Abstract
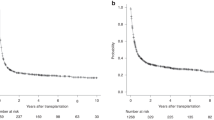
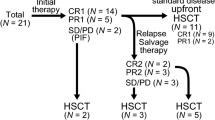
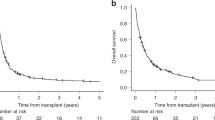
Adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) is an aggressive T cell lymphoma with a poor prognosis. Although allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) can be a curative treatment for ATL, a significant proportion of allo-HSCT recipients suffer from relapse/progression of ATL. Here we aimed to clarify the risk factors for and outcomes after posttransplant relapse/progression. We retrospectively reviewed 76 patients with ATL who received allo-HSCT at our institute. At the time of allo-HSCT, disease status was complete response in 17 patients, partial response in 29, stable disease (SD) in 18, and progressive disease (PD) in 12. In multivariate analysis, SD/PD at allo-HSCT, lymphoma subtype, reduced-intensity conditioning regimen, and time from diagnosis to allo-HSCT were associated with risk of relapse/progression. After allo-HSCT, 26 patients had relapse/progression at a median of 66 days (range, 13–2064 days). The 2-year overall survival rate after relapse/progression was only 19%. Compared with acute-type, lymphoma-type experienced local recurrence more frequently (1/15 acute vs. 7/11 lymphoma, P < 0.01) and had a significantly longer OS after relapse/progression (median; 112 days in acute vs. 554 days in lymphoma, P < 0.01). Since the prognosis of patients with ATL who experienced relapse/progression after allo-HSCT was poor, strategies to reduce the risk of these outcomes are warranted.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uchiyama T, Yodoi J, Sagawa K, Takatsuki K, Uchino H. Adult T-cell leukemia: clinical and hematologic features of 16 cases. Blood. 1977;50:481–92.
Uchiyama T. Human T cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) and human diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:15–37.
Verdonck K, Gonzalez E, Van Dooren S, Vandamme AM, Vanham G, Gotuzzo E. Human T-lymphotropic virus 1: recent knowledge about an ancient infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:266–81.
Satou Y, Matsuoka M. Implication of the HTLV-I bZIP factor gene in the leukemogenesis of adult T-cell leukemia. Int J Hematol. 2007;86:107–12.
Arisawa K, Soda M, Endo S, Kurokawa K, Katamine S, Shimokawa I, et al. Evaluation of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma incidence and its impact on non-Hodgkin lymphoma incidence in southwestern Japan. Int J Cancer. 2000;85:319–24.
Yamada Y, Atogami S, Hasegawa H, Kamihira S, Soda M, Satake M, et al. Nationwide survey of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) in Japan. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2011;52:1765–71.
Tsukasaki K, Utsunomiya A, Fukuda H, Shibata T, Fukushima T, Takatsuka Y, et al. VCAP-AMP-VECP compared with biweekly CHOP for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG9801. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5458–64.
Yamamoto K, Utsunomiya A, Tobinai K, Tsukasaki K, Uike N, Uozumi K, et al. Phase I study of KW-0761, a defucosylated humanized anti-CCR4 antibody, in relapsed patients with adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1591–8.
Ishida T, Joh T, Uike N, Yamamoto K, Utsunomiya A, Yoshida S, et al. Defucosylated anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody (KW-0761) for relapsed adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: a multicenter phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:837–42.
Fukushima T, Nomura S, Shimoyama M, Shibata T, Imaizumi Y, Moriuchi Y, et al. Japan Clinical Oncology Group prognostic index and characterization of long-term survivors of aggressive adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma (JCOG0902A). Br J Haematol. 2014;166:739–48.
Ishida T, Jo T, Takemoto S, Suzushima H, Uozumi K, Yamamoto K, et al. Dose-intensified chemotherapy alone or in combination with mogamulizumab in newly diagnosed aggressive adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma: a randomized phase II study. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:672–82.
Ishida T, Hishizawa M, Kato K, Tanosaki R, Fukuda T, Taniguchi S, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma with special emphasis on preconditioning regimen: a nationwide retrospective study. Blood. 2012;120:1734–41.
