Abstract
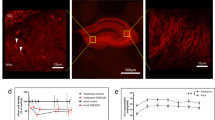
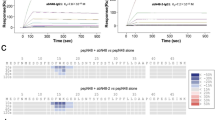
Research shows that chronic pain may induce depression-like behaviors through impairing adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) in the ventral dentate gyrus (DG), whereas restoration of AHN may effectively alleviate depression. The C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2) is a chemokine receptor involved in various neural activities of the hippocampus including AHN. In this study we investigated the role of CXCR2 of neural stem cells (NSCs) in the ventral DG in regulating both AHN and depression-like behaviors of mice with chronic neuropathic pain. Chronic neuropathic pain was induced in mice by the spared nerve injury (SNI) surgery; mechanical allodynia and depression-like behaviors were monitored, then mouse DG was collected for analysis. We observed that chronic neuropathic pain significantly decreased the number of immature neurons in the ventral DG by inhibiting the neuronal differentiation of NSCs; specific overexpression of CXCR2 in NSCs by injecting the adeno-associated virus (AAV) into the DG restored adult neurogenesis accompanied by alleviated depression-like behaviors in SNI mice. In contrast, the knockdown of CXCR2 in hippocampal NSCs of naive mice was sufficient to inhibit adult neurogenesis, inducing depression-like behaviors. Moreover, we found that the Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway was downregulated in the ventral DG of SNI mice, which was restored after CXCR2 overexpression or infusing a CXCR2 agonist CXCL1 into the ventral DG. We conclude that CXCR2 expressed in hippocampal NSCs is crucial for regulating adult neurogenesis and chronic pain-induced depression-like behavior, thus representing a new target for the treatment of chronic pain comorbid depression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaro-Díaz L, Montoro CI, Fischer-Jbali LR, Galvez-Sánchez CM. Chronic pain and emotional stroop: a systematic review. J Clin Med. 2022;11:3259.
Flores-García M, Rizzo A, Garçon-Poca MZ, Fernández-Dueñas V, Bonaventura J. Converging circuits between pain and depression: The ventral tegmental area as a therapeutic hub. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1278023.
Toda T, Parylak SL, Linker SB, Gage FH. The role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in brain health and disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24:67–87.
Knezevic E, Nenic K, Milanovic V, Knezevic NN. The role of cortisol in chronic stress, neurodegenerative diseases, and psychological disorders. Cells. 2023;12:2726.
Gohari J, Grosman-Rimon L, Arazi M, Caspi-Avissar N, Granot D, Gleitman S, et al. Clinical factors and pre-surgical depression scores predict pain intensity in cardiac surgery patients. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022;22:204.
Bonilla-Jaime H, Sanchez-Salcedo JA, Estevez-Cabrera MM, Molina-Jimenez T, Cortes-Altamirano JL, Alfaro-Rodriguez A. Depression and pain: Use of antidepressants. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20:384–402.
Chiou CS, Huang CC, Liang YC, Tsai YC, Hsu KS. Impairment of long-term depression in the anterior cingulate cortex of mice with bone cancer pain. Pain. 2012;153:2097–108.
Xu Y, Zhu X, Chen Y, Chen Y, Zhu Y, Xiao S, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates mechanical allodynia and anxiety-like behaviors induced by chronic neuropathic pain via regulating rostral anterior cingulate cortex-dorsal raphe nucleus neural circuit. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023;29:4043–58.
Xia SH, Hu SW, Ge DG, Liu D, Wang D, Zhang S, et al. Chronic pain impairs memory formation via disruption of neurogenesis mediated by mesohippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling. Biol Psychiatry. 2020;88:597–610.
Li Y, Liu X, Fu Q, Fan W, Shao X, Fang J, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates depression-like behaviors comorbid to chronic neuropathic pain via tet1-mediated restoration of adult neurogenesis. Stem Cells. 2023;41:384–99.
Toda T, Gage FH. Review: Adult neurogenesis contributes to hippocampal plasticity. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;373:693–709.
Levone BR, Cryan JF, O’Leary OF. Specific sub-regions of the longitudinal axis of the hippocampus mediate behavioural responses to chronic psychosocial stress. Neuropharmacology. 2021;201:108843.
