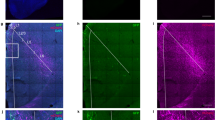
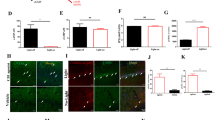
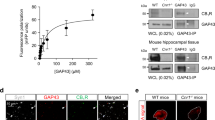
Abstract
Itch causes a strong urge to scratch and induces negative emotions, such as aversion and anxiety. Antihistamine medications are key in the clinical management of pruritus, but their therapeutic efficacy in controlling moderate and severe itching remains limited. The neural circuits in the brain that process itching and itch-induced aversion and anxiety remain unclear so far. Human brain imaging suggests that the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) is involved in processing the emotional and motivational components of itching. In this study, we investigated the mechanisms by which glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in mPFC differentially regulated pruritic sensation and emotion through cannabinoid type 1 receptors (CB1Rs). Chloroquinoline (CQ)-induced acute and calcipotriol (MC903)-induced chronic itch models were established. Fiberoptic calcium imaging was used to detect the activity of the two types of neurons in response to itching. The CB1R antagonist AM251 (0.5 mg in 200 nL) was microinjected into the mPFC through the implanted cannula. We showed that chemogenetic activation of glutamatergic neurons and inhibition of GABAergic neurons in the mPFC reduced scratching and chronic itch-induced anxiety. GABAergic, but not glutamatergic, neurons were involved in acute itch-induced aversion. CB1Rs on glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons modulated chronic itch-induced scratching and anxiety in divergent manners. However, CB1Rs did not affect acute itch-induced scratching. CB1Rs on GABAergic, but not glutamatergic, neurons regulated acute itch-induced aversion. These results may guide the development of therapeutic strategies targeting CB1Rs to treat itch-induced sensory and emotional responses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schonmann Y, Mansfield KE, Hayes JF, Abuabara K, Roberts A, Smeeth L, et al. Atopic eczema in adulthood and risk of depression and anxiety: a population-based cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8:248–57.e16.
Patel KR, Immaneni S, Singam V, Rastogi S, Silverberg JI. Association between atopic dermatitis, depression, and suicidal ideation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:402–10.
Umehara Y, Kiatsurayanon C, Trujillo-Paez JV, Chieosilapatham P, Peng G, Yue H, et al. Intractable itch in atopic dermatitis: causes and treatments. Biomedicines. 2021;9:229.
Moosa AS, Leng NSY, Kum CL, Tan NC. A qualitative research study on the illness perception of chronic pruritus in older asian adults based on the common-sense model of self-regulation. Health Expect. 2021;24:1801–11.
Angley M, Drews-Botsch C, Lewis TT, Badell M, Lim SS, Howards PP. Adverse perinatal outcomes before and after diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus among African American women. Arthritis Care Res. 2022;74:904–11.
Dong X, Dong X. Peripheral and central mechanisms of itch. Neuron. 2018;98:482–94.
Zeng F, Zeng F, Sugiyama N, Nogami M, Murakami T. A case of rectal dissemination of gastric cancer diagnosed by simultaneous 18F-FDG PET/MRI. Clin Nucl Med. 2023;48:e441–e3.
Zheng J, Zhang XM, Tang W, Li Y, Wang P, Jin J, et al. An insular cortical circuit required for itch sensation and aversion. Curr Biol. 2024;34:1453–68.e6.
Samineni VK, Grajales-Reyes JG, Grajales-Reyes GE, Tycksen E, Copits BA, Pedersen C, et al. Cellular, circuit and transcriptional framework for modulation of itch in the central amygdala. Elife. 2021;10:e68130.
Su XY, Chen M, Yuan Y, Li Y, Guo SS, Luo HQ, et al. Central processing of itch in the midbrain reward center. Neuron. 2019;102:858–72.e5.
Chen T, Zhu SJ, Xu S, Wang YQ, Aji A, Zhang C, et al. Resting-state fMRI reveals changes within the anxiety and social avoidance circuitry of the brain in mice with psoriasis-like skin lesions. Exp Dermatol. 2023;32:1900–14.
