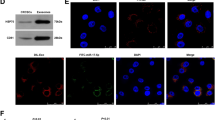
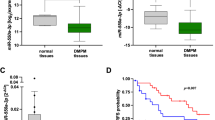
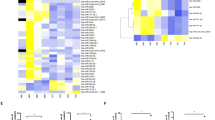
Abstract
Exosomes mediate cell-to-cell communication by releasing miRNAs, mRNA, etc. However, there is little research about the effects on the donor cells after miRNAs are excreted out of cells through exosomes. Here, we found that miR-378a-3p was specifically enriched in exosomes and inhibited cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and colony formation in ESCC. In addition, miR-378a-3p was sorted into exosomes through TOM1L1 and extracted mainly out of ESCC cells. Overexpression of TOM1L1 led to tumor suppressor miR-378a-3p accumulation in exosomes rather than in donor cells, promoting ESCC progression. Moreover, miR-378a-3p targets DYRK1A that directly binds to NPM1 and the phosphorylation state of NPM1 at Ser125 to suppress tumor growth. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that TOM1L1-mediated the tumor suppressor miR-378a-3p into exosomes and excreted out of cells to promote tumor progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
Lin Y, Totsuka Y, He Y, Kikuchi S, Qiao Y, Ueda J, et al. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer in Japan and China. J Epidemiol. 2013;23:233–42.
Wang T, Liu NS, Seet LF, Hong W. The emerging role of VHS domain-containing Tom1, Tom1L1 and Tom1L2 in membrane trafficking. Traffic. 2010;11:1119–28.
Zhang L, Zhou Y, Cheng C, Cui H, Cheng L, Kong P, et al. Genomic analyses reveal mutational signatures and frequently altered genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;96:597–611.
Tran GD, Sun XD, Abnet CC, Fan JH, Dawsey SM, Dong ZW, et al. Prospective study of risk factors for esophageal and gastric cancers in the Linxian general population trial cohort in China. Int J Cancer. 2005;113:456–63.
Kalra H, Drummen GP, Mathivanan S. Focus on extracellular vesicles: introducing the next small big thing. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:170.
Qazi REM, Sajid Z, Zhao C, Hussain I, Iftikhar F, Jameel M, et al. Lyophilization based isolation of exosomes. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:10477.
Gross JC, Chaudhary V, Bartscherer K, Boutros M. Active Wnt proteins are secreted on exosomes. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14:1036–45.
Chagraoui J, Girard S, Spinella JF, Simon L, Bonneil E, Mayotte N, et al. UM171 preserves epigenetic marks that are reduced in ex vivo culture of human HSCs via potentiation of the CLR3-KBTBD4 complex. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28:48–62.e6.
Wang L, Liu H, Wu Q, Liu Y, Yan Z, Chen G, et al. miR-451a was selectively sorted into exosomes and promoted the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through CAB39. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024;31:1060–9.
Guduric-Fuchs J, O’Connor A, Camp B, O’Neill CL, Medina RJ, Simpson DA. Selective extracellular vesicle-mediated export of an overlapping set of microRNAs from multiple cell types. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:357.
Yu X, Odenthal M, Fries JW. Exosomes as miRNA carriers: formation-function-future. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:2028.
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand M, Lee JJ, Lötvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:654–9.
Hinds PW, Weinberg RA. Tumor suppressor genes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994;4:135–41.
Yao Y, Bellon M, Shelton SN, Nicot C. Tumor suppressors p53, p63taα, p63tay, p73α, and p73β use distinct pathways to repress telomerase expression. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:20737–47.
Hoppe-Seyler K, Bossler F, Braun JA, Herrmann AL, Hoppe-Seyler F. The HPV E6/E7 oncogenes: key factors for viral carcinogenesis and therapeutic targets. Trends Microbiol. 2018;26:158–68.
