Abstract
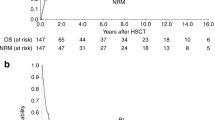
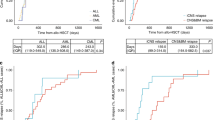
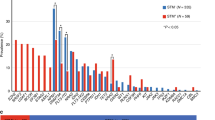
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is a clonal hematopoietic stem cell malignancy and the only curable therapy is allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). However, allo-HSCT is not appropriate for all CMML patients, and relapse is the leading cause of treatment failure. This project conducted a nationwide multicenter real-world study to develop a novel prediction scoring system for early relapse. A total of 238 CMML patients from twenty-seven medical centers treated with allo-HSCT, and 307 adult patients with CMML who underwent allo-HSCT in a publicly available research dataset from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplantation Registry (CIBMTR) database were included. Independent prognostic factors for the early relapse of CMML posttransplantation were identified according to competing risk regression methods. Four prognostic factors were identified: bone marrow blasts >10% (hazard ratio [HR], 4.262; P = 0.014), age >60 years (HR, 6.221; P = 0.007), hemoglobin level <100 g/L (HR, 3.695; P = 0.004), and non TET2 gene mutation (HR, 3.425; P = 0.017). A risk-grading scoring system was developed based on the regression coefficients and patients were stratified into low-risk (0–1 point), intermediate-risk (1.5–2 points) and high-risk ( > 2 points) groups. The validated internal c-statistic was 0.767 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.674–0.860), and the external c-statistic was 0.769 (95% CI, 0.703–0.836). In the derivation cohort, the cumulative incidence rates of early relapse in the low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk groups were 1.35% (95% CI: 1–4%), 10.40% (95% CI: 4–16%), and 29.54% (95% CI: 16–39%) (P < 0.001), respectively. This scoring system can be utilized to early identification of patients at a high risk of relapse and contributing to the implementation of urgent medical support.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are not publicly available due to their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants but are available on request from the corresponding author, Xiao-Hui Zhang, PhD, MD.
References
Chan O, Renneville A, Padron E. Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia diagnosis and management. Leukemia. 2021;35:1552–62.
Khoury JD, Solary E, Abla O, Akkari Y, Alaggio R, Apperley JF, et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia. 2022;36:1703–19.
Itzykson R, Fenaux P, Bowen D, Cross NCP, Cortes J, De Witte T, et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemias in Adults: Recommendations From the European Hematology Association and the European LeukemiaNet. Hemasphere. 2018;2:e150.
de Witte T, Bowen D, Robin M, Malcovati L, Niederwieser D, Yakoub-Agha I, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for MDS and CMML: recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2017;129:1753–62.
Eissa H, Gooley TA, Sorror ML, Nguyen F, Scott BL, Doney K, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: relapse-free survival is determined by karyotype and comorbidities. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2011;17:908–15.
Liu HD, Ahn KW, Hu ZH, Hamadani M, Nishihori T, Wirk B, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adult chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2017;23:767–75.
Kongtim P, Popat U, Jimenez A, Gaballa S, El Fakih R, Rondon G, et al. Treatment with hypomethylating agents before allogeneic stem cell transplant improves progression-free survival for patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:47–53.
Kröger N, Zabelina T, Guardiola P, Runde V, Sierra J, Biezen AV, et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation of adult chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia. A report on behalf of the Chronic Leukaemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Br J Haematol. 2002;118:67–73.
Woo J, Choi DR, Storer BE, Yeung C, Halpern AB, Salit RB, et al. Impact of clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular profiles on long-term survival after transplantation in patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 2020;105:652–60.
Park S, Labopin M, Yakoub-Agha I, Delaunay J, Dhedin N, Deconinck E, et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: a report from the Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle et de Therapie Cellulaire. Eur J Haematol. 2013;90:355–64.
Deschler B, Ihorst G, Schnitzler S, Bertz H, Finke J. Geriatric assessment and quality of life in older patients considered for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a prospective risk factor and serial assessment analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2018;53:565–75.
Itonaga H, Aoki K, Aoki J, Ishikawa T, Ishiyama K, Uchida N, et al. Prognostic impact of donor source on allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation outcomes in adults with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: a nationwide retrospective analysis in Japan. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2018;24:840–8.
