Abstract
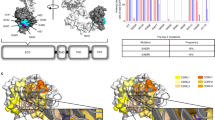
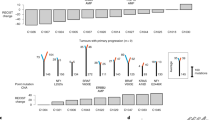
Cetuximab induces responses in about 13% of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC). We describe the molecular mechanism of acquired resistance to cetuximab, which could be overcome by switching to a different anti-EGFR antibody. Biopsies were collected at three different time points: before the start of cetuximab (PRE-cetux), at acquired resistance to cetuximab (AR-cetux), and at acquired resistance to duligotuzumab (AR-duligo). Biopsies were analyzed using tumor and normal whole-exome sequencing, RNASeq, and targeted panel sequencing with ultra-deep coverage to generate differential mutation and expression profiles. WES and targeted sequencing analysis identified an EGFR p.G465R extracellular domain mutation in AR-cetux biopsy. Furthermore, RNASeq confirmed the expression of this mutation in the tumor tissue. This mutation prevented the binding of cetuximab to EGFR and was not present in PRE-cetux and AR-duligo biopsies, suggesting a potential mechanism of acquired resistance to cetuximab. Molecular dynamic simulations confirmed that duligotuzumab effectively binds EGFR with a p.G465R mutation. Interestingly, the p.G465R mutation improved the stability of the duligotuzumab-EGFR complex as compared to the wild-type EGFR. This is the first report of an EGFR ECD mutation associated with acquired resistance to cetuximab, posing a need for further validation. We suggest appropriate serial mutational profiling to identify ECD mutations should be considered for select patients with initial cetuximab benefit.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Code availability
The codes used in different analyses in this study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived With disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:524.
Johnson DE, Burtness B, Leemans CR, Lui VWY, Bauman JE, Grandis JR. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2020;6:92.
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:127–37.
Grandis JR, Tweardy DJ. Elevated levels of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA are early markers of carcinogenesis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3579–84.
Ongkeko WM, Altuna X, Weisman RA, Wang-Rodriguez J. Expression of protein tyrosine kinases in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005;124:71–6.
Keck MK, Zuo Z, Khattri A, Stricker TP, Brown CD, Imanguli M, et al. Integrative analysis of head and neck cancer identifies two biologically distinct HPV and three non-HPV subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:870–81.
Vokes EE, Seiwert TY. EGFR-directed treatments in SCCHN. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:672–3.
Cassell A, Grandis JR. Investigational EGFR-targeted therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010;19:709–22.
Peeters M, Price T, Van Laethem JL. Anti–epidermal growth factor receptor monotherapy in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: where are we today? Oncologist. 2009;14:29–39.
Vermorken JB, Trigo J, Hitt R, Koralewski P, Diaz-Rubio E, Rolland F, et al. Open-label, uncontrolled, multicenter phase II study to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of cetuximab as a single agent in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck who failed to respond to platinum-based therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2171–7.
Seiwert TY, Zuo Z, Keck MK, Khattri A, Pedamallu CS, Stricker T, et al. Integrative and comparative genomic analysis of HPV-positive and HPV-negative head and neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:632–41.
Fayette J, Wirth L, Oprean C, Udrea A, Jimeno A, Rischin D, et al. Randomized Phase II Study of Duligotuzumab (MEHD7945A) vs. Cetuximab in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (MEHGAN Study). Front Oncol. 2016;6:232.
Mekata E, Endo Y, Sonoda H, Shimizu T, Kawai Y, Umeda T, et al. Cetuximab as salvage monotherapy in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: a single-center report. Oncol Lett. 2013;6:1011–4.
Zhang S, Zheng M, Nie D, Xu L, Tian H, Wang M, et al. Efficacy of cetuximab plus PD-1 inhibitor differs by HPV status in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Immunother Cancer. 2022;10:e005158.
Jelinek MJ, Vokes EE. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Blockade in Head and Neck Cancer: What Remains? [Internet]. 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.01981.