Garman A, Ash AM, Kokkinos EK, Nerland D, Winter L, Langreck CB, et al. Novel hippocampal genes involved in enhanced susceptibility to chronic pain-induced behavioral emotionality. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024;964:176273.
Yun S, Reynolds RP, Petrof I, White A, Rivera PD, Segev A, et al. Stimulation of entorhinal cortex-dentate gyrus circuitry is antidepressive. Nat Med. 2018;24:658–66.
Xu C, Fan W, Zhang Y, Loh HH, Law PY. Kappa opioid receptor controls neural stem cell differentiation via a mir-7a/pax6 dependent pathway. Stem Cells. 2021;39:600–16.
Li HH, Liu Y, Chen HS, Wang J, Li YK, Zhao Y, et al. Pdgf-bb-dependent neurogenesis buffers depressive-like behaviors by inhibition of gabaergic projection from medial septum to dentate gyrus. Adv Sci. 2023;10:e2301110.
Tang X, Walter E, Wohleb E, Fan Y, Wang C. Atg5 (autophagy related 5) in microglia controls hippocampal neurogenesis in alzheimer disease. Autophagy. 2024;20:847–62.
Villeda SA, Luo J, Mosher KI, Zou B, Britschgi M, Bieri G, et al. The ageing systemic milieu negatively regulates neurogenesis and cognitive function. Nature. 2011;477:90–4.
Edman LC, Mira H, Erices A, Malmersjo S, Andersson E, Uhlen P, et al. Alpha-chemokines regulate proliferation, neurogenesis, and dopaminergic differentiation of ventral midbrain precursors and neurospheres. Stem Cells. 2008;26:1891–900.
Huang F, Lan Y, Qin L, Dong H, Shi H, Wu H, et al. Astragaloside iv promotes adult neurogenesis in hippocampal dentate gyrus of mouse through cxcl1/cxcr2 signaling. Molecules. 2018;23:2178.
Schultheiss C, Abe P, Hoffmann F, Mueller W, Kreuder AE, Schutz D, et al. Cxcr4 prevents dispersion of granule neuron precursors in the adult dentate gyrus. Hippocampus. 2013;23:1345–58.
Shen Y, Jing L, Zhang Y, Bao H, Vohra A, Si Y, et al. Cxcr5 knockdown attenuates hippocampal neurogenesis deficits and cognitive impairment in a mouse model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Neuroscience. 2020;433:212–20.
Zonis S, Breunig JJ, Mamelak A, Wawrowsky K, Bresee C, Ginzburg N, et al. Inflammation-induced gro1 triggers senescence in neuronal progenitors: effects of estradiol. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15:260.
Chai HH, Fu XC, Ma L, Sun HT, Chen GZ, Song MY, et al. The chemokine cxcl1 and its receptor cxcr2 contribute to chronic stress-induced depression in mice. FASEB J. 2019;33:8853–64.
Salter MW, Stevens B. Microglia emerge as central players in brain disease. Nat Med. 2017;23:1018–27.
Bot M, Chan MK, Jansen R, Lamers F, Vogelzangs N, Steiner J, et al. Serum proteomic profiling of major depressive disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2015;5:e599.
Abbadie C. Chemokines, chemokine receptors and pain. Trends Immunol. 2005;26:529–34.
Heppt J, Wittmann MT, Schaffner I, Billmann C, Zhang J, Vogt-Weisenhorn D, et al. Beta-catenin signaling modulates the tempo of dendritic growth of adult-born hippocampal neurons. EMBO J. 2020;39:e104472.
Tao W, Ruan J, Wu R, Zhao M, Zhao T, Qi M, et al. A natural carotenoid crocin exerts antidepressant action by promoting adult hippocampal neurogenesis through wnt/beta-catenin signaling. J Adv Res. 2023;43:219–31.
Xiao Z, Cao Z, Yang J, Jia Z, Du Y, Sun G, et al. Baicalin promotes hippocampal neurogenesis via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in a chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced mouse model of depression. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;190:114594.
Arredondo SB, Valenzuela-Bezanilla D, Mardones MD, Varela-Nallar L. Role of Wnt signaling in adult hippocampal neurogenesis in health and disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:860.
Han H, Xu M, Wang J, Li MD, Yang Z. Crispr/cas9 based gene editing of frizzled class receptor 6 (fzd6) reveals its role in depressive symptoms through disrupting wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J Adv Res. 2024;58:129–38.
