Abstract
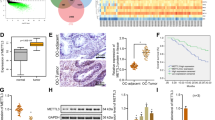
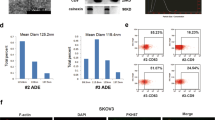
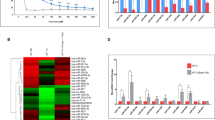
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) functions as an RNA methyltransferase that controls the modification of N(6)-methyladenosine (m6A) to influence the biosynthesis, decay, and translation of mRNAs. This study aims to investigate the regulation of METTL3-mediated promotion of microRNA-126-5p (miR-126-5p) in the progression of ovarian cancer and to identify the mechanisms in relation to phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. We found high expression of miR-126-5p in ovarian cancer samples compared to paired adjacent samples, and also in ovarian cancer cell lines. Gain-of-function experiments demonstrated that overexpression of miR-126-5p promoted ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and inhibited their apoptosis. Luciferase reporter assay identified that miR-126-5p could directly bind to PTEN. By targeting PTEN, miR-126-5p could activate the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Furthermore, the RNA methyltransferase METTL3 promoted the maturation of miR-126-5p via the m6A modification of pri-miR-126-5p. Finally, in vitro and in vivo experiments substantiated that silencing of METTL3 impeded the progression and tumorigenesis of ovarian cancer by impairing the miR-126-5p-targeted inhibition of PTEN and thus blocking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Coherently, knockdown of METTL3 inhibited the effect of miR-126-5p to upregulate PTEN, and thus prevents PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway activation, thereby suppressing the development of ovarian cancer. These findings highlight potential targets for the future ovarian cancer treatment as well as tumorigenic mechanisms mediated by m6A modification.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Furuya M. Ovarian cancer stroma: pathophysiology and the roles in cancer development. Cancers. 2012;4:701–24.
Kaldawy A, Segev Y, Lavie O, Auslender R, Sopik V, Narod SA. Low-grade serous ovarian cancer: a review. Gynecol Oncol. 2016;143:433–8.
Elsherif SB, Faria SC, Lall C, Iyer R, Bhosale PR. Ovarian cancer genetics and implications for imaging and therapy. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2019;43:835–45.
Ferriss JS, Java JJ, Bookman MA, Fleming GF, Monk BJ, Walker JL, et al. Ascites predicts treatment benefit of bevacizumab in front-line therapy of advanced epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube and peritoneal cancers: an NRG Oncology/GOG study. Gynecol Oncol. 2015;139:17–22.
Teplinsky E, Muggia F. Targeting HER2 in ovarian and uterine cancers: challenges and future directions. Gynecol Oncol. 2014;135:364–70.
Ediriweera MK, Tennekoon KH, Samarakoon SR. Role of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in ovarian cancer: biological and therapeutic significance. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;59:147–60.
Rojas V, Hirshfield KM, Ganesan S, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L. Molecular characterization of epithelial ovarian cancer: implications for diagnosis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:2113.
Gross AL, Kurman RJ, Vang R, Shih IeM, Visvanathan K. Precursor lesions of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma: morphological and molecular characteristics. J Oncol. 2010;2010:126295.
Yang F, Jin H, Que B, Chao Y, Zhang H, Ying X, et al. Dynamic m(6)A mRNA methylation reveals the role of METTL3-m(6)A-CDCP1 signaling axis in chemical carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2019;38:4755–72.
Hua W, Zhao Y, Jin X, Yu D, He J, Xie D, et al. METTL3 promotes ovarian carcinoma growth and invasion through the regulation of AXL translation and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Gynecol Oncol. 2018;151:356–65.
Huang B, Ding C, Zou Q, Wang W, Li H. Cyclophosphamide regulates N6-methyladenosine and m6A RNA enzyme levels in human granulosa cells and in ovaries of a premature ovarian aging mouse model. Front Endocrinol. 2019;10:415.
Liang S, Guan H, Lin X, Li N, Geng F, Li J. METTL3 serves an oncogenic role in human ovarian cancer cells partially via the AKT signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2020;19:3197–204.
Wu G, Cao L, Zhu J, Tan Z, Tang M, Li Z, et al. Loss of RBMS3 confers platinum resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer via activation of miR-126-5p/beta-catenin/CBP signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:1022–35.
Han B, Chu C, Su X, Zhang N, Zhou L, Zhang M, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent primary microRNA-126 processing activated PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway drove the development of pulmonary fibrosis induced by nanoscale carbon black particles in rats. Nanotoxicology. 2020;14:1–20.
Zhao W, Han T, Li B, Ma Q, Yang P, Li H. miR-552 promotes ovarian cancer progression by regulating PTEN pathway. J Ovarian Res. 2019;12:121.
Hao B, Zhang J. miRNA-21 inhibition suppresses the human epithelial ovarian cancer by targeting PTEN signal pathway. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2019;26:2026–9.
Li J, Jiang K, Zhao F. Icariin regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of human ovarian cancer cells through microRNA-21 by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2. Oncol Rep. 2015;33:2829–36.
Liu Y, Lin F, Chen Y, Wang R, Liu J, Jin Y, et al. Cryptotanshinone inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. J Cancer. 2020;11:488–99.
Li B, Zhang J, Su Y, Hou Y, Wang Z, Zhao L, et al. Overexpression of PTEN may increase the effect of pemetrexed on A549 cells via inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and carbohydrate metabolism. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20:3793–801.
Bai H, Li H, Li W, Gui T, Yang J, Cao D, et al. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is a potential predictor of distinct invasive and migratory capacities in human ovarian cancer cell lines. Oncotarget. 2015;6:25520–32.