Chang Y, Jin H, Cui Y, Yang F, Chen K, Kuang W, et al. PUS7-dependent pseudouridylation of ALKBH3 mRNA inhibits gastric cancer progression. Clin Transl Med. 2024;14:e1811.
Kim JW, Moon SW, Mo HY, Son HJ, Choi EJ, Yoo NJ, et al. Concurrent inactivating mutations and expression losses of RGS2, HNF1a, and CAPN12 candidate tumor suppressor genes in colon cancers. Pathol Res Pract. 2023;241:154288.
Cojocaru E, Lozneanu L, Giuşcă SE, Căruntu ID, Danciu M. Renal carcinogenesis—insights into signaling pathways. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2015;56:15–9.
Kobayashi H. [The cell cycle and the tumor suppressor genes]. Rinsho Byori. 1996;44:3–11.
Llinàs-Arias P, Esteller M. Epigenetic inactivation of tumour suppressor coding and non-coding genes in human cancer: an update. Open Biol. 2017;7:170152.
Li M, Xu H, Qi Y, Pan Z, Li B, Gao Z, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes deliver the tumor suppressor miR-3591-3p to induce M2 macrophage polarization and promote glioma progression. Oncogene. 2022;41:4618–32.
Au Yeung CL, Co NN, Tsuruga T, Yeung TL, Kwan SY, Leung CS, et al. Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11150.
Ponath V, Hoffmann N, Bergmann L, Mäder C, Alashkar Alhamwe B, Preußer C, et al. Secreted ligands of the NK cell receptor NKp30: B7-H6 is in contrast to BAG6 only marginally released via extracellular vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:2189.
Audic S, Claverie JM. The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res. 1997;7:986–95.
Briand J, Garnier D, Nadaradjane A, Clément-Colmou K, Potiron V, Supiot S, et al. Radiotherapy-induced overexpression of exosomal miRNA-378a-3p in cancer cells limits natural killer cells cytotoxicity. Epigenomics. 2020;12:397–408.
Yang Q, Zhao S, Shi Z, Cao L, Liu J, Pan T, et al. Chemotherapy-elicited exosomal miR-378a-3p and miR-378d promote breast cancer stemness and chemoresistance via the activation of EZH2/STAT3 signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40:120.
Liu Z, Zhao Y, Kong P, Liu Y, Huang J, Xu E, et al. Integrated multi-omics profiling yields a clinically relevant molecular classification for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2023;41:181–195.e9.
Qin Y, Liang R, Lu P, Lai L, Zhu X. Depicting the implication of miR-378a in cancers. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022;21:15330338221134385.
Hu M, Yang J, Xu Y, Liu J. MDH1 and MDH2 promote cell viability of primary AT2 cells by increasing glucose uptake. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022;2022:2023500.
Zhang Z, Miao L, Xin X, Zhang J, Yang S, Miao M, et al. Underexpressed CNDP2 participates in gastric cancer growth inhibition through activating the MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Med. 2014;20:17–28.
Liu H, Ma Y, He HW, Wang JP, Jiang JD, Shao RG. SLC9A3R1 stimulates autophagy via BECN1 stabilization in breast cancer cells. Autophagy. 2015;11:2323–34.
Yuan Q, Yin L, He J, Zeng Q, Liang Y, Shen Y, et al. Metabolism of asparagine in the physiological state and cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 2024;22:163.
Yin X, He Z, Chen K, Ouyang K, Yang C, Li J, et al. Unveiling the impact of CDK8 on tumor progression: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1386929.
Jabbour E, Cortes J, O’Brien S, Giles F, Kantarjian H. New targeted therapies for chronic myelogenous leukemia: opportunities to overcome imatinib resistance. Semin Hematol. 2007;44:S25–31.
Chevalier C, Roche S, Bénistant C. Vesicular trafficking regulators are new players in breast cancer progression: role of TOM1L1 in ERBB2-dependent invasion. Mol Cell Oncol. 2016;3:e1182241.
