Abstract
Background
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in the tumor microenvironment (TME) primarily polarize into the M2-phenotype. Our previous study showed that the small GTPase Rab37 mediates IL-6 trafficking in macrophages for M2 polarization. Here, we uncover an unconventional role of Rab37, independent of vesicle trafficking, in promoting M2 polarization of TAMs.
Methods
The gene profiles in wild-type and Rab37 knockout (KO) bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were analyzed using cDNA microarray. The mechanism of Rab37 in regulating the interferon (IFN) pathway was confirmed through in vitro/vivo assays and clinical studies.
Results
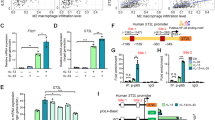
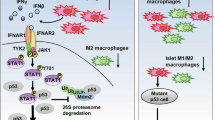
Type I IFN signaling was highly enriched in BMDMs from Rab37 KO mice. Moreover, Rab37 induction and decreased type I IFN genes were observed in macrophages treated with lung cancer-conditioned medium and epigenetic drugs, indicating an epigenetic regulation of Rab37 in TAMs. Mechanistically, GDP-bound Rab37 interacted with the nuclear localization sequence of STAT1 to sequest it in the cytosol from its transcription activities, thus leading to the downregulation of IFN genes. Clinically, CD163+/Rab37+/STAT1cytosol in TAMs expression signature correlated with advanced tumor stages and poor survival of lung cancer patients.
Conclusions
Our findings highlight the cytosolic interaction of Rab37-STAT1 in M2 TAM polarization, with CD163+/Rab37+/STAT1cytosol TAMs as a lung cancer prognosis biomarker.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Anderson NM, Simon MC. The tumor microenvironment. Curr Biol. 2020;30:R921–25.
Huang YK, Wang M, Sun Y, Di Costanzo N, Mitchell C, Achuthan A, et al. Macrophage spatial heterogeneity in gastric cancer defined by multiplex immunohistochemistry. Nat Commun. 2019;10:3928.
Pombo Antunes AR, Scheyltjens I, Lodi F, Messiaen J, Antoranz A, Duerinck J, et al. Single-cell profiling of myeloid cells in glioblastoma across species and disease stage reveals macrophage competition and specialization. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24:595–610.
Wang Y, Liu B, Min Q, Yang X, Yan S, Ma Y, et al. Spatial transcriptomics delineates molecular features and cellular plasticity in lung adenocarcinoma progression. Cell Discov. 2023;9:96.
Mantovani A, Marchesi F, Malesci A, Laghi L, Allavena P. Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14:399–416.
Ruffell B, Coussens LM. Macrophages and therapeutic resistance in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2015;27:462–72.
Chen S, Morine Y, Tokuda K, Yamada S, Saito Y, Nishi M, et al. Cancer‑associated fibroblast‑induced M2‑polarized macrophages promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the plasminogen activator inhibitor‑1 pathway. Int J Oncol. 2021;59:59.
Tzeng HT, Su CC, Chang CP, Lai WW, Su WC, Wang YC. Rab37 in lung cancer mediates exocytosis of soluble ST2 and thus skews macrophages toward tumor-suppressing phenotype. Int J Cancer. 2018;143:1753–63.
Yin Y, Liu B, Cao Y, Yao S, Liu Y, Jin G, et al. Colorectal cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles promote tumor immune evasion by upregulating PD-L1 expression in tumor-associated macrophages. Adv Sci. 2022;9:2102620.
Hensler M, Kasikova L, Fiser K, Rakova J, Skapa P, Laco J, et al. M2-like macrophages dictate clinically relevant immunosuppression in metastatic ovarian cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e000979.
Sato-Kaneko F, Yao S, Ahmadi A, Zhang SS, Hosoya T, Kaneda MM, et al. Combination immunotherapy with TLR agonists and checkpoint inhibitors suppresses head and neck cancer. JCI Insight. 2017;2:e93397.
