Abstract
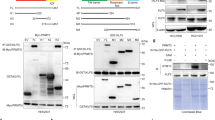
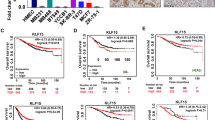
Basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) is the most malignant subtype of breast cancer because of its aggressive clinical behaviour and lack of effective targeted agents. Krüppel-like factor 5 (KLF5) is an oncogenic transcription factor that is highly expressed in BLBC. The deubiquitinase (DUB) BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1) stabilizes KLF5 and promotes BLBC growth and metastasis. Therefore, pharmacological inhibition of the BAP1‒KLF5 axis is an effective therapeutic strategy for BLBC. Here, through screening, we identified a series of tetrahydro-β-carboline derivatives that effectively reduced the protein expression of KLF5 and exhibited strong antitumour activity. Among the investigated compounds, the lead compound LN-439A presented the strongest antitumour activity and inhibitory effect on KLF5 expression. LN-439A suppressed the proliferation and migration of BLBC cells, induced G2/M arrest, and induced apoptosis. Mechanistically, LN-439A functions as a small molecule catalytic inhibitor of BAP1 by binding to the catalytic pocket of BAP1, leading to the ubiquitination and degradation of KLF5. Consistent with this finding, the overexpression of KLF5 suppressed the antitumour effects of LN-439A. In summary, LN-439A is a promising therapeutic agent for BLBC that functions by targeting the BAP1‒KLF5 axis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12–49.
Jiang D, Qiu T, Peng J, Li S, Tala, Ren W, et al. YB-1 is a positive regulator of KLF5 transcription factor in basal-like breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29:1283–95.
Bianchini G, Balko JM, Mayer IA, Sanders ME, Gianni L. Triple-negative breast cancer: challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016;13:674–90.
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Ellis IO. Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 2007;109:25–32.
Wang F, Luo M, Qu H, Cheng Y. BAP1 promotes viability and migration of ECA109 cells through KLF5/CyclinD1/FGF-BP1. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11:1497–503.
Wei W, Chen W, He N. HDAC4 induces the development of asthma by increasing Slug-upregulated CXCL12 expression through KLF5 deacetylation. J Transl Med. 2021;19:258.
Su A, Yao K, Zhang H, Wang Y, Zhang H, Tang J. DANCR induces cisplatin resistance of triple-negative breast cancer by KLF5/p27 signaling. Am J Pathol. 2023;193:248–58.
Chen P, Qian XK, Zhang YF, Sun XG, Shi XJ, Gao YS. KLF5 promotes proliferation in gastric cancer via regulating p21 and CDK4. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci. 2020;24:4224–31.
Liu R, Shi P, Nie Z, Liang H, Zhou Z, Chen W, et al. Mifepristone suppresses basal triple-negative breast cancer stem cells by down-regulating KLF5 expression. Theranostics. 2016;6:533–44.
Shi P, Liu W, Tala, Wang H, Li F, Zhang H, et al. Metformin suppresses triple-negative breast cancer stem cells by targeting KLF5 for degradation. Cell Discov. 2017;3:17010.
Liu R, Zhi X, Zhou Z, Zhang H, Yang R, Zou T, et al. Mithramycin A suppresses basal triple-negative breast cancer cell survival partially via down-regulating Kruppel-like factor 5 transcription by Sp1. Sci Rep. 2018;8:1138.
Chen CH, Yang N, Zhang Y, Ding J, Zhang W, Liu R, et al. Inhibition of super enhancer downregulates the expression of KLF5 in basal-like breast cancers. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15:1733–42.
Wang X, Qiu T, Wu Y, Yang C, Li Y, Du G, et al. Arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 methylates and stabilizes KLF5 via decreasing its phosphorylation and ubiquitination to promote basal-like breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28:2931–45.
Kong Y, Ren W, Fang H, Shah NA, Shi Y, You D, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) promote KLF5 ubiquitination and degradation in basal-like breast cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18:2104–15.
Tung CH, Huang MF, Liang CH, Wu YY, Wu JE, Hsu CL, et al. alpha-Catulin promotes cancer stemness by antagonizing WWP1-mediated KLF5 degradation in lung cancer. Theranostics. 2022;12:1173–86.
Luan Y, Wang P. FBW7-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of KLF5. World J Biol Chem. 2014;5:216–23.
