Abstract
Background
We aimed to establish a predictive prognostic risk-stratification model for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in the rituximab era.
Methods
The data of 1406 primary DLBCL patients from the Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center were analysed to establish a nomogram prognostic index (NPI) model for predicting overall survival (OS) based on pre-treatment indicators. An independent cohort of 954 DLBCL patients from three other hospitals was used for external validation.
Results
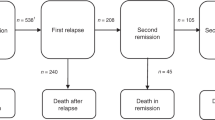
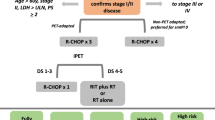
Age, performance status, stage, lactate dehydrogenase, number of extranodal sites, BCL2, CD5 expression, B symptoms and absolute lymphocyte and monocyte count were the main factors of the NPI model and could stratify the patients into four distinct categories based on their predicted OS. The calibration curve demonstrated satisfactory agreement between the predicted and actual 5-year OS of the patients. The concordance index of the NPI model (0.794) was higher than the IPI (0.759) and NCCN-IPI (0.750), and similar results were obtained upon external validation. For CD5 + DLBCL patients, systemic treatment with high-dose methotrexate was associated with superior OS compared to R-CHOP-based immunochemotherapy alone.
Conclusions
We established and validated an accurate prediction model, which performed better than IPI and NCCN-IPI for prognostic stratification of DLBCL patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teras, L. R., DeSantis, C. E., Cerhan, J. R., Morton, L. M., Jemal, A. & Flowers, C. R. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA Cancer J. Clin. 66, 443–459 (2016).
Gu, X., Zheng, R., Xia, C., Zeng, H., Zhang, S., Zou, X. et al. Interactions between life expectancy and the incidence and mortality rates of cancer in China: a population-based cluster analysis. Cancer Commun. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-018-0308-x (2018).
Pfreundschuh, M., Kuhnt, E., Trumper, L., Osterborg, A., Trneny, M., Shepherd, L. et al. CHOP-like chemotherapy with or without rituximab in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma: 6-year results of an open-label randomised study of the MabThera International Trial (MInT) Group. Lancet Oncol. 12, 1013–1022 (2011).
Coiffier, B., Thieblemont, C., Van Den Neste, E., Lepeu, G., Plantier, I., Castaigne, S. et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood 116, 2040–2045 (2010).
Shipp, M. A., Harrington, D. P., Anderson, J. R., Armitage, J. O., Bonadonna, G., Brittinger, G. et al. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkins-lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 329, 987–994 (1993).
Zhou, Z., Sehn, L. H., Rademaker, A. W., Gordon, L. I., LaCasce, A. S., Crosby-Thompson, A. et al. An enhanced International Prognostic Index (NCCN-IPI) for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated in the rituximab era. Blood 123, 837–842 (2014).
Sehn, L. H., Berry, B., Chhanabhai, M., Fitzgerald, C., Gill, K., Hoskins, P. et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 109, 1857–1861 (2007).
Prochazka, K. T., Melchardt, T., Posch, F., Schlick, K., Deutsch, A., Beham-Schmid, C. et al. NCCN-IPI score-independent prognostic potential of pretreatment uric acid levels for clinical outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Br. J. Cancer 115, 1264–1272 (2016).
Montalban, C., Diaz-Lopez, A., Dlouhy, I., Rovira, J., Lopez-Guillmermo, A., Alonso, S. et al. Validation of the NCCN-IPI for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): the addition of beta(2)-microglobulin yields a more accurate GELTAMO-IPI. Br. J. Haematol. 176, 918–928 (2017).
Schmitz, R., Wright, G. W., Huang, D. W., Johnson, C. A., Phelan, J. D., Wang, J. Q. et al. Genetics and pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 378, 1396–1407 (2018).
Chapuy, B., Stewart, C., Dunford, A. J., Kim, J., Kamburov, A., Redd, R. A. et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 24, 679–690 (2018).
Oh, S. Y., Kim, W. S., Kim, J. S., Kim, S. J., Yoon, D. H., Yang, D. H. et al. Phase II study of R-CVP followed by rituximab maintenance therapy for patients with advanced marginal zone lymphoma: consortium for improving survival of lymphoma (CISL) study. Cancer Commun. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-019-0403-7 (2019).
Wright, G. W., Huang, D. W., Phelan, J. D., Coulibaly, Z. A., Roulland, S., Young, R. M. et al. A probabilistic classification tool for genetic subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma with therapeutic implications. Cancer Cell 37, 551–568 (2020).
Yang, R., Shao, T., Long, M., Shi, Y., Liu, Q., Yang, L. et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes tumor growth and predicts poor prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Commun. 40, 551–555 (2020).
Bari, A., Marcheselli, L., Sacchi, S., Marcheselli, R., Pozzi, S., Ferri, P. et al. Prognostic models for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era: a never-ending story. Ann. Oncol. 21, 1486–1491 (2010).