Wu M, Chen Y, Shen Z, Zhu Y, Xiao S, Zhu X, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates anxiety-like behaviors induced by chronic neuropathic pain via regulating different dopamine receptors of the basolateral amygdala. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59:5299–311.
Chai W, Tai Y, Shao X, Liang Y, Zheng GQ, Wang P, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates pain responses and inflammation in a rat model of acute gout arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018:2598975.
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 1994;53:55–63.
Papp M, Willner P, Muscat R. An animal model of anhedonia: Attenuation of sucrose consumption and place preference conditioning by chronic unpredictable mild stress. Psychopharmacology. 1991;104:255–9.
Guo W, Patzlaff NE, Jobe EM, Zhao X. Isolation of multipotent neural stem or progenitor cells from both the dentate gyrus and subventricular zone of a single adult mouse. Nat Protoc. 2012;7:2005–12.
O’Leary OF, Cryan JF. A ventral view on antidepressant action: Roles for adult hippocampal neurogenesis along the dorsoventral axis. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014;35:675–87.
Hill JD, Zuluaga-Ramirez V, Gajghate S, Winfield M, Persidsky Y. Activation of gpr55 increases neural stem cell proliferation and promotes early adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175:3407–21.
Ocasio JK, Bates RDP, Rapp CD, Gershon TR. Gsk-3 modulates shh-driven proliferation in postnatal cerebellar neurogenesis and medulloblastoma. Development. 2019;146:dev177550.
Song Y, Shi R, Liu Y, Cui F, Han L, Wang C, et al. M2 microglia extracellular vesicle mir-124 regulates neural stem cell differentiation in ischemic stroke via aak1/notch. Stroke. 2023;54:2629–39.
Hanifa M, Singh M, Randhawa PK, Jaggi AS, Bali A. A focus on rho/rock signaling pathway: an emerging therapeutic target in depression. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;946:175648.
Chan KL, Poller WC, Swirski FK, Russo SJ. Central regulation of stress-evoked peripheral immune responses. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2023;24:591–604.
Kofod J, Elfving B, Nielsen EH, Mors O, Kohler-Forsberg O. Depression and inflammation: correlation between changes in inflammatory markers with antidepressant response and long-term prognosis. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022;54:116–25.
Beurel E, Toups M, Nemeroff CB. The bidirectional relationship of depression and inflammation: double trouble. Neuron. 2020;107:234–56.
Trojan E, Slusarczyk J, Chamera K, Kotarska K, Glombik K, Kubera M, et al. The modulatory properties of chronic antidepressant drugs treatment on the brain chemokine - chemokine receptor network: a molecular study in an animal model of depression. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:779.
Sun X, Peng X, Cao Y, Zhou Y, Sun Y. Adnp promotes neural differentiation by modulating wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2984.
Vachon P, Millecamps M, Low L, Thompsosn SJ, Pailleux F, Beaudry F, et al. Alleviation of chronic neuropathic pain by environmental enrichment in mice well after the establishment of chronic pain. Behav Brain Funct. 2013;9:22.
Apkarian AV, Mutso AA, Centeno MV, Kan L, Wu M, Levinstein M, et al. Role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in persistent pain. Pain. 2016;157:418–28.
Ruetz TJ, Pogson AN, Kashiwagi CM, Gagnon SD, Morton B, Sun ED, et al. Crispr-cas9 screens reveal regulators of ageing in neural stem cells. Nature. 2024;634:1150–9.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the technical support from the Public Platform of Medical Research Center, Academy of Chinese Medical Science, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University. This work was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Health Program (Grant No. 2025KY985), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LY22H270004), Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Grant No. 2022FSYYZZ11), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82030112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XJL, SW, ZHL, AAL, HSP, and YXC collected and assembled the data; XJL, SW, YJW, YXC, and CX analyzed and interpreted the data; XJL and CX wrote the manuscript; JGL and CX provided conception, design, financial and administrative support, and final approval of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Xj., Wu, S., Liu, Zh. et al. CXCR2 modulates chronic pain comorbid depression in mice by regulating adult neurogenesis in the ventral dentate gyrus. Acta Pharmacol Sin 46, 1567–1579 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01496-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01496-9