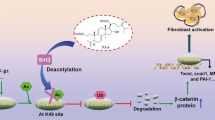
Abstract
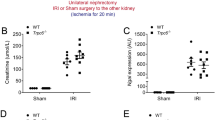
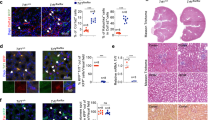
Previous studies on acute kidney injury (AKI) have predominantly focused on renal tubular cells, while the specific role of fibroblasts has been largely neglected. Recent evidence shows that PU.1/Spi1, a transcription factor, is an important modulator of fibroblast activation, whereas pharmacological and genetic silencing of PU.1/Spi1 disrupts the fibrotic network and reprograms activated fibroblasts into quiescent fibroblasts. In this study we investigated whether and how PU.1/Spi1 regulated renal fibroblast activation during AKI. An AKI model was established in male mice by clamping bilateral renal arteries for 30 min. Mice were sacrificed and blood and kidney samples were collected 48 h after the surgery. We showed that the expression level of PU.1/Spi1 was significantly upregulated in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced AKI and PU.1/Spi1 was specifically localized in fibroblasts. Meanwhile, we observed that a massive activation of fibroblasts occurred at the early stage of AKI. PU.1/Spi1 knockout significantly attenuated the activation of fibroblasts along with the decreased release of inflammatory factors and tubular injury. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that GATA binding protein 2 (Gata2), an evolutionarily conserved gene, might be a downstream target gene of PU.1/Spi1. In primary cultured mouse kidney fibroblasts subjected to hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R), the expression levels of PU.1/Spi1, Gata2 and α-SMA were significantly upregulated. Activated fibroblasts exhibited elevated proliferative capacity, evidenced by upregulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and cell cycle proteins such as cyclin B1 and cyclin D3. The secretion of inflammatory factors was increased in the activated fibroblasts. Conditioned medium from H/R-treated fibroblasts induced tubular cell injury and increased apoptosis. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation and promoter-luciferase assays, we demonstrated that PU.1/Spi1 was able to bind to the promoter region of Gata2 and enhanced its transcription. Our results show that interstitial fibroblasts are activated at the early stage of I/R-induced AKI and involved in renal injury. Upregulated PU.1/Spi1 stimulates fibroblast activation by upregulating its downstream gene Gata2. Inhibiting the activation of fibroblasts may have a beneficial effect on AKI.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kellum JA, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G, Ronco C, Zarbock A, Anders HJ. Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:52.
Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet. 2012;380:756–66.
Basile DP. The endothelial cell in ischemic acute kidney injury: implications for acute and chronic function. Kidney Int. 2007;72:151–6.
Raup-Konsavage WM, Wang Y, Wang WW, Feliers D, Ruan H, Reeves WB. Neutrophil peptidyl arginine deiminase-4 has a pivotal role in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2018;93:365–74.
de Oliveira RC, Wilson SE. Fibrocytes, wound healing, and corneal fibrosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020;61:28.
Talbott HE, Mascharak S, Griffin M, Wan DC, Longaker MT. Wound healing, fibroblast heterogeneity, and fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29:1161–80.
Lynch MD, Watt FM. Fibroblast heterogeneity: implications for human disease. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:26–35.
Tiggelman AMB, Boers W, Lintherst C, Brand HS, Sala M, Chamuleau RAF. Interleukin-6 production by human liver (myo)fibroblasts in culture - evidence for a regulatory role of lps, Il-1-beta and Tnf-alpha. J Hepatol. 1995;23:295–306.
Travers JG, Kamal FA, Robbins J, Yutzey KE, Blaxall BC. Cardiac fibrosis: the fibroblast awakens. Circ Res. 2016;118:1021–40.
Aggarwal S, Wang ZX, Pacheco DRF, Rinaldi A, Rajewski A, Callemeyn J, et al. SOX9 switch links regeneration to fibrosis at the single-cell level in mammalian kidneys. Science. 2024;383:eadd6371.
Humphreys BD, Bonventre JV. Mesenchymal stem cells in acute kidney injury. Annu Rev Med. 2008;59:311–25.
Zhou D, Fu H, Xiao L, Mo H, Zhuo H, Tian X, et al. Fibroblast-specific beta-catenin signaling dictates the outcome of AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29:1257–71.
Bendavid Y, Giddens EB, Letwin K, Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia-virus - insertional activation of a new member of the Ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to C-Ets-1. Gene Dev. 1991;5:908–18.
Zhao XH, Bartholdy B, Yamamoto Y, Evans EK, Alberich-Jordà M, Staber PB, et al. PU.1-c-Jun interaction is crucial for PU.1 function in myeloid development. Commun Biol. 2022;5:961.
Li GL, Hao WK, Hu WX. Transcription factor PU.1 and immune cell differentiation (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2020;46:1943–50.
Ralvenius WT, Andresen JL, Huston MM, Penney J, Bonner JM, Fenton OS, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of anti-PU.1 siRNA via localized intracisternal administration reduces neuroinflammation. Adv Mater. 2024;36:e2309225.