Chen YJ, Li GN, Li XJ, Wei LX, Fu MJ, Cheng ZL, et al. Targeting IRG1 reverses the immunosuppressive function of tumor-associated macrophages and enhances cancer immunotherapy. Sci Adv. 2023;9:eadg0654.
Ma S, Sun B, Duan S, Han J, Barr T, Zhang J, et al. YTHDF2 orchestrates tumor-associated macrophage reprogramming and controls antitumor immunity through CD8+ T cells. Nat Immunol. 2023;24:255–66.
Zhang X, Li S, Malik I, Do MH, Ji L, Chou C, et al. Reprogramming tumour-associated macrophages to outcompete cancer cells. Nature. 2023;619:616–23.
Platanias LC. Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:375–86.
Müller E, Speth M, Christopoulos PF, Lunde A, Avdagic A, Øynebråten I, et al. Both type I and type II interferons can activate antitumor M1 macrophages when combined with TLR stimulation. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2520.
Ye Q, Luo F, Yan T. Transcription factor KLF4 regulated STAT1 to promote M1 polarization of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Aging. 2022;14:5669–80.
Shao Z, Chen L, Zhang Z, Wu Y, Mou H, Jin X, et al. KERS-inspired nanostructured mineral coatings boost IFN-γ mRNA therapeutic index for antitumor immunotherapy. Adv Mater. 2023;35:e2304296.
Kim HS, Kim DC, Kim HM, Kwon HJ, Kwon SJ, Kang SJ, et al. STAT1 deficiency redirects IFN signalling toward suppression of TLR response through a feedback activation of STAT3. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13414.
Stenmark H. Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:513–25.
Homma Y, Hiragi S, Fukuda M. Rab family of small GTPases: an updated view on their regulation and functions. FEBS J. 2021;288:36–55.
Haley R, Wang Y, Zhou Z. The small GTPase RAB-35 defines a third pathway that is required for the recognition and degradation of apoptotic cells. PLoS Genet. 2018;14:e1007558.
Takahashi T, Minami S, Tsuchiya Y, Tajima K, Sakai N, Suga K, et al. Cytoplasmic control of Rab family small GTPases through BAG6. EMBO Rep. 2019;20:e46794.
Zheng J, Duan B, Sun S, Cui J, Du J, Zhang Y. Folliculin Interacts with Rab35 to Regulate EGF-Induced EGFR Degradation. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:688.
Thomas JD, Zhang YJ, Wei YH, Cho JH, Morris LE, Wang HY, et al. Rab1A is an mTORC1 activator and a colorectal oncogene. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:754–69.
Cheng KW, Agarwal R, Mitra S, Lee JS, Carey M, Gray JW, et al. Rab25 increases cellular ATP and glycogen stores protecting cancer cells from bioenergetic stress. EMBO Mol Med. 2012;4:125–41.
Wheeler DB, Zoncu R, Root DE, Sabatini DM, Sawyers CL. Identification of an oncogenic RAB protein. Science. 2015;350:211–7.
Luo ML, Gong C, Chen CH, Hu H, Huang P, Zheng M, et al. The Rab2A GTPase promotes breast cancer stem cells and tumorigenesis via Erk signaling activation. Cell Rep. 2015;11:111–24.
Kuo IY, Yang YE, Yang PS, Tsai YJ, Tzeng HT, Cheng HC, et al. Converged Rab37/IL-6 trafficking and STAT3/PD-1 transcription axes elicit an immunosuppressive lung tumor microenvironment. Theranostics. 2021;11:7029–44.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:15545–50.
Tugal D, Liao X, Jain MK. Transcriptional control of macrophage polarization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33:1135–44.
Wu CY, Tseng RC, Hsu HS, Wang YC, Hsu MT. Frequent down-regulation of hRAB37 in metastatic tumor by genetic and epigenetic mechanisms in lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2009;63:360–7.
