Abstract
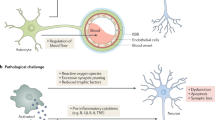
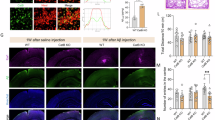
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease worldwide. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation is closely associated with AD pathogenesis. Abnormal deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) expression is associated with neuroinflammation. Identification of functional DUBs in microglia may provide novel targets for AD treatment. Here, we found that the levels of DUB, ovarian tumor deubiquitinase 1 (OTUD1), were upregulated in AD model mice and amyloid-beta-induced microglia. OTUD1 knockdown in microglia significantly inhibited neuroinflammation, thereby improving cognitive impairment in AD model mice. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis coupled with co-immunoprecipitation revealed the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ), a key transcription factor regulating microglial inflammation, as an OTUD1-interacting protein. Mechanistically, OTUD1 bound to C/EBPβ and maintained its stability by removing the K48 ubiquitin chain at K253 of C/EBPβ, thereby activating the C/EBPβ–nuclear factor-κB-mediated inflammatory responses in microglia. Overall, our results revealed the roles of the OTUD1–C/EBPβ axis in mediating the microglial inflammatory responses and AD pathology, facilitating the development of new strategies targeting microglial neuroinflammation for AD treatment.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023;19:1598–695.
Sharma H, Chang K-A, Hulme J, An SSA. Mammalian models in Alzheimer’s research: an update. Cells. 2023;12:2459.
Srivastava S, Ahmad R, Khare SK. Alzheimer’s disease and its treatment by different approaches: A review. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;216:113320.
Ocañas SR, Pham KD, Cox JEJ, Keck AW, Ko S, Ampadu FA, et al. Microglial senescence contributes to female-biased neuroinflammation in the aging mouse hippocampus: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20:188.
Yang Y, García-Cruzado M, Zeng H, Camprubí-Ferrer L, Bahatyrevich-Kharitonik B, Bachiller S, et al. LPS priming before plaque deposition impedes microglial activation and restrains Aβ pathology in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav Immun. 2023;113:228–47.
Schaffer Aguzzoli C, Ferreira PCL, Povala G, Ferrari-Souza JP, Bellaver B, Soares Katz C, et al. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and microglial activation in patients with Alzheimer disease. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:e2345175.
Lin J, Zheng Y, Zhao N, Cui F, Wu S. Herpesvirus latent infection promotes stroke via activating the OTUD1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15:8976–92.
Oikawa D, Gi M, Kosako H, Shimizu K, Takahashi H, Shiota M, et al. OTUD1 deubiquitinase regulates NF-κB- and KEAP1-mediated inflammatory responses and reactive oxygen species-associated cell death pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:694.
Zhang Z, Wang D, Wang P, Zhao Y, You F. OTUD1 negatively regulates type I IFN induction by disrupting noncanonical ubiquitination of IRF3. J Immunol. 2020;204:1904–18.
Lu D, Song J, Sun Y, Qi F, Liu L, Jin Y, et al. Mutations of deubiquitinase OTUD1 are associated with autoimmune disorders. J Autoimmun. 2018;94:156–65.
Wang M, Han X, Yu T, Wang M, Luo W, Zou C, et al. OTUD1 promotes pathological cardiac remodeling and heart failure by targeting STAT3 in cardiomyocytes. Theranostics. 2023;13:2263–80.
Wang M, Yu T, Wang Q, Han X, Hu X, Ye S, et al. OTUD1 promotes hypertensive kidney fibrosis and injury by deubiquitinating CDK9 in renal epithelial cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;45:765–76.
Sun J, Li L, Xiong L, Chen F, She L, Tang H, et al. Parthenolide alleviates cognitive dysfunction and neurotoxicity via regulation of AMPK/GSK3β(Ser9)/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;169:115909.
She L, She L, Sun J, Xiong L, Li A, Li L, et al. Ginsenoside RK1 improves cognitive impairments and pathological changes in Alzheimer’s disease via stimulation of the AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2024;122:155168.
Li Y, Zhang ZH, Huang SL, Yue ZB, Yin XS, Feng ZQ, et al. Whey protein powder with milk fat globule membrane attenuates Alzheimer’s disease pathology in 3×Tg-AD mice by modulating neuroinflammation through the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ signaling pathway. J Dairy Sci. 2023;106:5253–65.
Zhao X, Sun J, Xiong L, She L, Li L, Tang H, et al. β-amyloid binds to microglia Dectin-1 to induce inflammatory response in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19:3249–65.
Huang Z, Shen S, Wang M, Li W, Wu G, Huang W, et al. Mouse endothelial OTUD1 promotes angiotensin II‐induced vascular remodeling by deubiquitinating SMAD3. EMBO Rep. 2023;24:e56135.
Ali M, Garcia P, Lunkes LP, Sciortino A, Thomas M, Heurtaux T, et al. Single cell transcriptome analysis of the THY-Tau22 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease reveals sex-dependent dysregulations. Cell Death Discov. 2024;10:119.
Yan Y, Wang X, Chaput D, Shin MK, Koh Y, Gan L, et al. X-linked ubiquitin-specific peptidase 11 increases tauopathy vulnerability in women. Cell. 2022;185:3913–30.e19.
Ndoja A, Reja R, Lee SH, Webster JD, Ngu H, Rose CM, et al. Ubiquitin ligase COP1 suppresses neuroinflammation by degrading c/EBPβ in microglia. Cell. 2020;182:1156–69.e12.
Tsukada J, Yoshida Y, Kominato Y, Auron PE. The CCAAT/enhancer (C/EBP) family of basic-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors is a multifaceted highly-regulated system for gene regulation. Cytokine. 2011;54:6–19.
