Abstract
Background
Pediatric-inspired non-transplant regimens for adolescent and adult ALL patients are becoming standard in many institutions. We aimed to compare a cohort of patients receiving a pediatric-inspired protocol to a cohort of patients treated with adult type ALL therapy followed by allografting after achieving CR1.
Method
Eighty-five adolescent and adult ALL patients treated with CALGB 19802 protocol who received MSD transplant in CR1 were retrospectively compared to a matched cohort of 72 adolescent and adult ALL patients treated with a modified version of Children’s Cancer Group (CCG) 1900 protocol.
Results
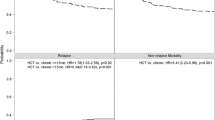
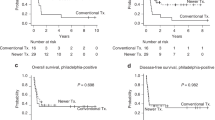
The five years OS in the allo-HCT cohort was 63.1% compared to 80.2% in the pediatric-inspired chemotherapy arm (P = 0.03). The five years EFS in the allo-HCT arm was 58.8% compared to 61.6% in the pediatric-inspired chemotherapy arm (P = 0.07). The five years DFS in the allo-HCT arm was 58.8% as compared to 71.9% in the pediatric-inspired chemotherapy arm (P = 0.07). The relapse rate in the allo-HCT cohort was 30.58% compared to 21.68% in the pediatric-inspired chemotherapy arm (P = 0.16). The NRM in the allo-HCT cohort was 10.59 as compared to 6.45 in the pediatric-inspired chemotherapy arm (P = 0.3).
Conclusion
For adolescent and adult patients with Ph-negative ALL, pediatric-inspired chemotherapy resulted in higher OS compared to allo-HCT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
El Fakih R, Ahmed S, Alfraih F, Hanbali A. Hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adult patients. Hematol/Oncol stem cell Ther. 2017;10:252–8.
Pui C-H, Campana D, Pei D, Bowman WP, Sandlund JT, Kaste SC, et al. Treating childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia without cranial irradiation. N. Engl J Med. 2009;360:2730–41.
Avramis VI, Sencer S, Periclou AP, Sather H, Bostrom BC, Cohen LJ, et al. A randomized comparison of native Escherichia coli asparaginase and polyethylene glycol conjugated asparaginase for treatment of children with newly diagnosed standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Children’s Cancer Group study. Blood, J Am Soc Hematol. 2002;99:1986–94.
Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, Tallman MS, Buck G, Fielding AK, et al. In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993). Blood. 2008;111:1827–33.
Kantarjian HM, O’Brien S, Smith TL, Cortes J, Giles FJ, Beran M, et al. Results of treatment with hyper-CVAD, a dose-intensive regimen, in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:547.
Thomas X, Boiron JM, Huguet F, Dombret H, Bradstock K, Vey N, et al. Outcome of treatment in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: analysis of the LALA-94 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:4075–86.
Giebel S, Labopin M, Beelen D, Browne P, Volin L, Kyrcz-Krzemien S, et al. Improving results of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission: an analysis from Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica: haematol. 2016.145631.
Gupta V, Richards S. Rowe J. Allogeneic, but not autologous, hematopoietic cell transplantation improves survival only among younger adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first remission: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Blood. 2013;121:339–50.
Fielding AK, Richards SM, Chopra R, Lazarus HM, Litzow MR, Buck G, et al. Outcome of 609 adults after relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL); an MRC UKALL12/ECOG 2993 study. Blood. 2007;109:944–50.
Huguet F, Leguay T, Raffoux E, Thomas X, Beldjord K, Delabesse E, et al. Pediatric-inspired therapy in adults with Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the GRAALL-2003 study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:911–8.
De Bont J, Van Der Holt B, Dekker A, Sonneveld P, Pieters R. Significant difference in outcome for adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated on pediatric vs adult protocols in the Netherlands. Leukemia. 2004;18:2032–5.
Stock W, Luger SM, Advani AS, Yin J, Harvey RC, Mullighan CG, et al. A pediatric regimen for older adolescents and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of CALGB 10403. Blood, J Am Soc Hematol. 2019;133:1548–59.
Huguet F, Chevret S, Leguay T, Thomas X, Boissel N, Escoffre-Barbe M, et al. Intensified therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: report of the randomized GRAALL-2005 clinical trial. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2018;36:2514–23.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann H, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 Consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone marrow Transplant. 1995;15:825.
Sullivan KM. Acute and chronic graft‐versus‐host disease in man. Int J Cell Cloning. 1986;4:42–93.
Health UDo, Services H. National Cancer Institute: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Version 4.03. 2010. In, 2016.
Rowe JM. Prognostic factors in adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. British J of haematol. 2010;150:389–405.
Sebban C, Lepage E, Vernant JP, Gluckman E, Attal M, Reiffers J, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission: a comparative study. French Group of Therapy of Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12:2580–7.
