Abstract
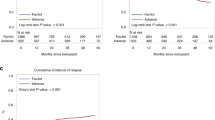
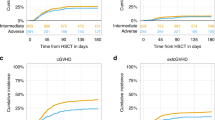
We retrospectively analyzed the impact of conditioning intensity on transplant outcomes according to their cytogenetic/molecular risk in a cohort of 1823 patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and intermediate- or adverse-risk cytogenetics in first complete remission (CR1). These patients received their first hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) using post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy). The intermediate-risk cytogenetic group included 1386 (76%) patients, and 608 (34%) had mutated FLT3-ITD. Myeloablative conditioning was used in 930 patients (51%), while 1130 (62%) received an intensified conditioning (score ≥2.5) based on the transplant conditioning intensity (TCI) score. Conditioning intensity using the myeloablative/reduced intensity stratification did not impact transplant outcomes across the entire cohort. However, a higher TCI score was associated with a lower risk of relapse, with no effect on survival. In specific cytogenetic risk groups, a higher TCI score did not influence outcomes in the adverse-risk group. In the intermediate-risk group, the impact varied with FLT3-ITD status. Patients with FLT3-ITD mutation who received a higher TCI showed a beneficial effect on relapse, leukemia-free survival (LFS), and overall survival. Conversely, in FLT3-ITD wild-type patients, more intense conditioning had a detrimental effect on graft-versus-host disease-free, and relapse-free survival with no effect on other outcomes. In conclusion, for AML patients in CR1 undergoing HSCT with PTCy, it is crucial to consider cytogenetic risk and molecular status when selecting the conditioning regimen. Intensive conditioning should be considered for patients with intermediate-risk cytogenetics and mutated FLT3-ITD but should probably be avoided for those with wild-type FLT3-ITD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article are available in the ALWP of the EBMT in Saint Antoine Hospital, Paris.
References
Scott BL, Pasquini MC, Logan BR, Wu J, Devine SM, Porter DL, et al. Myeloablative versus reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1154–61.
Aoudjhane M, Labopin M, Gorin NC, Shimoni A, Ruutu T, Kolb HJ, et al. Comparative outcome of reduced intensity and myeloablative conditioning regimen in HLA identical sibling allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients older than 50 years of age with acute myeloblastic leukaemia: a retrospective survey. Leukemia. 2005;19:2304–12.
Santoro N, Labopin M, Ciceri F, Van Lint MT, Nasso D, Blaise D, et al. Impact of conditioning intensity on outcomes of haploidentical stem cell transplantation for patients with acute myeloid leukemia 45 years of age and over. Cancer. 2019;125:1499–506.
Ringdén O, Labopin M, Ehninger G, Niederwieser D, Olsson R, Basara N, et al. Reduced intensity conditioning compared with myeloablative conditioning using unrelated donor transplants in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4570–7.
Bacigalupo A. Third EBMT/AMGEN Workshop on reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplants (RIC-HSCT), and panel consensus. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2004;33:691–6.
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, et al. Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2009;15:1628–33.
Spyridonidis A, Labopin M, Savani BN, Niittyvuopio R, Blaise D, Craddock C, et al. Redefining and measuring transplant conditioning intensity in current era: a study in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55:1114–25.
Hourigan CS, Dillon LW, Gui G, Logan BR, Fei M, Ghannam J, et al. Impact of conditioning intensity of allogeneic transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia with genomic evidence of residual disease. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:1273–83.
Döhner H, Estey E, Grimwade D, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Büchner T, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2017;129:424–47.
Kaplan EL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1958;53:457–81.
Fine JP, Gray RJ. A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc. 1999;94:496–509.
Gooley TA, Leisenring W, Crowley J, Storer BE. Estimation of failure probabilities in the presence of competing risks: New representations of old estimators. Stat Med. 1999;18:695–706.
Cox DR. Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc B.1972;34:187–220.