Endhardt KU, Khattri A, Keck M, Braegelmann J, Mahmutoglu D, Leung K, et al. Abstract 5472: Role of Harvey Ras (HRAS) mutations in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Cancer Res. 2012;72:5472–5472.
Misale S, Yaeger R, Hobor S, Scala E, Janakiraman M, Liska D, et al. Emergence of KRAS mutations and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Nature. 2012;486:532–6.
Diaz Jr, Williams LA, Wu RT, Kinde J, Hecht JR I, Berlin J, et al. The molecular evolution of acquired resistance to targeted EGFR blockade in colorectal cancers. Nature. 2012;486:537–40.
Misale S, Arena S, Lamba S, Siravegna G, Lallo A, Hobor S, et al. Blockade of EGFR and MEK intercepts heterogeneous mechanisms of acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in colorectal cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:224ra26.
Yonesaka K, Zejnullahu K, Okamoto I, Satoh T, Cappuzzo F, Souglakos J, et al. Activation of ERBB2 signaling causes resistance to the EGFR-directed therapeutic antibody cetuximab. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:99ra86.
Bardelli A, Corso S, Bertotti A, Hobor S, Valtorta E, Siravegna G, et al. Amplification of the MET Receptor Drives Resistance to Anti-EGFR therapies in colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:658–73.
Rabinowits G, Haddad RI. Overcoming resistance to EGFR inhibitor in head and neck cancer: A review of the literature. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:1085–9.
Xia W, Lau YK, Zhang HZ, Xiao FY, Johnston DA, Liu AR, et al. Combination of EGFR, HER-2/neu, and HER-3 is a stronger predictor for the outcome of oral squamous cell carcinoma than any individual family members. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:4164–74.
Bertotti A, Papp E, Jones S, Adleff V, Anagnostou V, Lupo B, et al. The genomic landscape of response to EGFR blockade in colorectal cancer. Nature. 2015;526:263–7.
Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature. 2015;517:576–82.
Alsahafi E, Begg K, Amelio I, Raulf N, Lucarelli P, Sauter T, et al. Clinical update on head and neck cancer: molecular biology and ongoing challenges. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:540.
Edge SB. American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC cancer staging manual. 650 p.
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009;10:R25.
Chen S, Huang T, Zhou Y, Han Y, Xu M, Gu J. AfterQC: automatic filtering, trimming, error removing and quality control for fastq data. BMC Bioinforma. 2017;18:80.
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, et al. The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010;20:1297–303.
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e164–e164.
Kim D, Pertea G, Trapnell C, Pimentel H, Kelley R, Salzberg SL. TopHat2: accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013;14:R36.
Schaefer G, Haber L, Crocker LM, Shia S, Shao L, Dowbenko D, et al. A two-in-one antibody against HER3 and EGFR has superior inhibitory activity compared with monospecific antibodies. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:472–86.
DeLano WL. PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. 2010.
Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B, et al. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX. 2015;1–2:19–25.
Schmid N, Eichenberger AP, Choutko A, Riniker S, Winger M, Mark AE, et al. Definition and testing of the GROMOS force-field versions 54A7 and 54B7. Eur Biophys J. 2011;40:843–56.
Mark P, Nilsson L. Structure and dynamics of the TIP3P, SPC, and SPC/E water models at 298 K. J Phys Chem A. 2001;105:9954–60.
Bixon M, Lifson S. Potential functions and conformations in cycloalkanes. Tetrahedron. 1967;23:769–84.
Bussi G, Donadio D, Parrinello M. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J Chem Phys. 2007;126:014101.
Parrinello M, Rahman A. Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: a new molecular dynamics method. J Appl Phys. 1981;52:7182–90.
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N ⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys. 1993;98:10089–92.
Cuendet MA, van Gunsteren WF. On the calculation of velocity-dependent properties in molecular dynamics simulations using the leapfrog integration algorithm. J Chem Phys. 2007;127:184102.
