Abstract
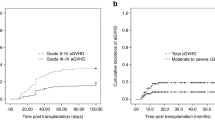
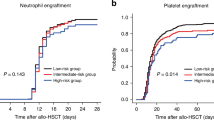
Our study aimed to compare treatment outcomes between hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) from haploidentical donors (HID) and immunosuppressive therapy (IST) in adults with acquired severe aplastic anemia (SAA). The medical records of 113 SAA adults who received IST, including rabbit ATG and cyclosporin (N = 37), or HID HSCT (N = 76) within 6 months of diagnosis at two institutions were retrospectively reviewed. Estimated 8-year overall survival (OS) was comparable between the IST and HID HSCT groups (75.6 vs. 83.7%, respectively, P = 0.328), but failure free survival (FFS) was significantly lower in IST group than HID HSCT group (38.5 vs. 83.7%, respectively, P = 0.001). Furthermore, a significant improvement in FFS was observed with HSCT over IST in patients under 40 years old. At the last follow-up, patients in HSCT group achieved better Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) than those in IST group (100 [20–100] vs. 90 [20–100], P = 0.002). In terms of blood count, 83.1% (54/65) of patients in HSCT group showed complete recovery compared to only 38.2% (13/34) in IST group (P < 0.001). These data suggest that HID HSCT could be an effective alternative treatment option for SAA adults, and additional prospective studies are necessary.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Killick SB, Bown N, Cavenagh J, Dokal I, Foukaneli T, Hill A et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of adult aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13853.
Kosaka Y, Yagasaki H, Sano K, Kobayashi R, Ayukawa H, Kaneko T, et al. Prospective multicenter trial comparing repeated immunosuppressive therapy with stem-cell transplantation from an alternative donor as second-line treatment for children with severe and very severe aplastic anemia. Blood. 2008;111:1054–9. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-08-099168.
Bacigalupo A. How I treat acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2017;129:1428–36. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-08-693481.
Rosenfeld SJ, Kimball J, Vining D, Young NS. Intensive immunosuppression with antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine as treatment for severe acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 1995;85:3058–65.
Kojima S, Hibi S, Kosaka Y, Yamamoto M, Tsuchida M, Mugishima H, et al. Immunosuppressive therapy using antithymocyte globulin, cyclosporine, and danazol with or without human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in children with acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2000;96:2049–54.
Bacigalupo A, Giammarco S, Sica S. Bone marrow transplantation versus immunosuppressive therapy in patients with acquired severe aplastic anemia. Int J Hematol. 2016;104:168–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-016-2037-8.
Rosenfeld S, Follmann D, Nunez O, Young NS. Antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine for severe aplastic anemia: association between hematologic response and long-term outcome. JAMA. 2003;289:1130–5.
Scheinberg P, Young NS. How I treat acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2012;120:1185–96. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-12-274019.
Scheinberg P, Nunez O, Weinstein B, Scheinberg P, Biancotto A, Wu CO, et al. Horse versus rabbit antithymocyte globulin in acquired aplastic anemia. N Eng J Med. 2011;365:430–8. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1103975.
Marsh JC, Bacigalupo A, Schrezenmeier H, Tichelli A, Risitano AM, Passweg JR, et al. Prospective study of rabbit antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine for aplastic anemia from the EBMT Severe Aplastic Anaemia Working Party. Blood. 2012;119:5391–6. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-02-407684.
Viollier R, Passweg J, Gregor M, Favre G, Kuhne T, Nissen C, et al. Quality-adjusted survival analysis shows differences in outcome after immunosuppression or bone marrow transplantation in aplastic anemia. Ann Hematol. 2005;84:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-004-0930-3.
Xu LP, Liu KY, Liu DH, Han W, Chen H, Chen YH, et al. A novel protocol for haploidentical hematopoietic SCT without in vitro T-cell depletion in the treatment of severe acquired aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012;47:1507–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.79.
Im HJ, Koh KN, Choi ES, Jang S, Kwon SW, Park CJ, et al. Excellent outcome of haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children and adolescents with acquired severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19:754–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.01.023.
Gao L, Li Y, Zhang Y, Chen X, Gao L, Zhang C, et al. Long-term outcome of HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic SCT without in vitro T-cell depletion for adult severe aplastic anemia after modified conditioning and supportive therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49:519–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.224.
Clay J, Kulasekararaj AG, Potter V, Grimaldi F, McLornan D, Raj K, et al. Nonmyeloablative peripheral blood haploidentical stem cell transplantation for refractory severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:1711–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.06.028.
Esteves I, Bonfim C, Pasquini R, Funke V, Pereira NF, Rocha V, et al. Haploidentical BMT and post-transplant Cy for severe aplastic anemia: a multicenter retrospective study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015;50:685–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.20.
Xu LP, Wang SQ, Wu DP, Wang JM, Gao SJ, Jiang M et al. Haplo-identical transplantation for acquired severe aplastic anaemia in a multicentre prospective study. Br J Haematol. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14225.
