.
Navarro Negredo P, Yeo RW, Brunet A. Aging and rejuvenation of neural stem cells and their niches. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27:202–23.
Weitzner DS, Engler-Chiurazzi EB, Kotilinek LA, Ashe KH, Reed MN. Morris Water Maze Test: optimization for mouse strain and testing environment. J Vis Exp. 2015. https://doi.org/10.3791/52706.
Tucker LB, Velosky AG, Mccabe JT. Applications of the Morris water maze in translational traumatic brain injury research. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;88:187–200.
Kumar A, Pareek V, Faiq MA, Kumar P, Raza K, Prasoon P, et al. Regulatory role of NGFs in neurocognitive functions. Rev Neurosci. 2017;28:649–73.
Paul J, Gottmann K, Lessmann V. NT-3 regulates BDNF-induced modulation of synaptic transmission in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuroreport. 2001;12:2635–9.
Hofer M, Pagliusi SR, Hohn A, Leibrock J, Barde YA. Regional distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in the adult mouse brain. EMBO J. 1990;9:2459–64.
Eggert S, Kins S, Endres K, Brigadski T. Brothers in arms: proBDNF/BDNF and sAPPα/β-signaling and their common interplay with ADAM10, TrkB, p75NTR, sortilin, and sorLA in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Chem. 2022;403:43–71.
Andreska T, Luningschror P, Sendtner M. Regulation of TrkB cell surface expression-a mechanism for modulation of neuronal responsiveness to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Cell Tissue Res. 2020;382:5–14.
Santello M, Toni N, Volterra A. Astrocyte function from information processing to cognition and cognitive impairment. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:154–66.
Dallerac G, Rouach N. Astrocytes as new targets to improve cognitive functions. Prog Neurobiol. 2016;144:48–67.
Yeh CY, Vadhwana B, Verkhratsky A, Rodriguez JJ. Early astrocytic atrophy in the entorhinal cortex of a triple transgenic animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. ASN Neuro. 2011;3:271–9.
Olabarria M, Noristani HN, Verkhratsky A, Rodriguez JJ. Concomitant astroglial atrophy and astrogliosis in a triple transgenic animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Glia. 2010;58:831–8.
van Bodegraven EJ, van Asperen JV, Robe PAJ, Hol EM. Importance of GFAP isoform-specific analyses in astrocytoma. Glia. 2019;67:1417–33.
Messing A, Brenner M. GFAP at 50. ASN Neuro. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759091420949680.
Mather M. Aging and cognition. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2010;1:346–62.
Chen X, Li Y, Chen W, Nong Z, Huang J, Chen C. Protective effect of hyperbaric oxygen on cognitive impairment induced by D-galactose in mice. Neurochem Res. 2016;41:3032–41.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (№82104166, №81730098 and №82030110), Medical Innovation Major Project (№16CXZ009), and Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Project (№21140901000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CH and ZW performed most of the experiments and data analyses and wrote the paper. SLZ, WJH, SNW and YZ performed some experiments and/or data analysis. CYM designed the study, performed data analysis, and wrote and revised the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, C., Wang, Z., Zheng, Sl. et al. Metrnl regulates cognitive dysfunction and hippocampal BDNF levels in D-galactose-induced aging mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 44, 741–751 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-01009-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-01009-y
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cognitive–exercise dual-task training delays natural aging/d-galactose-induced cognitive decline in mice
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2026)
-
Ketogenic Diet Mitigates Age-Related Cognitive Decline and Neuroinflammation in Rats, While Antibiotics Exacerbate Brain Health Risks
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2025)
-
Deregulation of Neuroinflammatory and Neurotrophic Factors as Biological Events Triggered by D-Galactose Chronic Administration in Wistar Rats
NeuroMolecular Medicine (2025)
-
Electro-Acupuncture Therapy Alleviates Post-Stroke Insomnia by Regulating Sirt1 and the Nrf2-ARE Pathway
NeuroMolecular Medicine (2025)
-
Chronic vascular pathogenesis results in the reduced serum Metrnl levels in ischemic stroke patients
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2024)