Luo Y, Chen C. The roles and regulation of the KLF5 transcription factor in cancers. Cancer Sci. 2021;112:2097–117.
Qin J, Zhou Z, Chen W, Wang C, Zhang H, Ge G, et al. BAP1 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by deubiquitinating KLF5. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8471.
Wu Y, Qin J, Li F, Yang C, Li Z, Zhou Z, et al. USP3 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation by deubiquitinating KLF5. J Biol Chem. 2019;294:17837–47.
Zhang T, Su F, Wang B, Liu L, Lu Y, Su H, et al. Ubiquitin specific peptidase 38 epigenetically regulates KLF transcription factor 5 to augment malignant progression of lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2024;43:1190–202.
Yue X, Liu T, Wang X, Wu W, Wen G, Yi Y, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of BAP1 recruits HERC2 to competitively dissociate BRCA1-BARD1, suppresses DNA repair and sensitizes CRC to radiotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13:3382–99.
Thomas JF, Valencia-Sanchez MI, Tamburri S, Gloor SL, Rustichelli S, Godinez-Lopez V, et al. Structural basis of histone H2A lysine 119 deubiquitination by Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase BAP1/ASXL1. Sci Adv. 2023;9:eadg9832.
Machida YJ, Machida Y, Vashisht AA, Wohlschlegel JA, Dutta A. The deubiquitinating enzyme BAP1 regulates cell growth via interaction with HCF-1. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:34179–88.
Xia YK, Zeng YR, Zhang ML, Liu P, Liu F, Zhang H, et al. Tumor-derived neomorphic mutations in ASXL1 impairs the BAP1-ASXL1-FOXK1/K2 transcription network. Protein Cell. 2021;12:557–77.
Ishii Y, Kolluri KK, Pennycuick A, Zhang X, Nigro E, Alrifai D, et al. BAP1 and YY1 regulate expression of death receptors in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Biol Chem. 2021;297:101223.
Campagne A, Lee MK, Zielinski D, Michaud A, Le Corre S, Dingli F, et al. BAP1 complex promotes transcription by opposing PRC1-mediated H2A ubiquitylation. Nat Commun. 2019;10:348.
Mashtalir N, Daou S, Barbour H, Sen NN, Gagnon J, Hammond-Martel I, et al. Autodeubiquitination protects the tumor suppressor BAP1 from cytoplasmic sequestration mediated by the atypical ubiquitin ligase UBE2O. Mol Cell. 2014;54:392–406.
Carbone M, Yang H, Pass HI, Krausz T, Testa JR, Gaudino G. BAP1 and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:153–9.
Kang M, Park SG, Lee SA, Kim S, Lee D, Shirbhate ME, et al. Targeting BAP1 with small compound inhibitor for colon cancer treatment. Sci Rep. 2023;13:2264.
Kumar N, Alrifai D, Kolluri KK, Sage EK, Ishii Y, Guppy N, et al. Retrospective response analysis of BAP1 expression to predict the clinical activity of systemic cytotoxic chemotherapy in mesothelioma. Lung Cancer. 2019;127:164–6.
Wang L, Birch NW, Zhao Z, Nestler CM, Kazmer A, Shilati A, et al. Epigenetic targeted therapy of stabilized BAP1 in ASXL1 gain-of-function mutated leukemia. Nat Cancer. 2021;2:515–26.
Tsuboyama N, Wang R, Szczepanski AP, Chen H, Zhao Z, Shi L, et al. Therapeutic targeting of BAP1/ASXL3 sub-complex in ASCL1-dependent small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 2022;41:2152–62.
Zhang Y, Chen J, Mi D, Ling J, Li H, He P, et al. Discovery of YH677 as a cancer stemness inhibitor that suppresses triple-negative breast cancer growth and metastasis by regulating the TGFbeta signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2023;560:216142.
Tang Y, Wang X, Li Z, He Z, Yang X, Cheng X, et al. Heparin prevents caspase-11-dependent septic lethality independent of anticoagulant properties. Immunity. 2021;54:454–67.e6.
Shen Y, Zhu Q, Xiao M, Yin L, Feng W, Feng J, et al. Inhibitory effect of the novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor DCC-2036 on triple-negative breast cancer stem cells through AXL-KLF5 positive feedback loop. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:749.
Sahtoe DD, van Dijk WJ, Ekkebus R, Ovaa H, Sixma TK. BAP1/ASXL1 recruitment and activation for H2A deubiquitination. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10292.