Liu QM, Yu JJ, Wang LH, Tang YL, Zhou Q, Ji SH, et al. Inhibition of PU.1 ameliorates metabolic dysfunction and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2020;73:361–70.
Wohlfahrt T, Rauber S, Uebe S, Luber M, Soare A, Ekici A, et al. PU.1 controls fibroblast polarization and tissue fibrosis. Nature. 2019;566:344.
Zhang Y, Tang PM, Niu Y, Garcia Cordoba CA, Huang XR, Yu C, et al. Long non-coding RNA LRNA9884 promotes acute kidney injury via regulating NF-κB-mediated transcriptional activation of MIF. Front Physiol. 2020;11:590027.
Coca SG, Singanamala S, Parikh CR. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012;81:442–8.
Xue JL, Daniels F, Star RA, Kimmel PL, Eggers PW, Molitoris BA, et al. Incidence and mortality of acute renal failure in medicare beneficiaries, 1992 to 2001. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1135–42.
Venkatachalam MA, Weinberg JM, Kriz W, Bidani AK. Failed tubule recovery, AKI-CKD transition, and kidney disease progression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26:1765–76.
Maremonti F, Meyer C, Linkermann A. Mechanisms and models of kidney tubular necrosis and nephron loss. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022;33:472–86.
Zuk A, Bonventre JV. Acute kidney injury. Annu Rev Med. 2016;67:293–307.
Leaf DE, Rajapurkar M, Lele SS, Mukhopadhyay B, Boerger EAS, Mc Causland FR, et al. Iron, hepcidin, and death in human AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;30:493–504.
Li X, Yuan F, Xiong Y, Tang Y, Li Z, Ai J, et al. FAM3A plays a key role in protecting against tubular cell pyroptosis and acute kidney injury. Redox Biol. 2024;74:103225.
Lin QS, Li S, Jiang N, Jin HJ, Shao XH, Zhu XY, et al. Inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome attenuates apoptosis in contrast-induced acute kidney injury through the upregulation of HIF1A and BNIP3-mediated mitophagy. Autophagy. 2021;17:2975–90.
Wynn TA, Ramalingam TR. Mechanisms of fibrosis: therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat Med. 2012;18:1028–40.
Sakai N, Wada T, Yokoyama H, Lipp M, Ueha S, Matsushima K, et al. Secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine (SLC/CCL21)/CCR7 signaling regulates fibrocytes in renal fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:14098–103.
Baues M, Dasgupta A, Ehling J, Prakash J, Boor P, Tacke F, et al. Fibrosis imaging: current concepts and future directions. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;121:9–26.
Kinchen J, Chen HH, Parikh K, Antanaviciute A, Jagielowicz M, Fawkner-Corbett D, et al. Structural remodeling of the human colonic mesenchyme in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell. 2018;175:372–86.e17.
West NR, Hegazy AN, Owens BMJ, Bullers SJ, Linggi B, Buonocore S, et al. Oncostatin M drives intestinal inflammation and predicts response to tumor necrosis factor-neutralizing therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Med. 2017;23:579–89.
Huang B, Chen Z, Geng L, Wang J, Liang H, Cao Y, et al. Mucosal profiling of pediatric-onset colitis and IBD reveals common pathogenics and therapeutic pathways. Cell. 2019;179:1160–76.e24.
Komatsu N, Takayanagi H. Mechanisms of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis - immune cell-fibroblast-bone interactions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18:415–29.
Zhang Y, Huang H, Kong Y, Xu C, Dai L, Geng X, et al. Kidney tubular transcription co-activator, Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP), controls the expression of collecting duct aquaporins and water homeostasis. Kidney Int. 2023;103:501–13.
Estrela GR, Freitas-Lima LC, Budu A, Arruda AC, Perilhao MS, Fock RA, et al. Chronic kidney disease induced by cisplatin, folic acid and renal ischemia reperfusion induces anemia and promotes GATA-2 activation in mice. Biomedicines. 2021;9:769.
Patient RK, McGhee JD. The GATA family (vertebrates and invertebrates). Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002;12:416–22.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Natural National Science Foundation of China (No. 82370718 to Jian-ying Niu, No. 82370695, 82070712 to Li-min Lu), and National Clinical Research Center for Aging and Medicine, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University (2024KF2004) to Li-min Lu, the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (14DZ2260200, the project of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Kidney and Blood Purification).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CZ and LML conceived and designed the study. CZ performed the experiment and drafted the manuscript. GLX and MN contributed to the material preparation and data collection. JYL, XW, HJG, LHZ and ZHY performed formal analysis. LZ and CX contributed technical support. LML and JYN supervised the findings and reviewed the final manuscript. All the authors declared no competing interests.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zong, C., Xu, Gl., Ning, M. et al. PU.1/Spi1 exacerbates ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury via upregulating Gata2 and promoting fibroblast activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 46, 2251–2266 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01530-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01530-w
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
In vitro models to mimic tumor endothelial cell-mediated immune cell reprogramming in lung adenocarcinoma
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2025)