Papoiu ADP, Kraft RA, Coghill RC, Yosipovitch G. Butorphanol suppression of histamine itch is mediated by nucleus accumbens and septal nuclei: a pharmacological fMRI study. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:560–8.
Pan Q, Guo SS, Chen M, Su XY, Gao ZL, Wang Q, et al. Representation and control of pain and itch by distinct prefrontal neural ensembles. Neuron. 2023;111:2414–31.e7.
Chen M, He T, Yi XH, Tang MC, Long JH, Wang PJ, et al. Infralimbic cortex-medial striatum projections modulate the itch processing. Exp Neurol. 2022;354:114101.
Zhang TT, Guo SS, Wang HY, Jing Q, Yi X, Hu ZH, et al. An anterior cingulate cortex-to-midbrain projection controls chronic itch in mice. Neurosci Bull. 2023;39:793–807.
Ziegler DR, Cullinan WE, Herman JP. Distribution of vesicular glutamate transporter mRNA in rat hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol. 2002;448:217–29.
Bai L, Xu H, Collins JF, Ghishan FK. Molecular and functional analysis of a novel neuronal vesicular glutamate transporter. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:36764–9.
Vrettou M, Granholm L, Todkar A, Nilsson KW, Wallen-Mackenzie A, Nylander I, et al. Ethanol affects limbic and striatal presynaptic glutamatergic and DNA methylation gene expression in outbred rats exposed to early-life stress. Addict Biol. 2017;22:369–80.
Vrettou M, Yan L, Nilsson KW, Wallen-Mackenzie A, Nylander I, Comasco E. DNA methylation of vesicular glutamate transporters in the mesocorticolimbic brain following early-life stress and adult ethanol exposure-an explorative study. Sci Rep. 2021;11:15322.
Mao X, Staiger JF. Multimodal cortical neuronal cell type classification. Pflug Arch. 2024;476:721–33.
Huang ZJ. Toward a genetic dissection of cortical circuits in the mouse. Neuron. 2014;83:1284–302.
Harris KD, Shepherd GM. The neocortical circuit: themes and variations. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:170–81.
Xu P, Chen A, Li Y, Xing X, Lu H. Medial prefrontal cortex in neurological diseases. Physiol Genomics. 2019;51:432–42.
Li JN, Wu XM, Zhao LJ, Sun HX, Hong J, Wu FL, et al. Central medial thalamic nucleus dynamically participates in acute itch sensation and chronic itch-induced anxiety-like behavior in male mice. Nat Commun. 2023;14:2539.
Gaffal E, Cron M, Glodde N, Bald T, Kuner R, Zimmer A, et al. Cannabinoid 1 receptors in keratinocytes modulate proinflammatory chemokine secretion and attenuate contact allergic inflammation. J Immunol. 2013;190:4929–36.
Liu X, Li L, Jiang J, Ge W, Huang Y, Jin Z, et al. Role of type I cannabinoid receptor in sensory neurons in psoriasiform skin inflammation and pruritus. J Invest Dermatol. 2023;143:812–21.e3.
Christensen R, Kristensen PK, Bartels EM, Bliddal H, Astrup A. Efficacy and safety of the weight-loss drug rimonabant: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2007;370:1706–13.
Bilir KA, Anli G, Ozkan E, Gunduz O, Ulugol A. Involvement of spinal cannabinoid receptors in the antipruritic effects of win 55,212-2, a cannabinoid receptor agonist. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:553–8.
Lisboa SF, Borges AA, Nejo P, Fassini A, Guimaraes FS, Resstel LB. Cannabinoid Cb1 receptors in the dorsal hippocampus and prelimbic medial prefrontal cortex modulate anxiety-like behavior in rats: additional evidence. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015;59:76–83.
Imperatore R, Morello G, Luongo L, Taschler U, Romano R, De Gregorio D, et al. Genetic deletion of monoacylglycerol lipase leads to impaired cannabinoid receptor Cb(1)R signaling and anxiety-like behavior. J Neurochem. 2015;135:799–813.
