Abstract
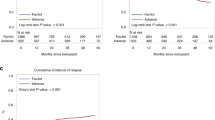
It remains unclear about the role of the EVI1 gene in AML patients with 11q23/MLL rearrangement (MLL-r AML) undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). We analyzed the clinical value of EVI1 gene quantification in 96 MLL-r AML patients. High EVI1 expression was found in 73% (70/96) of MLL-r AML patients, and EVI1-high MLL-r AML patients were characterized by high WBC counts (P = 0.046) and low platelet counts (P < 0.001) and commonly had t(6;11) (P = 0.032). In addition, a significant difference was observed in the SETD2 gene mutation between the EVI1 high and low groups (0% vs. 50%, P < 0.001). EVI1-high MLL-r AML patients had worse 2-year OS (49.8% vs. 79.7%, P = 0.01) and 2-year PFS (40.2% vs. 68.1%, P = 0.014) than EVI1-low patients. In 57 MLL-r AML patients undergoing allo-HSCT, poorer 2-year PFS (48.6% vs. 72.4%, P = 0.039) and higher CIR (33.2% vs. 11.1%, P = 0.035) were observed in the EVI1-high patients. Multivariate analysis revealed that pre-EVI1+ was the sole independent factor of high CIR (P = 0.035, HR = 4.97, 95% CI: 1.12–22.04). EVI1+ at 100 days post allo-HSCT was associated with a significantly higher 2-year CIR (P = 0.017). The quantification of the EVI1 gene could be used as an additional marker for early predicting relapse in allo-HSCT MLL-r AML patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloomfield CD, Archer KJ, Mrozek K, Lillington DM, Kaneko Y, Head DR, et al. 11q23 balanced chromosome aberrations in treatment-related myelodysplastic syndromes and acute leukemia: report from an international workshop. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002;33:362–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.10046.
BH J, Gill Super NR, McCabe MJ, Thirman R, Larson MM, Le Beau, et al. Rearrangements of the MLL gene in therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia in patients previously treated with agents targeting DNA-topoisomerase I1. Blood. 1993;82:3705–11.
Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, Walker H, Chatters S, Goldstone AH, et al. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials. Blood. 2010;116:354–65. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-11-254441.
Gole B, Wiesmuller L. Leukemogenic rearrangements at the mixed lineage leukemia gene (MLL)-multiple rather than a single mechanism. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015;3:41. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2015.00041.
Dohner H, Estey E, Grimwade D, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Buchner T, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2017;129:424–47. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-08-733196.
Goyama S, Yamamoto G, Shimabe M, Sato T, Ichikawa M, Ogawa S, et al. Evi-1 is a critical regulator for hematopoietic stem cells and transformed leukemic cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3:207–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2008.06.002.
Barjesteh van Waalwijk van Doorn-Khosrovani S, Erpelinck C, van Putten WL, Valk PJ, van der Poel-van de Luytgaarde S, Hack R, et al. High EVI1 expression predicts poor survival in acute myeloid leukemia: a study of 319 de novo AML patients. Blood. 2003;101:837–45. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-05-1459.
Haas K, Kundi M, Sperr WR, Esterbauer H, Ludwig WD, Ratei R, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of different mRNA 5’-end variants of the oncogene EVI1 in 266 patients with de novo AML: EVI1 and MDS1/EVI1 overexpression both predict short remission duration. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2008;47:288–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.20532.
Groschel S, Lugthart S, Schlenk RF, Valk PJ, Eiwen K, Goudswaard C, et al. High EVI1 expression predicts outcome in younger adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia and is associated with distinct cytogenetic abnormalities. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2101–7. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.26.0646.
Groschel S, Schlenk RF, Engelmann J, Rockova V, Teleanu V, Kuhn MW, et al. Deregulated expression of EVI1 defines a poor prognostic subset of MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemias: a study of the German-Austrian Acute Myeloid Leukemia Study Group and the Dutch-Belgian-Swiss HOVON/SAKK Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.41.5505.
Matsuo H, Kajihara M, Tomizawa D, Watanabe T, Saito AM, Fujimoto J, et al. EVI1 overexpression is a poor prognostic factor in pediatric patients with mixed lineage leukemia-AF9 rearranged acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2014;99:e225–7. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2014.107128.
Gordon MY, Blackett NM. Reconstruction of the hematopoietic system after stem cell transplantation. Cell Transplant. 1998;7:339–44.
BB D, Cheson PA, Cassileth DR, Head CA, Schiffer JM, Bennett CD, et al. Report of the National Cancer Institute-Sponsored Workshop on definitions of diagnosis and response in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8:813–9.
Flowers MED, Kansu E, Sullivan KM. Pathophysiology and treatment of graft versus host disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1999;13:1091–112.