Chen, Y., Neelapu, S., Feng, L., Bi, W., Yang, T.-H., Wang, M. et al. Prognostic significance of baseline peripheral absolute neutrophil, monocyte and serum 2-microglobulin level in patients with diffuse large b-cell lymphoma: a new prognostic model. Br. J. Haematol. 175, 290–299 (2016).
Kanemasa, Y., Shimoyama, T., Sasaki, Y., Tamura, M., Sawada, T., Omuro, Y. et al. Beta-2 microglobulin as a significant prognostic factor and a new risk model for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 35, 440–446 (2017).
Kim, D. H., Baek, J. H., Chae, Y. S., Kim, Y. K., Kim, H. J., Park, Y. H. et al. Absolute lymphocyte counts predicts response to chemotherapy and survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 21, 2227–2230 (2007).
Wilcox, R. A., Ristow, K., Habermann, T. M., Inwards, D. J., Micallef, I. N. M., Johnston, P. B. et al. The absolute monocyte and lymphocyte prognostic score predicts survival and identifies high-risk patients in diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 25, 1502–1509 (2011).
Tsuyama, N., Sakata, S., Baba, S., Mishima, Y., Nishimura, N., Ueda, K. et al. BCL2 expression in DLBCL: reappraisal of immunohistochemistry with new criteria for therapeutic biomarker evaluation. Blood 130, 489–500 (2017).
Johnson, N. A., Slack, G. W., Savage, K. J., Connors, J. M., Ben-Neriah, S., Rogic, S. et al. Concurrent expression of MYC and BCL2 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 30, 3452–3459 (2012).
Hu, S., Xu-Monette, Z. Y., Tzankov, A., Green, T., Wu, L., Balasubramanyam, A. et al. MYC/BCL2 protein coexpression contributes to the inferior survival of activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and demonstrates high-risk gene expression signatures: a report from The International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program. Blood 121, 4021–4031 (2013).
Yamaguchi, M., Seto, M., Okamoto, M., Ichinohasama, R., Nakamura, N., Yoshino, T. et al. De novo CD5(+) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study of 109 patients. Blood 99, 815–821 (2002).
Niitsu, N., Okamoto, M., Tamaru, J. I., Yoshino, T., Nakamura, N., Nakamura, S. et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics and treatment outcome of the addition of rituximab to chemotherapy for CD5-positive in comparison with CD5-negative diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 21, 2069–2074 (2010).
Scott, D. W., Mottok, A., Ennishi, D., Wright, G. W., Farinha, P., Ben-Neriah, S. et al. Prognostic significance of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell of origin determined by digital gene expression in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue biopsies. J. Clin. Oncol. 33, 2848–2856 (2015).
Wight, J. C., Chong, G., Grigg, A. P. & Hawkes, E. A. Prognostication of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the molecular era: moving beyond the IPI. Blood Rev. 32, 400–415 (2018).
Staiger, A. M., Ziepert, M., Horn, H., Scott, D. W., Barth, T. F. E., Bernd, H.-W. et al. Clinical impact of the cell-of-origin classification and the MYC/BCL2 dual expresser status in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated within prospective clinical trials of the German High-grade Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 35, 2515–2526 (2017).
Yang, Y., Zhang, Y. J., Zhu, Y., Cao, J. Z., Yuan, Z. Y., Xu, L. M. et al. Prognostic nomogram for overall survival in previously untreated patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a multicenter study. Leukemia 29, 1571–1577 (2015).
Tian, X. P., Huang, W. J., Huang, H. Q., Liu, Y. H., Wang, L., Zhang, X. et al. Prognostic and predictive value of a microRNA signature in adults with T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. Leukemia 33, 2454–2465 (2019).
Liang, W., Zhang, L., Jiang, G., Wang, Q., Liu, L., Liu, D. et al. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting survival in patients with resected non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 33, 861–869 (2015).
Swerdlow, S. H., Campo, E., Pileri, S. A., Harris, N. L., Stein, H., Siebert, R. et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 127, 2375–2390 (2016).
Cheson, B. D., Fisher, R. I., Barrington, S. F., Cavalli, F., Schwartz, L. H., Zucca, E. et al. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J. Clin. Oncol. 32, 3059–3068 (2014).
Weiss, L., Melchardt, T., Habringer, S., Boekstegers, A., Hufnagl, C., Neureiter, D. et al. Increased body mass index is associated with improved overall survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 25, 171–176 (2014).
Cao, Y., Shi, Y.-X., Chen, J.-O., Tan, Y.-T., Cai, Y.-C., Luo, H.-Y. et al. Serum C-reactive protein as an important prognostic variable in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Tumor Biol. 33, 1039–1044 (2012).