Nagy-Pal P, Veres JM, Fekete Z, Karlocai MR, Weisz F, Barabas B, et al. Structural organization of perisomatic inhibition in the mouse medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci. 2023;43:6972–87.
Yeom M, Ahn S, Jang SY, Jang JH, Lee Y, Hahm DH, et al. Acupuncture attenuates comorbid anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors of atopic dermatitis through modulating neuroadaptation in the brain reward circuit in mice. Biol Res. 2022;55:28.
He ZX, Xi K, Liu KJ, Yue MH, Wang Y, Yin YY, et al. A nucleus accumbens Tac1 neural circuit regulates avoidance responses to aversive stimuli. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:4346.
Yin JB, Liang SH, Li F, Zhao WJ, Bai Y, Sun Y, et al. dmPFC-vlPAG projection neurons contribute to pain threshold maintenance and antianxiety behaviors. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:6555–70.
Mu D, Sun YG. Itch induces conditioned place aversion in mice. Neurosci Lett. 2017;658:91–6.
Samineni VK, Grajales-Reyes JG, Sundaram SS, Yoo JJ, Gereau RWT. Cell type-specific modulation of sensory and affective components of itch in the periaqueductal gray. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4356.
Kvitsiani D, Ranade S, Hangya B, Taniguchi H, Huang JZ, Kepecs A. Distinct behavioural and network correlates of two interneuron types in prefrontal cortex. Nature. 2013;498:363–6.
Takahashi S, Ochiai S, Jin J, Takahashi N, Toshima S, Ishigame H, et al. Sensory neuronal Stat3 is critical for IL-31 receptor expression and inflammatory itch. Cell Rep. 2023;42:113433.
Freund TF, Katona I, Piomelli D. Role of endogenous cannabinoids in synaptic signaling. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:1017–66.
Asano T, Takemoto H, Horita T, Tokutake T, Izuo N, Mochizuki T, et al. Sleep disturbance after cessation of cannabis administration in mice. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2023;43:505–12.
Xie JF, Wang LX, Ren WT, Wang C, Gao JX, Chen HL, et al. An alpha-hemoglobin-derived peptide (m)Vd-hemopressin (Alpha) promotes NREM sleep via the Cb1 cannabinoid receptor. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1213215.
Zhang Z, Gadotti VM, Chen L, Souza IA, Stemkowski PL, Zamponi GW. Role of prelimbic GABAergic circuits in sensory and emotional aspects of neuropathic pain. Cell Rep. 2015;12:752–9.
Pastor V, Medina JH. Medial prefrontal cortical control of reward- and aversion-based behavioral output: bottom-up modulation. Eur J Neurosci. 2021;53:3039–62.
Kuner R, Kuner T. Cellular circuits in the brain and their modulation in acute and chronic pain. Physiol Rev. 2021;101:213–58.
Sun Q, Li X, Ren M, Zhao M, Zhong Q, Ren Y, et al. A whole-brain map of long-range inputs to gabaergic interneurons in the mouse medial prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:1357–70.
Malik R, Li Y, Schamiloglu S, Sohal VS. Top-down control of hippocampal signal-to-noise by prefrontal long-range inhibition. Cell. 2022;185:1602–17.e17.
Dinh HT, Nishimaru H, Le QV, Matsumoto J, Setogawa T, Maior RS, et al. Preferential neuronal responses to snakes in the monkey medial prefrontal cortex support an evolutionary origin for ophidiophobia. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021;15:653250.
Fu S, Sun H, Wang J, Gao S, Zhu L, Cui K, et al. Impaired neuronal macroautophagy in the prelimbic cortex contributes to comorbid anxiety-like behaviors in rats with chronic neuropathic pain. Autophagy. 2024;20:1559–76.
Song H, Lu X, Du D, Peng Y, Pan W, Xu X, et al. Gegen-qinlian decoction-A traditional Chinese medicine formula-alleviates methamphetamine withdrawal induced anxiety by targeting gabaergic interneuron-pyramidal neuron pathway in mPFC. Addict Biol. 2023;28:e13314.
