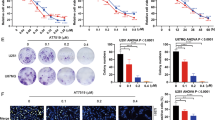
Abstract
CD73 (ecto-5’-nucleotidase) is a metabolic immune checkpoint that dephosphorylates AMP to produce adenosine. Adenosine plays a pivotal role in immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) through adenosine receptors expressed on various immune cells. AB680, a specific CD73 inhibitor, is currently undergoing clinical trials for highly refractory cancers. In this study, we investigated the antitumor effects and mechanisms of AB680 in glioblastoma (GBM). By analyzing the expression pattern of CD73 across all cell types in orthotopic naïve G422TN-GBM tumors (d 7), we found that CD73 and its associated adenosine metabolic signaling were significantly elevated in G422TN-GBM cells compared to all other cell types. High CD73 expression was also observed in human GBM samples and was correlated with shorter patient survival. Administration of AB680 significantly prolonged survival in G422TN-GBM-bearing mice, reduced tumor size, cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and enhanced microglia activation and anti-tumor immune responses. Metabolomic analysis revealed that AB680 markedly increased ADP and AMP levels in the TME of orthotopic G422TN-GBM, thereby stimulating the activation of P2RY12+ microglia to exert their M1-like anti-cancer functions, as confirmed by human GBM scRNA-seq and G422TN-GBM snRNA-seq data. Furthermore, AB680 combined with RT/TMZ exhibited synergistic therapeutic effects by reversing RT/TMZ-induced increases in adenosine levels and promoting the transformation of P2RY12+ microglia. Overall, this study demonstrates that targeting CD73 with AB680 alters purine metabolism in the GBM microenvironment, promotes the transformation of P2RY12+ microglia, and triggers robust anti-tumor immune responses. These results support the rationale for AB680-based therapeutic clinical trials for GBM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan AC, Ashley DM, López GY, Malinzak M, Friedman HS, Khasraw M. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:299–312.
Wu W, Klockow JL, Zhang M, Lafortune F, Chang E, Jin L, et al. Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM): an overview of current therapies and mechanisms of resistance. Pharmacol Res. 2021;171:105780.
Xiong M, Chen Z, Zhou C, Yang X, Hu W, Jiang Y, et al. PSMA PET/MR is a new imaging option for identifying glioma recurrence and predicting prognosis. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2024;19:383–95.
Chen Y, Wu J, Zhai L, Zhang T, Yin H, Gao H, et al. Metabolic regulation of homologous recombination repair by MRE11 lactylation. Cell. 2024;187:294–311.e21.
Agnihotri S, Zadeh G. Metabolic reprogramming in glioblastoma: the influence of cancer metabolism on epigenetics and unanswered questions. Neuro Oncol. 2016;18:160–72.
Garcia JH, Jain S, Aghi MK. Metabolic drivers of invasion in glioblastoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:683276.
Pellegatti P, Raffaghello L, Bianchi G, Piccardi F, Pistoia V, Di Virgilio F. Increased level of extracellular ATP at tumor sites: in vivo imaging with plasma membrane luciferase. PLoS One. 2008;3:e2599.
Khalafalla MG, Tran HN, Khalafalla FG. P2Y purinergic signaling in prostate cancer: emerging insights into pathophysiology and therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022;1877:188732.
Huang Z, Xie N, Illes P, Di Virgilio F, Ulrich H, Semyanov A, et al. From purines to purinergic signalling: molecular functions and human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:162.
Kepp O, Bezu L, Yamazaki T, Di Virgilio F, Smyth MJ, Kroemer G, et al. ATP and cancer immunosurveillance. Embo J. 2021;40:e108130.
Allard B, Allard D, Buisseret L, Stagg J. The adenosine pathway in immuno-oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17:611–29.
Azambuja JH, Gelsleichter NE, Beckenkamp LR, Iser IC, Fernandes MC, Figueiró F, et al. CD73 downregulation decreases in vitro and in vivo glioblastoma growth. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56:3260–79.
Wang L, Zhang J, Zhang W, Zheng M, Guo H, Pan X, et al. The inhibitory effect of adenosine on tumor adaptive immunity and intervention strategies. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024;14:1951–64.
Azambuja JH, Schuh RS, Michels LR, Gelsleichter NE, Beckenkamp LR, Iser IC, et al. Nasal administration of cationic nanoemulsions as CD73-siRNA delivery system for glioblastoma treatment: a new therapeutical approach. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57:635–49.