Hunault M, Harousseau JL, Delain M, Truchan-Graczyk M, Cahn JY, Witz F, et al. Better outcome of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia after early genoidentical allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT) than after late high-dose therapy and autologous BMT: a GOELAMS trial. Blood. 2004;104:3028–37.
Yanada M, Matsuo K, Suzuki T, Naoe T. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation as part of postremission therapy improves survival for adult patients with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a metaanalysis. Cancer. 2006;106:2657–63.
Ram R, Gafter-Gvili A, Vidal L, Paul M, Ben-Bassat I, Shpilberg O, et al. Management of adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission: systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer. 2010;116:3447–57.
Pidala J, Djulbegovic B, Anasetti C, Kharfan-Dabaja M, Kumar A Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in first complete remission. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011:CD008818.
Seftel MD, Neuberg D, Zhang M-J, Wang H-L, Ballen KK, Bergeron J, et al. Pediatric-inspired therapy compared to allografting for Philadelphia chromosome-negative adult ALL in first complete remission. Am J of hematol. 2016;91:322–9.
Dhedin N, Huynh A, Maury S, Tabrizi R, Beldjord K, Asnafi V, et al. Role of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with Ph-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2015;125:2486–96.
Hanbali A, Kotb A, El Fakih R, Alfraih F, Ahmed SO, Shaheen M, et al. Improved outcome of a pediatric-inspired protocol for high-risk adolescent and young adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients using peg-asparaginase and escalating dose of methotrexate: tolerability and outcome. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019;19:670–7.
DeAngelo DJ, Stevenson KE, Dahlberg SE, Silverman LB, Couban S, Supko JG, et al. Long-term outcome of a pediatric-inspired regimen used for adults aged 18-50 years with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2015;29:526–34.
Tomblyn MB, Arora M, Baker KS, Blazar BR, Brunstein CG, Burns LJ, et al. Myeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: analysis of graft sources and long-term outcome. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3634–41.
Gooley TA, Chien JW, Pergam SA, Hingorani S, Sorror ML, Boeckh M, et al. Reduced mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2091–101.
Wood WA, Lee SJ, Brazauskas R, Wang Z, Aljurf MD, Ballen KK, et al. Survival improvements in adolescents and young adults after myeloablative allogeneic transplantation for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:829–36.
Hayakawa F, Sakura T, Yujiri T, Kondo E, Fujimaki K, Sasaki O, et al. Markedly improved outcomes and acceptable toxicity in adolescents and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia following treatment with a pediatric protocol: a phase II study by the Japan Adult Leukemia Study Group. Blood Cancer J. 2014;4:e252.
Brandwein JM, Atenafu EG, Schuh AC, Yee KWL, Schimmer AD, Gupta V, et al. Predictors of outcome in adults with BCR-ABL negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with a pediatric-based regimen. Leukemia res. 2014;38:532–6.
Stock W, Luger SM, Advani AS, Geyer S, Harvey RC, Mullighan CG, et al. Favorable outcomes for older adolescents and young adults (AYA) with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): early results of US Intergroup Trial C10403. Blood. 2014;124:796.
Stock W, La M, Sanford B, Bloomfield CD, Vardiman JW, Gaynon P, et al. What determines the outcomes for adolescents and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated on cooperative group protocols? A comparison of Children’s Cancer Group and Cancer and Leukemia Group B studies. Blood. 2008;112:1646–54.
Boissel N, Auclerc MF, Lheritier V, Perel Y, Thomas X, Leblanc T, et al. Should adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia be treated as old children or young adults? Comparison of the French FRALLE-93 and LALA-94 trials. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:774–80.
Ramanujachar R, Richards S, Hann I, Goldstone A, Mitchell C, Vora A, et al. Adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: outcome on UK national paediatric (ALL97) and adult (UKALLXII/E2993) trials. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;48:254–61.
Kantarjian H, Stein A, Gökbuget N, Fielding AK, Schuh AC, Ribera J-M, et al. Blinatumomab versus chemotherapy for advanced acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:836–47.
Kantarjian HM, DeAngelo DJ, Stelljes M, Martinelli G, Liedtke M, Stock W, et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin versus standard therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:740–53.
Grupp SA, Kalos M, Barrett D, Aplenc R, Porter DL, Rheingold SR, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for acute lymphoid leukemia. New Eng J of Med. 2013;368:1509–18.
Beldjord K, Chevret S, Asnafi V, Huguet F, Boulland ML, Leguay T, et al. Oncogenetics and minimal residual disease are independent outcome predictors in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2014;123:3739–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.E, A.H designed and performed the research. T.E analyzed the data. R. E, A.H wrote the first draft. All the co-authors revised and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haroon, A., Alfraih, F., Hanbali, A. et al. Allogeneic transplant compared to pediatric-inspired therapy for Philadelphia chromosome-negative adolescent and adult ALL in first complete remission. Bone Marrow Transplant 57, 593–597 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-022-01595-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-022-01595-9