Xu LP, Jin S, Wang SQ, Xia LH, Bai H, Gao SJ, et al. Upfront haploidentical transplant for acquired severe aplastic anemia: registry-based comparison with matched related transplant. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:25 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0398-y.
Bacigalupo A, Hows J, Gluckman E, Nissen C, Marsh J, Van Lint MT, et al. Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) versus immunosuppression for the treatment of severe aplastic anaemia (SAA): a report of the EBMT SAA working party. Br J Haematol. 1988;70:177–82.
Dufour C, Veys P, Carraro E, Bhatnagar N, Pillon M, Wynn R, et al. Similar outcome of upfront-unrelated and matched sibling stem cell transplantation in idiopathic paediatric aplastic anaemia. A study on behalf of the UK Paediatric BMT Working Party, Paediatric Diseases Working Party and Severe Aplastic Anaemia Working Party of EBMT. Br J Haematol. 2015;171:585–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13614.
Mackarel J, Iatan M, Kumar L, Storey L, O’Marcaigh A, Smith O. In support of upfront stem cell transplantation as first-line therapy for paediatric patients with idiopathic severe aplastic anaemia who lack a sibling donor. Br J Haematol. 2017;177:806–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14097.
Choi YB, Yi ES, Lee JW, Sung KW, Koo HH, Yoo KH. Immunosuppressive therapy versus alternative donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for children with severe aplastic anemia who lack an HLA-matched familial donor. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.223.
Cheng Y, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Wu J, Wang F, Mo X. First-line choice for severe aplastic anemia in children: Transplantation from a haploidentical donor vs immunosuppressive therapy. Clin Transplant. 2018;32. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.13179.
Lee SE, Yahng SA, Cho BS, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, et al. Impact of pretransplant red cell transfusion on outcome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:1323–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.140.
Ades L, Mary JY, Robin M, Ferry C, Porcher R, Esperou H, et al. Long-term outcome after bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Blood. 2004;103:2490–7. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-07-2546.
Townsley DM, Scheinberg P, Winkler T, Desmond R, Dumitriu B, Rios O, et al. Eltrombopag added to standard immunosuppression for aplastic anemia. N Eng J Med. 2017;376:1540–50. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1613878.
Champlin RE, Horowitz MM, van Bekkum DW, Camitta BM, Elfenbein GE, Gale RP, et al. Graft failure following bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: risk factors and treatment results. Blood. 1989;73:606–13.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15:825–8.
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, McDonald GB, Striker GE, Sale GE, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med. 1980;69:204–17.
Xu LP, Xu ZL, Wang FR, Mo XD, Han TT, Han W, et al. Unmanipulated haploidentical transplantation conditioning with busulfan, cyclophosphamide and anti-thymoglobulin for adult severe aplastic anaemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53:188–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2017.237.
Kim H, Lee JH, Joo YD, Bae SH, Lee SM, Jo JC, et al. Comparable allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcome of a haplo-identical family donor with an alternative donor in adult aplastic anemia. Acta haematol. 2016;136:129–39. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445820.
Wang Z, Zheng X, Yan H, Li D, Wang H. Good outcome of haploidentical hematopoietic SCT as a salvage therapy in children and adolescents with acquired severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49:1481–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.187.
Wang Y, Chang YJ, Xu LP, Liu KY, Liu DH, Zhang XH. et al. Who is the best donor for a related HLA haplotype-mismatched transplant?. Blood. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-03-563130.
Yoshida N, Kobayashi R, Yabe H, Kosaka Y, Yagasaki H, Watanabe K, et al. First-line treatment for severe aplastic anemia in children: bone marrow transplantation from a matched family donor versus immunosuppressive therapy. Haematologica. 2014;99:1784–91. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2014.109355.
Bacigalupo A, Brand R, Oneto R, Bruno B, Socie G, Passweg J, et al. Treatment of acquired severe aplastic anemia: bone marrow transplantation compared with immunosuppressive therapy--The European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation experience. Semin Hematol. 2000;37:69–80.
Gupta V, Eapen M, Brazauskas R, Carreras J, Aljurf M, Gale RP, et al. Impact of age on outcomes after bone marrow transplantation for acquired aplastic anemia using HLA-matched sibling donors. Haematologica. 2010;95:2119–25. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2010.026682.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81670167 and 81670166), and Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81621001). We thank all colleagues for participating in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, ZL., Zhou, M., Jia, JS. et al. Immunosuppressive therapy versus haploidentical transplantation in adults with acquired severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 54, 1319–1326 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0410-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0410-3
This article is cited by
-
Similar outcomes between HLA-haploid and matched sibling donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a multicenter, retrospective study and severe aplastic anemia transplant-specific prognostic scoring system
Annals of Hematology (2024)
-
Meta-analysis of the results of haploidentical transplantation in the treatment of aplastic anemia
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
A multicentre trial of intensive immunosuppressive therapy combined with umbilical cord blood for the treatment of severe aplastic anaemia
Annals of Hematology (2022)
-
Haploidentical stem cell transplantation for aplastic anemia: the current advances and future challenges
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Allo-HSCT compared with immunosuppressive therapy for acquired aplastic anemia: a system review and meta-analysis
BMC Immunology (2020)