Daou S, Barbour H, Ahmed O, Masclef L, Baril C, Sen Nkwe N, et al. Monoubiquitination of ASXLs controls the deubiquitinase activity of the tumor suppressor BAP1. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4385.
Yu H, Mashtalir N, Daou S, Hammond-Martel I, Ross J, Sui G, et al. The ubiquitin carboxyl hydrolase BAP1 forms a ternary complex with YY1 and HCF-1 and is a critical regulator of gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:5071–85.
Moon S, Lee YK, Lee SW, Um SJ. Suppressive role of OGT-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of BAP1 in retinoic acid signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;492:89–95.
Jia X, Chen H, Ren Y, Dejizhuoga, Gesangyuzhen, Gao N, et al. BAP1 antagonizes WWP1-mediated transcription factor KLF5 ubiquitination and inhibits autophagy to promote melanoma progression. Exp Cell Res. 2021;402:112506.
Cheung M, Kadariya Y, Sementino E, Hall MJ, Cozzi I, Ascoli V, et al. Novel LRRK2 mutations and other rare, non-BAP1-related candidate tumor predisposition gene variants in high-risk cancer families with mesothelioma and other tumors. Hum Mol Genet. 2021;30:1750–61.
Yu L, Jearawiriyapaisarn N, Lee MP, Hosoya T, Wu Q, Myers G, et al. BAP1 regulation of the key adaptor protein NCoR1 is critical for gamma-globin gene repression. Genes Dev. 2018;32:1537–49.
Bononi A, Giorgi C, Patergnani S, Larson D, Verbruggen K, Tanji M, et al. BAP1 regulates IP3R3-mediated Ca2+ flux to mitochondria suppressing cell transformation. Nature. 2017;546:549–53.
Seo HR, Jeong D, Lee S, Lee HS, Lee SA, Kang SW, et al. CHIP and BAP1 act in concert to regulate INO80 ubiquitination and stability for DNA replication. Mol Cells. 2021;44:101–15.
Lee HS, Seo HR, Lee SA, Choi S, Kang D, Kwon J. BAP1 promotes stalled fork restart and cell survival via INO80 in response to replication stress. Biochem J. 2019;476:3053–66.
Lee HS, Lee SA, Hur SK, Seo JW, Kwon J. Stabilization and targeting of INO80 to replication forks by BAP1 during normal DNA synthesis. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5128.
Zhang Z, Liu Y, Xu Y, Xu Z, Jia J, Jin Y, et al. Abrogation of KLF5 sensitizes BRCA1-proficient pancreatic cancer to PARP inhibition. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2024;56:576–85.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFA0112300, 2023YFA1800403), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U2102203, 82260691, 82160461, 82472806), the Biomedical Projects of Yunnan Key Science and Technology Program (202302AA310046), the Yunnan Revitalization Talent Support Program (Yunling Shcolar Project to CC), Yunnan (Kunming) Academician Expert Workstation (YSZJGZZ-2020025 to CC), the Key Research and Development Program of Ningxia (2023BEG02010), the Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (202401AT070171), the Technology Innovation Team of Pathological Diagnosis of Triple Negative Breast Cancer in Kunming Medical University (grant number CXTD202208), Yunnan Revitalization Talent Support Program, Joint Special Funds for the Department of Science and Technology of Yunnan Province-Kunming Medical University (202401AY070001-026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TTW: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, data curation, writing original draft, writing review and editing. LLZ: methodology, resources, writing original draft, writing review and editing, funding acquisition. FBL: methodology, resources, writing original draft, writing review and editing. ZBZ: docking and molecular dynamics simulation, writing original draft, writing review and editing. JZ and DZM: synthesis of the compound, writing original draft, writing review and editing. JS and HYZ: help with animal experiments. CYW: funding acquisition. YHC: supervision, writing review and editing, funding acquisition. CC: supervision, project administration, writing review and editing, funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal experiment was approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of Kunming Medical University (kmmu20241035).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Tt., Zhang, Ll., Li, Fb. et al. LN-439A, a novel BAP1 inhibitor, suppresses the growth of basal-like breast cancer by degrading KLF5. Acta Pharmacol Sin 46, 715–727 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01361-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01361-1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Research progress of DUB enzyme in breast cancer
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2025)
-
Identification of a novel tRNA-derived small RNA fragment, tRF-16-2YU04DE, with the potential of inhibiting endometrial cancer progression
Medical Oncology (2025)