Zhou Q, Jiang N, Dong Y, Tian K. Dexmedetomidine alleviates anxiety-like behaviors in female mice with musculoskeletal pain through Sirt1/p53 axis. Brain Res Bull. 2023;201:110698.
Xue B, Ma YY, Zhu JY, Mu Y, Li YH, Shen F, et al. Chronic social comparison elicits depression- and anxiety-like behaviors and alterations in brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in male rats. Anim Cogn. 2023;26:1505–19.
Tremblay R, Lee S, Rudy B. GABAergic interneurons in the neocortex: from cellular properties to circuits. Neuron. 2016;91:260–92.
Miyoshi G. Elucidating the developmental trajectories of gabaergic cortical interneuron subtypes. Neurosci Res. 2019;138:26–32.
Tong X, Wu J, Sun R, Li H, Hong Y, Liu X, et al. Elevated dorsal medial prefrontal cortex to lateral habenula pathway activity mediates chronic stress-induced depressive and anxiety-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024;49:1402–11.
Granja-Galeano G, Dominguez-Rubio AP, Zappia CD, Wolfson M, Sanz-Blasco S, Aisemberg J, et al. CB1 receptor expression and signaling are required for dexamethasone-induced aversive memory consolidation. Neuropharmacology. 2023;239:109674.
Kano M, Ohno-Shosaku T, Hashimotodani Y, Uchigashima M, Watanabe M. Endocannabinoid-mediated control of synaptic transmission. Physiol Rev. 2009;89:309–80.
Wu J, Hua L, Liu W, Yang X, Tang X, Yuan S, et al. Electroacupuncture exerts analgesic effects by restoring hyperactivity via cannabinoid type 1 receptors in the anterior cingulate cortex in chronic inflammatory pain. Mol Neurobiol. 2024;61:2949–63.
Marinelli S, Pacioni S, Cannich A, Marsicano G, Bacci A. Self-modulation of neocortical pyramidal neurons by endocannabinoids. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:1488–90.
Cong J, Lu K, Zou W, Li Z, Guo Z, Tong X, et al. Astroglial CB1 cannabinoid receptors mediate CP 55,940-induced conditioned place aversion through cyclooxygenase-2 signaling in mice. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:772549.
Humburg BA, Jordan CJ, Zhang HY, Shen H, Han X, Bi GH, et al. Optogenetic brain-stimulation reward: a new procedure to re-evaluate the rewarding versus aversive effects of cannabinoids in dopamine transporter-Cre mice. Addict Biol. 2021;26:e13005.
Borges-Assis AB, Uliana DL, Hott SC, Guimaraes FS, Lisboa SF, Resstel LBM. Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis CB1 receptors and the FAAH enzyme modulate anxiety behavior depending on previous stress exposure. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2023;125:110739.
Gonczarowska N, Tomaz C, Caixeta FV, Malcher-Lopes R, Barros M, Nishijo H, et al. CB1 receptor antagonism in Capuchin monkeys alters social interaction and aversive memory extinction. Psychopharmacology. 2019;236:3413–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. He Zhu (Zhanjiang Central People’s Hospital) for kindly providing adult Vglut2-Cre and Vgat-Cre mice. This work was supported by grants from the National Youth Natural Science Foundation (82205275, 82305002) and the Chinese Postdoctoral Foundation (0106510145, 0106510062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ML and QT designed all the experiments and revised the manuscript. OYZM performed the virus injection, behavioral tests, and western blotting; analyzed the data; and drafted the manuscript. YY performed virus injection, analyzed the data, and revised the manuscript. BF performed the EEG. HYW assisted with the fiber photometry and performed the electrophysiology experiments. HL provided assistance with cannula implantation and optogenetic modulation. HJZ performed the western blotting. HLP edited the manuscript. WQG, KXW, LP, KLZ, SXW and HZ helped to revise the article. All the experiments were supervised by ML and QT. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhanmu, OY., Yang, Y., Feng, B. et al. Differential regulation of pruritic sensation and emotion by cannabinoid type 1 receptors on mPFC glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons. Acta Pharmacol Sin 46, 904–921 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01426-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01426-1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Central neural circuits underlying itch sensation
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2025)