Goswami S, Walle T, Cornish AE, Basu S, Anandhan S, Fernandez I, et al. Immune profiling of human tumors identifies CD73 as a combinatorial target in glioblastoma. Nat Med. 2020;26:39–46.
Quezada C, Garrido W, Oyarzún C, Fernández K, Segura R, Melo R, et al. 5’-ectonucleotidase mediates multiple-drug resistance in glioblastoma multiforme cells. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228:602–8.
Lawson KV, Kalisiak J, Lindsey EA, Newcomb ET, Leleti MR, Debien L, et al. Discovery of AB680: a potent and selective inhibitor of CD73. J Med Chem. 2020;63:11448–68.
Jeffrey JL, Lawson KV, Powers JP. Targeting metabolism of extracellular nucleotides via inhibition of ectonucleotidases CD73 and CD39. J Med Chem. 2020;63:13444–65.
Kim M, Min YK, Jang J, Park H, Lee S, Lee CH. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals distinct cellular factors for response to immunotherapy targeting CD73 and PD-1 in colorectal cancer. J Immunother Cancer 2021; 9:e002503.
Noh JY, Lee IP, Han NR, Kim M, Min YK, Lee SY, et al. Additive effect of CD73 inhibitor in colorectal cancer treatment with CDK4/6 inhibitor through regulation of PD-L1. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;14:769–88.
Chen Q, Yin H, He J, Xie Y, Wang W, Xu H, et al. Tumor microenvironment responsive CD8+ T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells to trigger CD73 inhibitor AB680-based synergistic therapy for pancreatic cancer. Adv Sci. 2023;10:e2302498.
Jacoberger-Foissac C, Cousineau I, Bareche Y, Allard D, Chrobak P, Allard B, et al. CD73 inhibits cGAS-STING and cooperates with CD39 to promote pancreatic cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2023;11:56–71.
Lawrence AR, Canzi A, Bridlance C, Olivié N, Lansonneur C, Catale C, et al. Microglia maintain structural integrity during fetal brain morphogenesis. Cell. 2024;187:962–80.e19.
Schädlich IS, Winzer R, Stabernack J, Tolosa E, Magnus T, Rissiek B. The role of the ATP-adenosine axis in ischemic stroke. Semin Immunopathol. 2023;45:347–65.
Shieh CH, Heinrich A, Serchov T, van Calker D, Biber K. P2X7-dependent, but differentially regulated release of IL-6, CCL2, and TNF-α in cultured mouse microglia. Glia. 2014;62:592–607.
Kenkhuis B, Somarakis A, Kleindouwel LRT, van Roon-Mom WMC, Höllt T, van der Weerd L. Co-expression patterns of microglia markers Iba1, TMEM119 and P2RY12 in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2022;167:105684.
Allard D, Cousineau I, Ma EH, Allard B, Bareche Y, Fleury H, et al. The CD73 immune checkpoint promotes tumor cell metabolic fitness. Elife. 2023;12:e84508.
Neo SY, Yang Y, Record J, Ma R, Chen X, Chen Z, et al. CD73 immune checkpoint defines regulatory NK cells within the tumor microenvironment. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:1185–98.
Antonioli L, Pacher P, Vizi ES, Haskó G. CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19:355–67.
Liu F, Zhou Q, Jiang HF, Zhang TT, Miao C, Xu XH, et al. Piperlongumine conquers temozolomide chemoradiotherapy resistance to achieve immune cure in refractory glioblastoma via boosting oxidative stress-inflamation-CD8+-T cell immunity. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023;42:118.
Liu F, Xu X, Li C, Li C, Li Y, Yin S, et al. Mannose synergizes with chemoradiotherapy to cure cancer via metabolically targeting HIF-1 in a novel triple-negative glioblastoma mouse model. Clin Transl Med. 2020;10:e226.
Horbinski C, Berger T, Packer RJ, Wen PY. Clinical implications of the 2021 edition of the WHO classification of central nervous system tumours. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022;18:515–29.
Zhang QL, Fu BM, Zhang ZJ. Borneol, a novel agent that improves central nervous system drug delivery by enhancing blood-brain barrier permeability. Drug Deliv. 2017;24:1037–44.
Liu F, Xu XH, Li CY, Zhang TT, Yin SL, Liu GQ, et al. Rapid tumor recurrence in a novel murine GBM surgical model is associated with Akt/PD-L1/vimentin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;569:1–9.
