Abstract
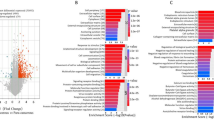
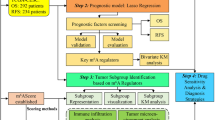
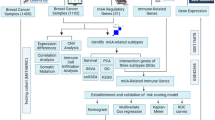
More than 24 regulators have been revealed to dynamically participant in N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation, and play critical roles in tumorigenesis and development of cancers. However, their functional roles have not been comprehensively clarified in breast cancer. Here we systematically analyzed the RNA sequencing data of 24 main m6A RNA methylation regulators in 775 breast cancer patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset. Consensus clustering of the 24 m6A regulators was carried out and identified two patient subgroups, RNA methylation 1/2 (RM1/2). RM1 demonstrated generally lower RNA methylation modification than that of RM2, and had significantly shorter overall survival. The hallmarks of PI3K/AKT signaling in cancer, KRAS signaling and angiogenesis were significantly enriched in RM1. Moreover, the association between m6A regulators and antitumor immune response was also investigated in this study and revealed that RM2 was associated with significantly higher expressions of HLA-A, higher numbers of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells, helper T cells and activated NK cells, but lower expressions of PD-L1, PD-L2, TIM3, and CCR4 than RM1. In conclusion, the expression pattern of m6A regulators was significantly correlated with the malignancy, prognosis and antitumor immune response in breast cancer, which might serve as potential targets and biomarkers for immunotherapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harbeck N, Gnant M. Breast cancer. Lancet. 2017;389(10074):1134–50.
Ponde NF, Zardavas D, Piccart M. Progress in adjuvant systemic therapy for breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16(1):27–44.
Wei SC, Duffy CR, Allison JP. Fundamental mechanisms of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(9):1069–86.
Esteva FJ, Hubbard-Lucey VM, Tang J, Pusztai L. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy combinations in metastatic breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(3):e175–86.
Adams S, Gray RJ, Demaria S, Goldstein L, Perez EA, Shulman LN, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers from two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials: ECOG 2197 and ECOG 1199. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(27):2959–66.
Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen YS, Hao YJ, Sun BF, et al. Nuclear m(6)A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates mRNA Splicing. Mol Cell. 2016;61(4):507–19.
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature. 2014;505(7481):117–20.
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han D, Ma H, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell 2015;161(6):1388–99.
Vu LP, Cheng Y, Kharas MG. The biology of m(6)A RNA methylation in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Cancer Discov. 2019;9(1):25–33.
Li Y, Xiao J, Bai J, Tian Y, Qu Y, Chen X, et al. Molecular characterization and clinical relevance of m(6)A regulators across 33 cancer types. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):137.
Han J, Wang JZ, Yang X, Yu H, Zhou R, Lu HC, et al. METTL3 promote tumor proliferation of bladder cancer by accelerating pri-miR221/222 maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):110.
Wang Q, Chen C, Ding Q, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Chen J, et al. METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification of HDGF mRNA promotes gastric cancer progression and has prognostic significance. Gut. 2020;69:1193–205.
Li Z, Weng H, Su R, Weng X, Zuo Z, Li C, et al. FTO plays an oncogenic role in acute myeloid leukemia as a N(6)-methyladenosine RNA demethylase. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(1):127–41.
Vu LP, Pickering BF, Cheng Y, Zaccara S, Nguyen D, Minuesa G, et al. The N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A)-forming enzyme METTL3 controls myeloid differentiation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia cells. Nat Med. 2017;23(11):1369–76.
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S, Lu Z, et al. m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(4):591–606.
Cui Q, Shi H, Ye P, Li L, Qu Q, Sun G, et al. m(6)A RNA methylation regulates the self-renewal and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Rep. 2017;18(11):2622–34.
Chen Y, Peng C, Chen J, Chen D, Yang B, He B, et al. WTAP facilitates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-HuR-dependent epigenetic silencing of ETS1. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):127.
Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, Tsang FH, Shen J, Cheng CL, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology. 2018;67(6):2254–70.
Cai X, Wang X, Cao C, Gao Y, Zhang S, Yang Z, et al. HBXIP-elevated methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of breast cancer via inhibiting tumor suppressor let-7g. Cancer Lett. 2018;415:11–19.