Ishitsuka K, Tamura K. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type I and adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e517–526.
Shimoyama M. Diagnostic criteria and classification of clinical subtypes of adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma. A report from the Lymphoma Study Group (1984–87). Br J Haematol. 1991;79:428–37.
Tsukasaki K, Hermine O, Bazarbachi A, Ratner L, Ramos JC, Harrington W Jr, et al. Definition, prognostic factors, treatment, and response criteria of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: a proposal from an international consensus meeting. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:453–9.
Giralt S, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Bacigalupo A, Horowitz M, Pasquini M, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning regimen workshop: defining the dose spectrum. Report of a workshop convened by the center for international blood and marrow transplant research. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009;15:367–9.
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, et al. Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009;15:1628–33.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15:825–8.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA, et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HLA-matched sibling donors. Transplantation. 1974;18:295–304.
Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software “EZR” for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:452–8.
Hishizawa M, Kanda J, Utsunomiya A, Taniguchi S, Eto T, Moriuchi Y, et al. Transplantation of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells for adult T-cell leukemia: a nationwide retrospective study. Blood. 2010;116:1369–76.
Kanda J, Hishizawa M, Utsunomiya A, Taniguchi S, Eto T, Moriuchi Y, et al. Impact of graft-versus-host disease on outcomes after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adult T-cell leukemia: a retrospective cohort study. Blood. 2012;119:2141–8.
Kato K, Choi I, Wake A, Uike N, Taniguchi S, Moriuchi Y, et al. Treatment of patients with adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma with cord blood transplantation: a Japanese nationwide retrospective survey. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:1968–74.
Itonaga H, Tsushima H, Taguchi J, Fukushima T, Taniguchi H, Sato S, et al. Treatment of relapsed adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: the Nagasaki Transplant Group experience. Blood. 2013;121:219–25.
Fuji S, Fujiwara H, Nakano N, Wake A, Inoue Y, Fukuda T, et al. Early application of related SCT might improve clinical outcome in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:205–11.
Fujiwara H, Fuji S, Wake A, Kato K, Takatsuka Y, Fukuda T, et al. Dismal outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for relapsed adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma, a Japanese Nationwide Study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52:484–8.
Fuji S, Yamaguchi T, Inoue Y, Utsunomiya A, Moriuchi Y, Uchimaru K, et al. Development of a modified prognostic index of patients with aggressive adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma aged 70 years or younger: a possible risk-adapted management strategies including allogeneic transplantation. Haematologica. 2017;102:1258–65.
Fuji S, Inoue Y, Utsunomiya A, Moriuchi Y, Uchimaru K, Choi I, et al. Pretransplantation anti-CCR4 antibody mogamulizumab against adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma is associated with significantly increased risks of severe and corticosteroid-refractory graft-versus-host disease, nonrelapse mortality, and overall mortality. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:3426–33.
Fuji S, Shindo T. Friend or foe? Mogamulizumab in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Stem Cell Investig. 2016;3:70.
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by the Practical Research for Innovative Cancer Control program of the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (15Ack0106136h0002) and by the National Cancer Research and Development Fund (26-A-26).
Author contributions
YI, SF, and TF participated in research design, data analysis, and writing of the paper. RT, YI, TT, AI, KO, SK, S-WK, and HN participated in writing of the paper. All authors approved the submission of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, Y., Fuji, S., Tanosaki, R. et al. Prognostic importance of pretransplant disease status for posttransplant outcomes in patients with adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 53, 1105–1115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0139-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0139-z
This article is cited by
-
Outcomes of patients aged 70 years or younger with aggressive ATL at core hospitals for ATL treatment in Tokyo
International Journal of Hematology (2025)
-
Impact of HLA-mismatched unrelated transplantation in patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
The HTLV-1 proviral status is a potential prognostic biomarker for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma treated with allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Impact of conditioning intensity and regimen on transplant outcomes in patients with adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Treatment of relapsed aggressive adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with mogamulizumab followed by lenalidomide
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)