Kumari R, Kumar R, Lynn A. g_mmpbsa —A GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations. J Chem Inf Model. 2014;54:1951–62.
Arena S, Bellosillo B, Siravegna G, Martínez A, Cañadas I, Lazzari L, et al. Emergence of multiple EGFR extracellular mutations during cetuximab treatment in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:2157–66.
Montagut C, Dalmases A, Bellosillo B, Crespo M, Pairet S, Iglesias M, et al. Identification of a mutation in the extracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor conferring cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer. Nat Med. 2012;18:221–3.
Hah JH, Zhao M, Pickering CR, Frederick MJ, Andrews GA, Jasser SA, et al. HRAS mutations and resistance to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Head Neck. 2014;36:1547–54.
Khattri A, Zuo Z, Brägelmann J, Keck MK, El Dinali M, Brown CD, et al. Rare occurrence of EGFRvIII deletion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:53–8.
Malone ER, Oliva M, Sabatini PJB, Stockley TL, Siu LL. Molecular profiling for precision cancer therapies. Genome Med. 2020;12:8.
Sánchez-Martín FJ, Bellosillo B, Gelabert-Baldrich M, Dalmases A, Cañadas I, Vidal J, et al. The First-in-class Anti-EGFR antibody mixture Sym004 overcomes cetuximab resistance mediated by EGFR extracellular domain mutations in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:3260–7.
Arena S, Siravegna G, Mussolin B, Kearns JD, Wolf BB, & Misale S, et al. MM-151 overcomes acquired resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal cancers harboring EGFR extracellular domain mutations. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8.
Iida M, Brand TM, Starr MM, Li C, Huppert EJ, Luthar N, et al. Sym004, a novel EGFR antibody mixture, can overcome acquired resistance to cetuximab. Neoplasia. 2013;15:1196–206.
Montagut C, Argilés G, Ciardiello F, Poulsen TT, Dienstmann R, Kragh M, et al. Efficacy of Sym004 in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapy and molecularly selected by circulating tumor DNA analyses. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:e175245.
Li Q, Dong H, Yang G, Song Y, Mou Y, Ni Y. Mouse tumor-bearing models as preclinical study platforms for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2020;10:212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK: Conceptualization, literature survey, data collection, study design, interpretation of data, writing—review and editing. SN: Next-generation sequencing data analysis, writing, and editing. NA: Molecular Dynamics simulations and writing. S Kaushik: Molecular Dynamics simulations, and writing. S Kochanny: Clinical data collection, review, writing, and editing. DG: Clinical data collection, review, and editing. MWG: Review of patient biopsies, review, and editing. EB: Review and editing. TYS: Conceptualization, study design, interpretation of data, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Arun Khattri received the financial support from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, in the form of Ramalingaswami Fellowship. The funding agency played no role in the study design, analysis, and interpretation of the results. Tanguy Y. Seiwert reports institutional research funding from Regeneron, Merck/MSD, BMS, Genentech, Cue Biopharma, Nanobiotix, Seattle Genetics, Exelixis, Astra Zeneca, IOBiotech, and Kura Oncology; and advisory board and consulting fees from Regeneron, Merck/MSD, Arcus, Astra Zeneca, Regeneron, IOBiotech, Seattle Genetics, Surface Oncology, Sanofi, iTeos, Innate Pharma, EMD Serono, Exelixis, Vir Therapeutics, and Eisei. He is on the DSMB for BioNTech, and the steering committee for IOBiotech.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khattri, A., Sheikh, N., Agrawal, N. et al. Switching anti-EGFR antibody re-sensitizes head and neck cancer patient following acquired resistance to cetuximab. Cancer Gene Ther 31, 1477–1485 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-024-00812-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-024-00812-5
This article is cited by
-
Multiple drugs
Reactions Weekly (2024)