Itonaga H, Iwanaga M, Aoki K, Aoki J, Ishiyama K, Ishikawa T, et al. Impacts of graft-versus-host disease on outcomes after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: A nationwide retrospective study. Leuk Res. 2016;41:48–55.
Zang DY, Deeg HJ, Gooley T, Anderson JE, Anasetti C, Sanders J, et al. Treatment of chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia by allogeneic marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol. 2000;110:217–22.
Sun YQ, Zhao C, Wang Y, Yan CH, Zhang XH, Xu LP, et al. Haploidentical stem cell transplantation in patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Sci China Life Sci. 2020;63:1261–4.
Sharma P, Shinde SS, Damlaj M, Hefazi Rorghabeh M, Hashmi SK, Litzow MR, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant in adult patients with myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasm (MDS/MPN) overlap syndromes. Leuk Lymphoma. 2017;58:872–81.
Onida F. Models of prognostication in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2017;12:513–21.
Motohashi K, Fujisawa S, Doki N, Kobayashi T, Mori T, Usuki K, et al. Cytogenetic risk stratification may predict allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation outcomes for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018;59:1332–7.
Mei M, Pillai R, Kim S, Estrada-Merly N, Afkhami M, Yang L, et al. The mutational landscape in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and its impact on allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcomes: a Center for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Research (CIBMTR) analysis. Haematologica. 2022;108:150–60.
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:2391–405.
Such E, Cervera J, Costa D, Sole F, Vallespi T, Luno E, et al. Cytogenetic risk stratification in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 2011;96:375–83.
Such E, Germing U, Malcovati L, Cervera J, Kuendgen A, Della Porta MG, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic scoring system for patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Blood. 2013;121:3005–15.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DAG, Gralnick H, et al. The chronic myeloid leukaemias: guidelines for distinguishing chronic granulocytic, atypical chronic myeloid, and chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia: Proposals by the French - American - British Cooperative Leukaemia Group. Br J Haematol. 1994;87:746–54.
Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, Craddock C, DiNardo CD, Dombret H, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140:1345–77.
Wang D, Sun Z, Zhu X, Zheng X, Zhou Y, Lu Y, et al. GARP-mediated active TGF-β1 induces bone marrow NK cell dysfunction in AML patients with early relapse post–allo-HSCT. Blood. 2022;140:2788–804.
Yuan XL, Lai XY, Wu YB, Yang LX, Shi JM, Liu LZ, et al. A novel risk model for predicting early relapse in acute myeloid leukemia patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2023;58:801–10.
Gao Y, Wu H, Shi Z, Gao F, Shi J, Luo Y, et al. Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes in patients with relapsed acute leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2023;58:863–73.
Varanasi PR, Ogonek J, Luther S, Dammann E, Stadler M, Ganser A, et al. Cytomegalovirus-specific CD8+ T-cells are associated with a reduced incidence of early relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0213739.
Dreger P, Corradini P, Kimby E, Michallet M, Milligan D, Schetelig J, et al. Indications for allogeneic stem cell transplantation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: the EBMT transplant consensus. Leukemia. 2007;21:12–7.
Laurenti L, Tarnani M, Chiusolo P, Sora F, Sica S. Allogeneic transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2010;2:e2010026.
Lee KL, Mark DB. Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med. 1996;15:361–87.
Bacher U, Haferlach T, Schnittger S, Kreipe H, Kroger N. Recent advances in diagnosis, molecular pathology and therapy of chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2011;153:149–67.
Zhou JY, Wang S, Yuan HL, Xu YJ, Huang XB, Gao SJ, et al. Impact of a novel prognostic model on allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation outcomes in patients with CMML. Am J Hematol. 2023;98:1394–406.
Kerbauy DM, Chyou F, Gooley T, Sorror ML, Scott B, Pagel JM, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005;11:713–20.
Wedge E, Hansen JW, Dybedal I, Creignou M, Ejerblad E, Lorenz F, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: clinical and molecular genetic prognostic factors in a nordic population. Transpl Cell Ther. 2021;27:991.e1–9.
Symeonidis A, van Biezen A, de Wreede L, Piciocchi A, Finke J, Beelen D, et al. Achievement of complete remission predicts outcome of allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia. A study of the Chronic Malignancies Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Br J Haematol. 2015;171:239–46.