Shi H, Wei J, He C. Where, when, and how: context-dependent functions of RNA methylation writers, readers, and erasers. Mol cell. 2019;74(4):640–50.
Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen Y-S, Yang Y-G. Dynamic transcriptomic mA decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 2018;28(6):616–24.
Meyer KD, Jaffrey SR. Rethinking mA readers, writers, and erasers. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2017;33:319–42.
Ciriello G, Gatza ML, Beck AH, Wilkerson MD, Rhie SK, Pastore A, et al. Comprehensive molecular portraits of invasive lobular breast cancer. Cell. 2015;163(2):506–19.
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng W, Xu Y, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods. 2015;12(5):453–7.
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang Y, et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7(12):885–7.
Nachtergaele S, He C. Chemical modifications in the life of an mRNA transcript. Annu Rev Genet. 2018;52:349–72.
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149(7):1635–46.
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485(7397):201–6.
Roundtree IA, Evans ME, Pan T, He C. Dynamic RNA modifications in gene expression regulation. Cell. 2017;169(7):1187–200.
Hsu PJ, Shi H, He C. Epitranscriptomic influences on development and disease. Genome Biol. 2017;18(1):197.
Lan Q, Liu PY, Haase J, Bell JL, Huttelmaier S, Liu T. The critical role of RNA m(6)A methylation in cancer. Cancer Res. 2019;79(7):1285–92.
Panneerdoss S, Eedunuri VK, Yadav P, Timilsina S, Rajamanickam S, Viswanadhapalli S, et al. Cross-talk among writers, readers, and erasers of m(6)A regulates cancer growth and progression. Sci Adv. 2018;4:eaar8263. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar8263.
Chai RC, Wu F, Wang QX, Zhang S, Zhang KN, Liu YQ, et al. m(6)A RNA methylation regulators contribute to malignant progression and have clinical prognostic impact in gliomas. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(4):1204–25.
Swift S, Tucker A, Vinciotti V, Martin N, Orengo C, Liu X, et al. Consensus clustering and functional interpretation of gene-expression data. Genome Biol. 2004;5(11):R94.
Monti S, Tamayo P, Mesirov J, Golub T. Consensus clustering—a resampling-based method for class discovery and visualization of gene expression microarray data. Mach Learn. 2003;52(1-2):91–118.
Wang H, Xu B, Shi J. N6-methyladenosine METTL3 promotes the breast cancer progression via targeting Bcl-2. Gene. 2019;722:144076.
Wu L, Wu D, Ning J, Liu W, Zhang D. Changes of N6-methyladenosine modulators promote breast cancer progression. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):326.
Niu Y, Lin Z, Wan A, Chen H, Liang H, Sun L, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes breast tumor progression through inhibiting BNIP3. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):46.
Han D, Liu J, Chen C, Dong L, Liu Y, Chang R, et al. Anti-tumour immunity controlled through mRNA m(6)A methylation and YTHDF1 in dendritic cells. Nature. 2019;566(7743):270–4.
Wang H, Hu X, Huang M, Liu J, Gu Y, Ma L, et al. Mettl3-mediated mRNA m(6)A methylation promotes dendritic cell activation. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1898.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Jean J. Zhao (Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts, USA) for her suggestion in revising the paper, and the contributions from TCGA, TCIA, and CIBERSORT networks.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81201747), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (S2012040006323, 2014A030313023), and the open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China (HN2013-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, X., Tan, L., Ni, J. et al. Expression pattern of m6A regulators is significantly correlated with malignancy and antitumor immune response of breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 28, 188–196 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00208-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00208-1
This article is cited by
-
The role of RNA methylation in tumor immunity and its potential in immunotherapy
Molecular Cancer (2024)
-
Guanylate binding protein 4 shapes an inflamed tumor microenvironment and identifies immuno-hot tumors
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2024)
-
Targeting RNA N6-methyladenosine to synergize with immune checkpoint therapy
Molecular Cancer (2023)
-
m6A regulator-mediated methylation modification patterns and tumor microenvironment immune infiltration with prognostic analysis in esophageal cancer
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Molecular phenotypic linkage between N6-methyladenosine methylation and tumor immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)