He X, Wang Q, Cen J, Qiu H, Sun A, Chen S. et al. Predictive value of high EVI1 expression in AML patients undergoing myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in first CR. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:921–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.71.
Goemans BF, Zwaan CM, Miller M, Zimmermann M, Harlow A, Meshinchi S, et al. Mutations in KIT and RAS are frequent events in pediatric core-binding factor acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2005;19:1536–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403870.
Lavallee VP, Baccelli I, Krosl J, Wilhelm B, Barabe F, Gendron P, et al. The transcriptomic landscape and directed chemical interrogation of MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemias. Nat Genet. 2015;47:1030–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3371.
Grossmann V, Schnittger S, Poetzinger F, Kohlmann A, Stiel A, Eder C, et al. High incidence of RAS signalling pathway mutations in MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2013;27:1933–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.90.
Pigneux A, Labopin M, Maertens J, Cordonnier C, Volin L, Socie G, et al. Outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for adult patients with AML and 11q23/MLL rearrangement (MLL-r AML). Leukemia. 2015;29:2375–81. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.143.
Chen L, Chen W, Mysliwski M, Serio J, Ropa J, Abulwerdi FA, et al. Mutated Ptpn11 alters leukemic stem cell frequency and reduces the sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cells to Mcl1 inhibition. Leukemia. 2015;29:1290–300. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.18.
Libura M, Asnafi V, Tu A, Delabesse E, Tigaud I, Cymbalista F, et al. FLT3 and MLL intragenic abnormalities in AML reflect a common category of genotoxic stress. Blood. 2003;102:2198–204. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-01-0162.
Frohling S, Schlenk RF, Breitruck J, Benner A, Kreitmeier S, Tobis K, et al. Prognostic significance of activating FLT3 mutations in younger adults (16 to 60 years) with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: a study of the AML Study Group Ulm. Blood. 2002;100:4372–80. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-05-1440.
Jiang X, Bugno J, Hu C, Yang Y, Herold T, Q J. et al. Eradication of acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3 ligand-targeted miR-150 nanoparticles. Cancer Res. 2016;76:4470–80. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.
Zhu X, He F, Zeng H, Ling S, Chen A, Wang Y, et al. Identification of functional cooperative mutations of SETD2 in human acute leukemia. Nat Genet. 2014;46:287–93. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2894.
Wang Q, Cheng T. Evidences for mutations in the histone modifying gene SETD2 as critical drivers in leukemia development. Sci China Life Sci. 2014;57:944–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-014-4702-6.
Arai S, Yoshimi A, Shimabe M, Ichikawa M, Nakagawa M, Imai Y, et al. Evi-1 is a transcriptional target of mixed-lineage leukemia oncoproteins in hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2011;117:6304–14. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-07-234310.
Hidemasa Matsuo KY, Nakatani Kana, Kamikubo Yasuhiko, Tomizawa Daisuke, Taga Takashi, Nobutaka Kiyokawa. et al. Coexistence and prognostic significance of EVI1 expression and driver mutations in KMT2A-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2019;134(Supplement_1):1409. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2019-124652.
Gupta V, Tallman MS, He W, Logan BR, Copelan E, Gale RP, et al. Comparable survival after HLA-well-matched unrelated or matched sibling donor transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first remission with unfavorable cytogenetics at diagnosis. Blood. 2010;116:1839–48. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-04-278317.
Schuurhuis GJ, Heuser M, Freeman S, E M-CB, Buccisano F, Cloos J. et al. Minimal/measurable residual disease in AML: a consensus document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood. 2018;131:1275–91. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-09-801498.
Meyer C, Schneider B, Jakob S, Strehl S, Attarbaschi A, Schnittger S, et al. The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias. Leukemia. 2006;20:777–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404150.
Burmeister T, Marschalek R, Schneider B, Meyer C, Gokbuget N, Schwartz S, et al. Monitoring minimal residual disease by quantification of genomic chromosomal breakpoint sequences in acute leukemias with MLL aberrations. Leukemia. 2006;20:451–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404082.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81730003, 81870120), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20171205), the Social Development Project of Jiangsu Province (BE2019655), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), and the National Key Research and Development Program (2017ZX09304021, 2017YFA0104500, 2019YFC0840604). All the samples were from Jiangsu Biobank of Clinical Resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DW and YX contributed to the conception of the study and paper revision. SJ, YFan, and YFang contributed to collecting and performing the data analysis and preparing the paper. CH and JChen helped collect and perform data analysis and prepare the paper. JCen, HQ, and SC contributed to the data analysis and paper revision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, S., Fan, Y., Fang, Y. et al. The role of EVI1 gene quantification in AML patients with 11q23/MLL rearrangement after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 56, 470–480 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-01048-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-01048-1