Li C, Miao C, Ge Y, Wu J, Gao P, Yin S, et al. A molecularly distinct cell type in the midbrain regulates intermale aggression behaviors in mice. Theranostics. 2025;15:707–25.
Li CY, Jiang HF, Li L, Lai XJ, Liu QR, Yu SB, et al. Neuroglobin facilitates neuronal oxygenation through tropic migration under hypoxia or anemia in rat: how does the brain breathe? Neurosci Bull. 2023;39:1481–96.
Kale NS, Haug K, Conesa P, Jayseelan K, Moreno P, Rocca-Serra P, et al. MetaboLights: an open-access database repository for metabolomics data. Curr Protoc Bioinform. 2016;53:14.3.1–.3.8.
Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology Resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D330-d8.
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet. 2000;25:25–9.
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y, Morishima K. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:D353–d61.
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics. 2012;16:284–7.
Liberzon A, Subramanian A, Pinchback R, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Tamayo P, Mesirov JP. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:1739–40.
Barbie DA, Tamayo P, Boehm JS, Kim SY, Moody SE, Dunn IF, et al. Systematic RNA interference reveals that oncogenic KRAS-driven cancers require TBK1. Nature. 2009;462:108–12.
Wolock SL, Lopez R, Klein AM. Scrublet: computational identification of cell doublets in single-cell transcriptomic data. Cell Syst. 2019;8:281–91.e9.
Butler A, Hoffman P, Smibert P, Papalexi E, Satija R. Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species. Nat Biotechnol. 2018;36:411–20.
Tirosh I, Izar B, Prakadan SM, Wadsworth MH 2nd, Treacy D, Trombetta JJ, et al. Dissecting the multicellular ecosystem of metastatic melanoma by single-cell RNA-seq. Science. 2016;352:189–96.
Coy S, Wang S, Stopka SA, Lin JR, Yapp C, Ritch CC, et al. Single cell spatial analysis reveals the topology of immunomodulatory purinergic signaling in glioblastoma. Nat Commun. 2022;13:4814.
Sun R, Han R, McCornack C, Khan S, Tabor GT, Chen Y, et al. TREM2 inhibition triggers antitumor cell activity of myeloid cells in glioblastoma. Sci Adv. 2023;9:eade3559.
Korsunsky I, Millard N, Fan J, Slowikowski K, Zhang F, Wei K, et al. Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nat Methods. 2019;16:1289–96.
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15:550.
Gravendeel LA, Kouwenhoven MC, Gevaert O, de Rooi JJ, Stubbs AP, Duijm JE, et al. Intrinsic gene expression profiles of gliomas are a better predictor of survival than histology. Cancer Res. 2009;69:9065–72.
Langfelder P, Horvath S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008;9:559.
Trott O, Olson AJ. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem. 2010;31:455–61.
Sidders B, Zhang P, Goodwin K, O’Connor G, Russell DL, Borodovsky A, et al. Adenosine signaling is prognostic for cancer outcome and has predictive utility for immunotherapeutic response. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:2176–87.
Meng L, Chu X, Xing H, Liu X, Xin X, Chen L, et al. Improving glioblastoma therapeutic outcomes via doxorubicin-loaded nanomicelles modified with borneol. Int J Pharm. 2019;567:118485.
Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P, Brat DJ, Cree IA, Figarella-Branger D, et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23:1231–51.
Huse JT, Holland EC. Targeting brain cancer: advances in the molecular pathology of malignant glioma and medulloblastoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:319–31.
Lu T, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Pan X, Zhu X, Wang X, et al. CD73 in small extracellular vesicles derived from HNSCC defines tumour-associated immunosuppression mediated by macrophages in the microenvironment. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11:e12218.
Perrot I, Michaud HA, Giraudon-Paoli M, Augier S, Docquier A, Gros L, et al. Blocking antibodies targeting the CD39/CD73 immunosuppressive pathway unleash immune responses in combination cancer therapies. Cell Rep. 2019;27:2411–25.e9.
Poon CC, Sarkar S, Yong VW, Kelly JJP. Glioblastoma-associated microglia and macrophages: targets for therapies to improve prognosis. Brain. 2017;140:1548–60.
Zhang C, Zhou Y, Gao Y, Zhu Z, Zeng X, Liang W, et al. Radiated glioblastoma cell-derived exosomal circ_0012381 induce M2 polarization of microglia to promote the growth of glioblastoma by CCL2/CCR2 axis. J Transl Med. 2022;20:388.