Ennishi, D., Takeuchi, K., Yokoyama, M., Asai, H., Mishima, Y., Terui, Y. et al. CD5 expression is potentially predictive of poor outcome among biomarkers in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma receiving rituximab plus CHOP therapy. Ann. Oncol. 19, 1921–1926 (2008).
Hans, C. P., Weisenburger, D. D., Greiner, T. C., Gascoyne, R. D., Delabie, J., Ott, G. et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 103, 275–282 (2004).
Tadmor, T., Bari, A., Sacchi, S., Marcheselli, L., Liardo, E. V., Avivi, I. et al. Monocyte count at diagnosis is a prognostic parameter in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from a large multicenter study involving 1191 patients in the pre- and post-rituximab era. Haematologica 99, 125–130 (2014).
Lin, B., Chen, C., Qian, Y. & Feng, J. Prognostic role of peripheral blood lymphocyte/monocyte ratio at diagnosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a meta-analysis. Leuke Lymphoma 56, 2563–2568 (2015).
Markovic, O., Popovic, L., Marisavljevic, D., Jovanovic, D., Filipovic, B., Stanisavljevic, D. et al. Comparison of prognostic impact of absolute lymphocyte count, absolute monocyte count, absolute lymphocyte count/absolute monocyte count prognostic score and ratio in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 25, 296–302 (2014).
Wei, X., Huang, F., Wei, Y., Jing, H., Xie, M., Hao, X. et al. Low lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio predicts unfavorable prognosis in non-germinal center type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuke. Res. 38, 694–698 (2014).
Morschhauser, F., Feugier, P., Flinn, I. W., Gasiorowski, R. E., Greil, R., Illes, A. et al. Venetoclax plus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisolone (R-CHOP) improves outcomes in BCL2-positive first-line diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): first safety, efficacy and biomarker analyses from the phase II CAVALLI study. Blood 132, 5 (2019). (abstract 782).
Alizadeh, A. A., Eisen, M. B., Davis, R. E., Ma, C., Lossos, I. S., Rosenwald, A. et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403, 503–511 (2000).
Rosenwald, A., Wright, G., Chan, W. C., Connors, J. M., Campo, E., Fisher, R. I. et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 1937–1947 (2002).
Cai, Q.-Q., Hu, L.-Y., Geng, Q.-R., Chen, J., Lu, Z.-H., Rao, H.-L. et al. New risk factors and new tendency for central nervous system relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a retrospective study. Chin. J. Cancer https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-016-0150-y (2016).
Cai, Q., Fang, Y. & Young, K. H. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: molecular pathogenesis and advances in treatment. Transl. Oncol. 12, 523–538 (2019).
Schmitz, N., Zeynalova, S., Nickelsen, M., Kansara, R., Villa, D., Sehn, L. H. et al. CNS international prognostic index: a risk model for CNS relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. J. Clin. Oncol. 34, 3150–3156 (2016).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the physicians for their actively cooperating with us in collecting patient information, thank all the patients and their families for allowing us to analyse their data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.C., X.P.T., S.Y.M., L.Y.Z. and W.Y.L. contributed to study design, statistical analysis and figure and tables preparation. L.Y.Z., W.Y.L., L.W., L.L.G., Z.H.L., Y.D.W., G.Z.Z., N.S., Y.F., Y.C.Z. and P.P.L. performed data collecting. J.C., X.P.T., S.Y.M. and Q.Q.C. performed manuscript writing and reviewing. Q.Q.C. conceived and designed this study that led to the submission, acquired the data and played an important role in interpreting the results, she is also responsible for all aspects of the work to sure that all questions of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All authors agree with the contents of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed content for all patients was provided. Ethical approval of the dataset used for this project was obtained from The Institutional Review Board of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (Guangzhou, China, No. B2020–235–01). The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to publish
No consent was involved in this publication.
Data availability
The authenticity of this article has been validated by uploading the key raw data onto the Research Data Deposit public platform (www.researchdata.org.cn), with the approval RDD number as RDDA2020001739.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Funding information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81672686), Special Support Program of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (PT19020401), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou, China (202002030205) and Clinical Oncology Foundation of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (Y-XD2019–124).
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, J., Tian, X., Ma, S. et al. A nomogram prognostic index for risk-stratification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era: a multi-institutional cohort study. Br J Cancer 125, 402–412 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01434-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01434-6
This article is cited by
-
Nomogram for predicting the overall survival and disease-specific survival of adult patients with primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type based on the SEER database
Annals of Hematology (2025)
-
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the new era: prognostic tools for mapping risk
Annals of Hematology (2025)
-
Predictive value of prognostic nutritional index as prognostic biomarkers in patients with lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2024)
-
Recent advances in CD5+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Annals of Hematology (2024)
-
Development and validation of a novel risk stratification model and a survival rate calculator for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era: a multi-institutional cohort study
Annals of Hematology (2024)