Biard L, Labopin M, Chevret S, Resche-Rigon M. Investigating covariate-by-centre interaction in survival data. Stat Methods Med Res. 2018;27:920–32.
Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, Craddock C, DiNardo CD, Dombret H, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2022;140. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2022016867.
Sanz J, Galimard J-E, Labopin M, Afanasyev B, Sergeevich MI, Angelucci E, et al. Post-transplant cyclophosphamide containing regimens after matched sibling, matched unrelated and haploidentical donor transplants in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission, a comparative study of the ALWP of the EBMT. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:84.
Sanz J, Galimard J-E, Labopin M, Afanasyev B, Angelucci E, Ciceri F, et al. Post-transplant cyclophosphamide after matched sibling, unrelated and haploidentical donor transplants in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a comparative study of the ALWP EBMT. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:46.
Montoro J, Piñana JL, Hernández-Boluda JC, Hernani R, Lorenzo I, Pérez A, et al. Uniform graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis with posttransplant cyclophosphamide, sirolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from haploidentical, matched sibling and unrelated donors. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020;55:2147–59.
Lazzari L, Balaguer-Roselló A, Montoro J, Greco R, Hernani R, Lupo-Stanghellini MT, et al. Post-transplant cyclophosphamide and sirolimus based graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022;57:1389–98.
Sanz J, Labopin M, Blaise D, Raiola AM, Busca A, Vydra J, et al. Haploidentical stem cell donor choice for patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a study from the ALWP of the EBMT. Blood Adv. 2024;8:2332–41.
Shimoni A, Hardan I, Shem-Tov N, Yeshurun M, Yerushalmi R, Avigdor A, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in AML and MDS using myeloablative versus reduced-intensity conditioning: the role of dose intensity. Leukemia. 2006;20:322–8.
Gaballa S, Saliba R, Oran B, Brammer JE, Chen J, Rondon G, et al. Relapse risk and survival in patients with FLT3 acute myeloid leukemia undergoing stem cell transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2017;92:331.
Bazarbachi A, Labopin M, Battipaglia G, Djabali A, Forcade E, Arcese W, et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: in vivo T-cell depletion and posttransplant sorafenib maintenance improve survival. a retrospective acute leukemia working party-European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplant Study. Clin Hematol Int. 2019;1:58–74.
Solh MM, Solomon SR, Morris LE, Zhang X, Holland HK, Bashey A. The dilemma of conditioning intensity: when does myeloablative conditioning improve outcomes for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2019;25:606–12.
Bazarbachi A, Bug G, Baron F, Brissot E, Ciceri F, Dalle IA, et al. Clinical practice recommendation on hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia patients with FLT3-internal tandem duplication: a position statement from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica. 2020;105:1507–16.
Levis MJ, Hamadani M, Logan B, Jones RJ, Singh AK, Litzow M, et al. Gilteritinib as post-transplant maintenance for acute myeloid leukemia with internal tandem duplication mutation of FLT3. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.23.02474.
Griffin JD, Song Y, Yang H, Freimark J, Shah MV. Post‐transplant maintenance therapy in patients with FLT3‐mutated acute myeloid leukemia: Real‐world treatment patterns and outcomes. Eur J Haematol. 2021;107:553.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JS, ML, AS, MM, SP, and FC: designed the study. ML: performed statistical analysis and helped with the interpretation of the results. JS: wrote the manuscript. JV, DB, JP, JP, JM, GVG, PVDB, HLW, MR, PR, PC, MK, ME, JV, and EB: provided cases for the study. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The scientific board of the ALWP of EBMT approved this study. All patients gave written informed consent for the use of their data. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable for individual patient data. This is a pooled analysis.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sanz, J., Labopin, M., Versluis, J. et al. Cytogenetic and molecular risk-driven conditioning intensity in acute myeloid leukemia patients undergoing stem cell transplantation with post-transplant cyclophosphamide: a study from the acute leukemia working party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant 60, 529–534 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-025-02527-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-025-02527-z