Onida F, Sbianchi G, Radujkovic A, Sockel K, Kroger N, Sierra J, et al. Prognostic value of a new clinically-based classification system in patients with CMML undergoing allogeneic HCT: a retrospective analysis of the EBMT-CMWP. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022;57:896–902.
Pophali P, Matin A, Mangaonkar AA, Carr R, Binder M, Al-Kali A, et al. Prognostic impact and timing considerations for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2020;10:121.
Gagelmann N, Badbaran A, Beelen DW, Salit RB, Stolzel F, Rautenberg C, et al. A prognostic score including mutation profile and clinical features for patients with CMML undergoing stem cell transplantation. Blood Adv. 2021;5:1760–9.
Patnaik MM, Tefferi A. Cytogenetic and molecular abnormalities in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6:e393.
Tamari R, Rapaport F, Zhang N, McNamara C, Kuykendall A, Sallman DA, et al. Impact of high-molecular-risk mutations on transplantation outcomes in patients with myelofibrosis. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2019;25:1142–51.
Patnaik MM, Wassie EA, Padron E, Onida F, Itzykson R, Lasho TL, et al. Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia in young patients: molecular and cytogenetic predictors of survival and treatment outcome. Blood. 2014;124:4633.
Kröger N, Schroeder T, Zabelina T, Badbaran A, Bacher U, Kobbe G, et al. Post-allogeneic monitoring with molecular markers detected by pre-transplant next generation sequencing (NGS) predicts clinical relapse in patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). Blood. 2012;120:4212.
Schroeder T, Stelljes M, Christopeit M, Esseling E, Scheid C, Mikesch JH, et al. Azacitidine, lenalidomide and donor lymphocyte infusions for relapse of myelodysplastic syndrome, acute myeloid leukemia and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia after allogeneic transplant: the Azalena-Trial. Haematologica. 2023;108:3001–10.
Valcarcel D, Martino R, Caballero D, Martin J, Ferra C, Nieto JB, et al. Sustained remissions of high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome after reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation: chronic graft-versus-host disease is the strongest factor improving survival. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:577–84.
Hiramoto N, Kurosawa S, Tajima K, Okinaka K, Tada K, Kobayashi Y, et al. Positive impact of chronic graft-versus-host disease on the outcome of patients with de novo myelodysplastic syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a single-center analysis of 115 patients. Eur J Haematol. 2014;92:137–46.
Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, Storb R, Witherspoon RP, Fefer A, Fisher L, et al. Influence of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease on relapse and survival after bone marrow transplantation from HLA-identical siblings as treatment of acute and chronic leukemia [published erratum appears in Blood 1989 Aug 15;74(3):1180]. Blood. 1989;73:1720–8.
Weiden PL, Flournoy N, Thomas ED, Prentice R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, et al. Antileukemic effect of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of allogeneic-marrow grafts. N Engl J Med. 1979;300:1068–73.
Kolb HJ. Graft-versus-leukemia effects of transplantation and donor lymphocytes. Blood. 2008;112:4371–83.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFC2500304), the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82230004), National Natural Science of Foundation of China (No. 81970113) and Capital Health Research and Development of Special (No. 2022-1-4082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JYZ and XHZ contributed to the study design. JYZ, YXC, HLY, YJX, XBH, SJG, YCZ, FZ, XMS, YL, JMY, YHL, SQW, YJD, XZ, YMF, XD, HZ, ZMZ, KHB, MJ, TN, DMW, YC, LL and HY collected the data. JYZ, YXC, YHC, FRW, YYZ, and XDM performed data analysis. JYZ drafted and wrote the manuscript. WH, JZW, YW, HC, XYZ, YJC, KYL and XJH revised it critically. XHZ conceived and directed the study and revised the manuscript. The final version of the manuscript was critically reviewed and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, JY., Chen, YX., Yuan, HL. et al. A multifactorial risk scoring system for the prediction of early relapse in CMML patients with allo-HSCT: a nationwide representative multicenter study. Bone Marrow Transplant 60, 310–318 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-024-02480-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-024-02480-3
This article is cited by
-
Allogeneic Transplant for CMML
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2025)