Nakamura R, Sene A, Santeford A, Gdoura A, Kubota S, Zapata N, et al. IL10-driven STAT3 signalling in senescent macrophages promotes pathological eye angiogenesis. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7847.
Strehlow I, Schindler C. Amino-terminal signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) domains regulate nuclear translocation and STAT deactivation. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:28049–56.
McBride KM, Banninger G, McDonald C, Reich NC. Regulated nuclear import of the STAT1 transcription factor by direct binding of importin-alpha. EMBO J. 2002;21:1754–63.
Cho SH, Kuo IY, Lu PF, Tzeng HT, Lai WW, Su WC, et al. Rab37 mediates exocytosis of secreted frizzled-related protein 1 to inhibit Wnt signaling and thus suppress lung cancer stemness. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:868.
Shaughnessy R, Echard A. Rab35 GTPase and cancer: Linking membrane trafficking to tumorigenesis. Traffic. 2018;19:247–52.
Hegde M, Guruprasad KP, Ramachandra L, Satyamoorthy K, Joshi MB. Interleukin-6-mediated epigenetic control of the VEGFR2 gene induces disorganized angiogenesis in human breast tumors. J Biol Chem. 2020;295:12086–98.
Herrmann A, Lahtz C, Song J, Aftabizadeh M, Cherryholmes GA, Xin H, et al. Integrin α6 signaling induces STAT3-TET3-mediated hydroxymethylation of genes critical for maintenance of glioma stem cells. Oncogene. 2020;39:2156–69.
Zhang Y, Liu Z, Yang X, Lu W, Chen Y, Lin Y, et al. H3K27 acetylation activated-COL6A1 promotes osteosarcoma lung metastasis by repressing STAT1 and activating pulmonary cancer-associated fibroblasts. Theranostics. 2021;11:1473–92.
Li M, Xu Y, Liang J, Lin H, Qi X, Li F, et al. USP22 deficiency in melanoma mediates resistance to T cells through IFNγ-JAK1-STAT1 signal axis. Mol Ther. 2021;29:2108–20.
Ren Y, Zhao P, Liu J, Yuan Y, Cheng Q, Zuo Y, et al. Deubiquitinase USP2a sustains interferons antiviral activity by restricting ubiquitination of activated STAT1 in the nucleus. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:e1005764.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the support from the Human Biobank, Research Center of Clinical Medicine, National Cheng Kung University Hospital. We thank the technical services provided by the “Bioimaging Core Facility” of the National Core Facility for Biopharmaceuticals, Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, and the support from the Core Research Laboratory, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University.
Funding
This work was supported by Taiwan Ministry and Science Technology grant MOST 109-2327-B-006-004 and Taiwan National Science and Technology Council grant NSTC 112-2311-B-006-004-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chen-Tai Hong: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Formal analysis, Data curation. You-En Yang: Writing – original draft, Writing – revised draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Investigation, Visualization. Hsueh-Fen Juan: Software, Data curation, Investigation. Chih-Peng Chang: Methodology, Validation, Investigation. Yi-Ching Wang: Supervision, Project administration, Conceptualization, Validation, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Data curation, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments using mice were approved by the animal ethics committee of National Cheng Kung University and complied with all relevant ethical guidelines (#112062). All lung cancer samples were conducted in accordance with the requirements of Research Center of Clinical Medicine, National Cheng Kung University Hospital. The use of clinical samples was approved by the institutional review board of the hospital with the ethical number #A-ER-111-517. All patients provided informed consent for the use of the tumor tissues for research.
Consent for publication
All authors have reviewed the final version of the manuscript and are in agreement its content and submission.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, CT., Yang, YE., Juan, HF. et al. GDP-bound Rab37 modulates M2-like tumor-associated macrophage polarization by attenuating STAT1 translocation to downregulate the type I IFN pathway. Br J Cancer 132, 622–634 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-02955-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-02955-0