Fu B, Xiong Y, Sha Z, Xue W, Xu B, Tan S, et al. SEPTIN2 suppresses an IFN-γ-independent, proinflammatory macrophage activation pathway. Nat Commun. 2023;14:7441.
Xu X, Xu J, Wu J, Hu Y, Han Y, Gu Y, et al. Phosphorylation-mediated IFN-γR2 membrane translocation is required to activate macrophage innate response. Cell. 2018;175:1336–51.e17.
Klemm F, Maas RR, Bowman RL, Kornete M, Soukup K, Nassiri S, et al. Interrogation of the microenvironmental landscape in brain tumors reveals disease-specific alterations of immune cells. Cell. 2020;181:1643–60.e17.
Kilian M, Sheinin R, Tan CL, Friedrich M, Krämer C, Kaminitz A, et al. MHC class II-restricted antigen presentation is required to prevent dysfunction of cytotoxic T cells by blood-borne myeloids in brain tumors. Cancer Cell. 2023;41:235–51.e9.
Utzschneider DT, Delpoux A, Wieland D, Huang X, Lai CY, Hofmann M, et al. Active maintenance of T cell memory in acute and chronic viral infection depends on continuous expression of FOXO1. Cell Rep. 2018;22:3454–67.
Rao RR, Li Q, Gubbels Bupp MR, Shrikant PA. Transcription factor Foxo1 represses T-bet-mediated effector functions and promotes memory CD8+ T cell differentiation. Immunity. 2012;36:374–87.
Zhao Y, Hu X, Liu Y, Dong S, Wen Z, He W, et al. ROS signaling under metabolic stress: cross-talk between AMPK and AKT pathway. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:79.
Yegutkin GG, Boison D. ATP and adenosine metabolism in cancer: exploitation for therapeutic gain. Pharmacol Rev. 2022;74:797–822.
Xia C, Yin S, To KKW, Fu L. CD39/CD73/A2AR pathway and cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2023;22:44.
Xu S, Shao QQ, Sun JT, Yang N, Xie Q, Wang DH, et al. Synergy between the ectoenzymes CD39 and CD73 contributes to adenosinergic immunosuppression in human malignant gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2013;15:1160–72.
Stagg J, Golden E, Wennerberg E, Demaria S. The interplay between the DNA damage response and ectonucleotidases modulates tumor response to therapy. Sci Immunol. 2023;8:eabq3015.
Linden J, Koch-Nolte F, Dahl G. Purine release, metabolism, and signaling in the inflammatory response. Annu Rev Immunol. 2019;37:325–47.
Schafer ST, Mansour AA, Schlachetzki JCM, Pena M, Ghassemzadeh S, Mitchell L, et al. An in vivo neuroimmune organoid model to study human microglia phenotypes. Cell. 2023;186:2111–26.e20.
Caponegro MD, Oh K, Madeira MM, Radin D, Sterge N, Tayyab M, et al. A distinct microglial subset at the tumor-stroma interface of glioma. Glia. 2021;69:1767–81.
Butovsky O, Jedrychowski MP, Moore CS, Cialic R, Lanser AJ, Gabriely G, et al. Identification of a unique TGF-β-dependent molecular and functional signature in microglia. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17:131–43.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82173197 to XQC); the Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2024AFB978 to FL); the Jingzhou Joint Scientific Research Fund (Grant No. 2024LHY14 to FL); the Scientific Research Starting Foundation for Doctor, the First People’s Hospital of Jingzhou (Grant No. 2023DIF01 to FL); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32270715 to MFL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PPG performed experiments, acquisition and analysis of data, bioinformatics analysis, and wrote the manuscript. HFJ performed experiments, bioinformatics analysis, and wrote the manuscript. YWD, YS, EZY, JXW, XXL, SDW, ZHD, and XHX performed experiments. YWW, FL were involved in writing, review, and/or revision of the manuscript. QA and CM help experiments. XMH and MFL assisted with bioinformatics analysis and provided a server operating on the Linux platform for the purposes of our research. XQC designed the scheme of the study and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Pp., Jiang, Hf., Du, Yw. et al. CD73 inhibitor AB680 suppresses glioblastoma in mice by inhibiting purine metabolism and promoting P2RY12+ microglia transformation. Acta Pharmacol Sin (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01585-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01585-9