Abstract
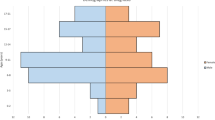
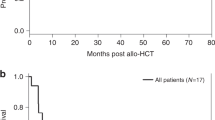
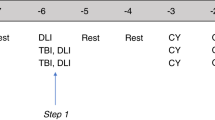
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is an aggressive and rare hematological malignancy with poor clinical outcomes. Stem cell transplantation helps to achieve long-term survival in adults. However, the benefit of haploidentical stem cell transplantation (HID-SCT) versus chemotherapy is unclear with BPDCN. We retrospectively analyzed 32 patients diagnosed with BPDCN including 15 who underwent HID-SCT and 17 who only received chemotherapy. The median age was 52 (range, 19–78) years. The ratio of male/female was 2.2. Skin, bone marrow and lymph node were the most three common sites of disease involvement. Compared with the chemotherapy group, patients in the HID-SCT group had significantly better progression-free survival (PFS; median, 7 months versus not reached, P < 0.001) and overall survival (OS; median, 13 months versus not reached, P < 0.001). The 4-year rates for PFS and OS in transplant patients were 74% (95% Confidence Interval [CI], 47, 100%) and 93% (79, 100%), respectively, compared to 0 in non-transplant patients. In conclusion, our results demonstrated HID-SCT could provide long-term remissions in BPDCN patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Roos-Weil D, Dietrich S, Boumendil A, Polge E, Bron D, Carreras E, et al. Stem cell transplantation can provide durable disease control in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: a retrospective study from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood. 2013;121:440–6.
Garnache-Ottou F, Vidal C, Biichlé S, Renosi F, Poret E, Pagadoy M, et al. How should we diagnose and treat blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm patients? Blood Adv. 2019;3:4238–51.
Zalmaï L, Viailly PJ, Biichle S, Cheok M, Soret L, Angelot-Delettre F, et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells proliferation associated with acute myeloid leukemia: phenotype profile and mutation landscape. Haematologica. 2021;106:3056–66.
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:2391–405.
Frankel AE, Woo JH, Ahn C, Pemmaraju N, Medeiros BC, Carraway HE, et al. Activity of SL-401, a targeted therapy directed to interleukin-3 receptor, in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm patients. Blood. 2014;124:385–92.
Lu Y, Sun RJ, Zhang JP, Xu F, Du ZC, Tong GL, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with myeloablative conditioning regimen for blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm patients in complete remission: a single center study. Leuk lymphoma. 2022;63:3092–9.
Bashir Q, Milton DR, Popat UR, Kebriaei P, Hosing C, Khouri IF, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN). Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022;57:51–6.
Pagano L, Valentini CG, Pulsoni A, Fisogni S, Carluccio P, Mannelli F, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm with leukemic presentation: an Italian multicenter study. Haematologica. 2013;98:239–46.
Cernan M, Szotkowski T, Hisemova M, Cetkovsky P, Sramkova L, Stary J, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: first retrospective study in the Czech Republic. Neoplasma. 2020;67:650–9.
Garnache-Ottou F, Feuillard J, Ferrand C, Biichle S, Trimoreau F, Seilles E, et al. Extended diagnostic criteria for plasmacytoid dendritic cell leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2009;145:624–36.
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114:937–51.
Yun S, Chan O, Kerr D, Vincelette ND, Idrees A, Mo Q, et al. Survival outcomes in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm by first-line treatment and stem cell transplant. Blood Adv. 2020;4:3435–42.
Cuglievan B, Connors J, He J, Khazal S, Yedururi S, Dai J, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: a comprehensive review in pediatrics, adolescents, and young adults (AYA) and an update of novel therapies. Leukemia. 2023;37:1767–78.
Pemmaraju N, Lane AA, Sweet KL, Stein AS, Vasu S, Blum W, et al. Tagraxofusp in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic-cell neoplasm. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1628–37.
Montero J, Stephansky J, Cai T, Griffin GK, Cabal-Hierro L, Togami K, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm is dependent on BCL2 and sensitive to venetoclax. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:156–64.
Alsidawi S, Westin GFM, Al-Kali A, Go RS. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. a population-based analysis from the SEER and NCDB Databases. Blood. 2016;128:4789.
Tsagarakis NJ, Kentrou NA, Papadimitriou KA, Pagoni M, Kokkini G, Papadaki H, et al. Acute lymphoplasmacytoid dendritic cell (DC2) leukemia: results from the Hellenic Dendritic Cell Leukemia Study Group. Leuk Res. 2010;34:438–46.
Pemmaraju N, Sweet KL, Stein AS, Wang ES, Rizzieri DA, Vasu S, et al. Long-term benefits of tagraxofusp for patients with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 2022;40:3032–6.
Jiang YL, Li Q, Yuan T, Jiang YY, Deng Q. Case report of anti-CD123 chimeric antigen receptor T-Cell therapy followed by radiotherapy for a recurrence of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. OncoTargets Ther. 2020;13:3425–30.
Poussard M, Angelot-Delettre F, Deconinck E. Conventional therapeutics in BPDCN patients-do they still have a place in the era of targeted therapies? Cancers. 2022;14:3767.
Liao C, Hu NX, Song H, Zhang JY, Shen DY, Xu XJ, et al. Pediatric blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: report of four cases and review of literature. Int J Hematol. 2021;113:751–9.
Aoki T, Suzuki R, Kuwatsuka Y, Kako S, Fujimoto K, Taguchi J, et al. Long-term survival following autologous and allogeneic stem cell transplantation for blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Blood. 2015;125:3559–62.
Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Al Malki MM, Deotare U, Raj RV, El-Jurdi N, Majhail N, et al. Haematopoietic cell transplantation for blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: a North American multicentre collaborative study. Br J Haematol. 2017;179:781–9.
Acknowledgements
RPG acknowledges support from the UK National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre. We thank all of the faculty members who participated in these studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL designed the study. JZ, FRW, SMY and YL analyzed the data. JZ, JL, RPG, YL and XDM prepared the typescript. YYZ, TZ, YQS, SZ, HZ, HC, PS, LW, JSJ and JW provided and collected the clinical data. All authors took responsibility for the content and agreed to submit for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
RPG is a consultant to Antengene Biotech LLC; Medical Director, FFF Enterprises Inc.; A speaker for Janssen Pharma and Hengrui Pharma; Board of Directors: Russian Foundation for Cancer Research Support and Scientific Advisory Board, StemRad Ltd.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Wang, F., Yang, S. et al. Survival outcomes between haploidentical stem cell transplantation and chemotherapy for blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Bone Marrow Transplant 60, 568–572 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-025-02528-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-025-02528-y