Deng J, Bai X, Feng X, Ni J, Beretov J, Graham P, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway alleviates ovarian cancer chemoresistance through reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and decreasing cancer stem cell marker expression. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:618.
Zhu H, Diao S, Lim V, Hu L, Hu J. FAM83D inhibits autophagy and promotes proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2019;51:509–16.
Li J, Feng L, Tian C, Tang YL, Tang Y, Hu FQ. Long noncoding RNA-JPX predicts the poor prognosis of ovarian cancer patients and promotes tumor cell proliferation, invasion and migration by the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:8135–44.
Li F. Expression and correlation of miR-124 and miR-126 in breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;17:5115–9.
Feng R, Beeharry MK, Lu S, Sah BK, Yuan F, Yan M, et al. Down-regulated serum miR-126 is associated with aggressive progression and poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2018;22:119–26.
Song C, Chen H, Wang T, Zhang W, Ru G, Lang J. Expression profile analysis of microRNAs in prostate cancer by next-generation sequencing. Prostate. 2015;75:500–16.
Lee YR, Chen M, Pandolfi PP. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor: new modes and prospects. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19:547–62.
Tanwar PS, Mohapatra G, Chiang S, Engler DA, Zhang L, Kaneko-Tarui T, et al. Loss of LKB1 and PTEN tumor suppressor genes in the ovarian surface epithelium induces papillary serous ovarian cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:546–53.
Wang J, Xu W, He Y, Xia Q, Liu S. LncRNA MEG3 impacts proliferation, invasion, and migration of ovarian cancer cells through regulating PTEN. Inflamm Res. 2018;67:927–36.
Jiang JH, Lv QY, Yi YX, Liao J, Wang XW, Zhang W. MicroRNA-200a promotes proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:6260–7.
Song MS, Salmena L, Pandolfi PP. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:283–96.
Salmena L, Carracedo A, Pandolfi PP. Tenets of PTEN tumor suppression. Cell. 2008;133:403–14.
Yu X, Chen Y, Tian R, Li J, Li H, Lv T, et al. miRNA-21 enhances chemoresistance to cisplatin in epithelial ovarian cancer by negatively regulating PTEN. Oncol Lett. 2017;14:1807–10.
Gong L, Zhang W, Yuan Y, Xing X, Li H, Zhao G. miR-222 promotes invasion and migration of ovarian carcinoma by targeting PTEN. Oncol Lett. 2018;16:984–90.
Zhu X, Shen H, Yin X, Yang M, Wei H, Chen Q, et al. Macrophages derived exosomes deliver miR-223 to epithelial ovarian cancer cells to elicit a chemoresistant phenotype. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:81.
He L, Zhu W, Chen Q, Yuan Y, Wang Y, Wang J, et al. Ovarian cancer cell-secreted exosomal miR-205 promotes metastasis by inducing angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2019;9:8206–20.
Tu J, Cheung HH, Lu G, Chen Z, Chan WY. MicroRNA-10a promotes granulosa cells tumor development via PTEN-AKT/Wnt regulatory axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:1076.
Aoki M, Fujishita T. Oncogenic roles of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Axis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;407:153–89.
Ben-Sahra I, Manning BD. mTORC1 signaling and the metabolic control of cell growth. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017;45:72–82.
Sun R, Cheng E, Velasquez C, Chang Y, Moore PS. Mitosis-related phosphorylation of the eukaryotic translation suppressor 4E-BP1 and its interaction with eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E). J Biol Chem. 2019;294:11840–52.
Siddiqui N, Sonenberg N. Signalling to eIF4E in cancer. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015;43:763–72.
Asadollahi R, Hyde CA, Zhong XY. Epigenetics of ovarian cancer: from the lab to the clinic. Gynecol Oncol. 2010;118:81–7.
Kelly AD, Issa JJ. The promise of epigenetic therapy: reprogramming the cancer epigenome. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017;42:68–77.
Ma S, Chen C, Ji X, Liu J, Zhou Q, Wang G, et al. The interplay between m6A RNA methylation and noncoding RNA in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:121.
Wang Y, Li Y, Toth JI, Petroski MD, Zhang Z, Zhao JC. N6-methyladenosine modification destabilizes developmental regulators in embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:191–8.
Luo GZ, MacQueen A, Zheng G, Duan H, Dore LC, Lu Z, et al. Unique features of the m6A methylome in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5630.
Yadav PK, Rajasekharan R. The m(6)A methyltransferase Ime4 and mitochondrial functions in yeast. Curr Genet. 2018;64:353–7.
Han J, Wang JZ, Yang X, Yu H, Zhou R, Lu HC, et al. METTL3 promote tumor proliferation of bladder cancer by accelerating pri-miR221/222 maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:110.
Alarcon CR, Lee H, Goodarzi H, Halberg N, Tavazoie SF. N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature. 2015;519:482–5.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge and appreciate our colleagues for their valuable efforts and comments on this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, X., Lv, X., Liu, D. et al. METTL3-mediated maturation of miR-126-5p promotes ovarian cancer progression via PTEN-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cancer Gene Ther 28, 335–349 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00222-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00222-3
This article is cited by
-
miR-126: a bridge between cancer and exercise
Cancer Cell International (2025)
-
Epigenetic regulation in female reproduction: the impact of m6A on maternal-fetal health
Cell Death Discovery (2025)
-
Mechanisms of apoptosis-related non-coding RNAs in ovarian cancer: a narrative review
Apoptosis (2025)
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation of LncRNA LINC01214 accelerates the progression of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by targeting miR-195-5p/ROCK1 axis
Cytotechnology (2025)
-
LncRNA MKLN1-AS promotes glioma tumorigenesis and growth via activating the Hippo pathway through miR-126-5p/TEAD1 axis
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2025)