Leutz A, Pless O, Lappe M, Dittmar G, Kowenz-Leutz E. Crosstalk between phosphorylation and multi-site arginine/lysine methylation in C/EBPs. Transcription. 2011;2:3–8.
Yi-Bin W, Xiang L, Bing Y, Qi Z, Fei-Tong J, Minghong W, et al. Inhibition of the CEBPβ-NFκB interaction by nanocarrier-packaged carnosic acid ameliorates glia-mediated neuroinflammation and improves cognitive function in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:318.
Mikami T, Majima S, Song H, Bode JW. Biocompatible lysine protecting groups for the chemoenzymatic synthesis of K48/K63 heterotypic and branched ubiquitin chains. ACS Cent Sci. 2023;9:1633–41.
Hu H, Sun S-C. Ubiquitin signaling in immune responses. Cell Res. 2016;26:457–83.
Tanji K, Mori F, Miki Y, Utsumi J, Sasaki H, Kakita A, et al. YOD1 attenuates neurogenic proteotoxicity through its deubiquitinating activity. Neurobiol Dis. 2018;112:14–23.
Zheng Q, Li G, Wang S, Zhou Y, Liu K, Gao Y, et al. Trisomy 21–induced dysregulation of microglial homeostasis in Alzheimer’s brains is mediated by USP25. Sci Adv. 2021;7:eabe1340.
Zhang XW, Feng N, Liu YC, Guo Q, Wang JK, Bai YZ, et al. Neuroinflammation inhibition by small-molecule targeting USP7 noncatalytic domain for neurodegenerative disease therapy. Sci Adv. 2022;8:eabo0789.
Song J, Zhang Y, Bai Y, Sun X, Lu Y, Guo Y, et al. The deubiquitinase OTUD1 suppresses secretory neutrophil polarization and ameliorates immunopathology of periodontitis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10:2303207.
Zhang Z, Fan Y, Xie F, Zhou H, Jin K, Shao L, et al. Breast cancer metastasis suppressor OTUD1 deubiquitinates SMAD7. Nat Commun. 2017;8:2116.
Gao C, Jiang J, Tan Y, Chen S. Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:359.
Cheng J, Dong Y, Ma J, Pan R, Liao Y, Kong X, et al. Microglial Calhm2 regulates neuroinflammation and contributes to Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Sci Adv. 2021;7:eabe3600.
Li Z, Chu S, He W, Zhang Z, Liu J, Cui L, et al. A20 as a novel target for the anti-neuroinflammatory effect of chrysin via inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway. Brain Behav Immun. 2019;79:228–35.
Wang Y, Yang Z, Wang Q, Ren Y, Wang Q, Li Z, et al. Bavachin exerted anti-neuroinflammatory effects by regulation of A20 ubiquitin-editing complex. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108085.
Zhang X, Liu T, Xu S, Gao P, Dong W, Liu W, et al. A pro-inflammatory mediator USP11 enhances the stability of p53 and inhibits KLF2 in intracerebral hemorrhage. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021;21:681–92.
Fonseca GJ, Seidman JS, Glass CK. Genome-wide approaches to defining macrophage identity and function. Microbiol Spectr. 2016;4:10.
Srinivasan K, Friedman BA, Larson JL, Lauffer BE, Goldstein LD, Appling LL, et al. Untangling the brain’s neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative transcriptional responses. Nat Commun. 2016:7:11295.
Wang Z-H, Gong K, Liu X, Zhang Z, Sun X, Wei ZZ, et al. C/EBPβ regulates delta-secretase expression and mediates pathogenesis in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1784.
Xu QQ, Su ZR, Yang W, Zhong M, Xian YF, Lin ZX, et al. Patchouli alcohol attenuates the cognitive deficits in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease via modulating neuropathology and gut microbiota through suppressing C/EBPβ/AEP pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20:19.
Lu J, Wu DM, Zheng YL, Hu B, Cheng W, Zhang ZF, et al. Troxerutin counteracts domoic acid–induced memory deficits in mice by inhibiting CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β–mediated inflammatory response and oxidative stress. J Immunol. 2013;190:3466–79.
Ren Q, Liu Z, Wu L, Yin G, Xie X, Kong W, et al. C/EBPβ: The structure, regulation, and its roles in inflammation-related diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;169:115938.
Xu J, Yu T, Pietronigro EC, Yuan J, Arioli J, Pei Y, et al. Peli1 impairs microglial Aβ phagocytosis through promoting C/EBPβ degradation. PLoS Biol. 2020;18:e3000837.
Fu D, Lala-Tabbert N, Lee H, Wiper-Bergeron N. Mdm2 promotes myogenesis through the ubiquitination and degradation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:10200–7.
Kim MS, Baek JH, Lee J, Sivaraman A, Lee K, Chun KH, et al. Deubiquitinase USP1 enhances CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPβ) stability and accelerates adipogenesis and lipid accumulation. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14:776.
Wang L, Wang P, Xu S, Li Z, Duan DD, Ye J, et al. The cross-talk between PARylation and SUMOylation in C/EBPβ at K134 site participates in pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18:783–99.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (ZCLQN25H3101 to LYS.), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21961142009 to GL), Zhejiang Provincial Key Scientific Project (2021C03041 to GL), and Medical and Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (2024KY055 to XZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GL and XZ contributed to the literature search and study design. LYS participated in the drafting of the article. LYS, LYL, HT, YQZ, FYG, JFS, LWL, and LX carried out the experiments. FC, QY and LJC contributed to data collection and analysis. WHZ contributes to methodology. GL and XZ revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
She, Ly., Li, Ly., Tang, H. et al. OTUD1 positively regulates microglia neuroinflammation and promotes the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease by deubiquitinating C/EBPβ. Acta Pharmacol Sin 46, 2608–2621 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01566-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01566-y