Chevalier C, Collin G, Descamps S, Touaitahuata H, Simon V, Reymond N, et al. TOM1L1 drives membrane delivery of MT1-MMP to promote ERBB2-induced breast cancer cell invasion. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10765.
Yanagida-Ishizaki Y, Takei T, Ishizaki R, Imakagura H, Takahashi S, Shin HW, et al. Recruitment of Tom1L1/Srcasm to endosomes and the midbody by Tsg101. Cell Struct Funct. 2008;33:91–100.
Jia S, Meng A. Tob genes in development and homeostasis. Dev Dyn. 2007;236:913–21.
Hutagalung AH, Novick PJ. Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology. Physiol Rev. 2011;91:119–49.
Wang QC, Zheng Q, Tan H, Zhang B, Li X, Yang Y, et al. TMCO1 is an ER Ca2+ load-activated Ca2+ channel. Cell. 2016;165:1454–66.
Sun J, Sheng W, Ma Y, Dong M. Potential role of Musashi-2 RNA-binding protein in cancer EMT. Oncotargets Ther. 2021;14:1969–80.
Rudack T, Jenrich S, Brucker S, Vetter IR, Gerwert K, Kötting C. Catalysis of GTP hydrolysis by small GTPases at atomic detail by integration of x-ray crystallography, experimental, and theoretical IR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:24079–90.
Deboever E, Fistrovich A, Hulme C, Dunckley T. The omnipresence of DYRK1A in human diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:9355.
Sebastiani G, Almeida-Toledano L, Serra-Delgado M, Navarro-Tapia E, Sailer S, Valverde O, et al. Therapeutic effects of catechins in less common neurological and neurodegenerative disorders. Nutrients. 2021;13:2232.
Giraud F, Pereira E, Anizon F, Moreau P. Recent advances in pain management: relevant protein kinases and their inhibitors. Molecules. 2021;26:2696.
Guo X, Zhang D, Zhang X, Jiang J, Xue P, Wu C, et al. Dyrk1A promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via down-regulating Spry2 and activating the ERK MAPK pathway. Tissue Cell. 2018;55:63–70.
Ionescu A, Dufrasne F, Gelbcke M, Jabin I, Kiss R, Lamoral-Theys D. DYRK1A kinase inhibitors with emphasis on cancer. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2012;12:1315–29.
Yang Y, Fan X, Liu Y, Ye D, Liu C, Yang H, et al. Function and inhibition of DYRK1A: emerging roles of treating multiple human diseases. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;212:115521.
Becker W, Joost HG. Structural and functional characteristics of Dyrk, a novel subfamily of protein kinases with dual specificity. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1999;62:1–17.
Soundararajan M, Roos AK, Savitsky P, Filippakopoulos P, Kettenbach AN, Olsen JV, et al. Structures of Down syndrome kinases, DYRKs, reveal mechanisms of kinase activation and substrate recognition. Structure. 2013;21:986–96.
Murano K, Okuwaki M, Hisaoka M, Nagata K. Transcription regulation of the rRNA gene by a multifunctional nucleolar protein, B23/nucleophosmin, through its histone chaperone activity. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:3114–26.
Okuwaki M. The structure and functions of NPM1/Nucleophsmin/B23, a multifunctional nucleolar acidic protein. J Biochem. 2008;143:441–8.
Lim MJ, Wang XW. Nucleophosmin and human cancer. Cancer Detect Prev. 2006;30:481–90.
Enomoto T, Lindström MS, Jin A, Ke H, Zhang Y. Essential role of the B23/NPM core domain in regulating ARF binding and B23 stability. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:18463–72.
Mashouri L, Yousefi H, Aref AR, Ahadi AM, Molaei F, Alahari SK. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:75.
de Visser KE, Joyce JA. The evolving tumor microenvironment: from cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Cancer Cell. 2023;41:374–403.
Wang L, Liu H, Liu Y, Guo S, Yan Z, Chen G, et al. Potential markers of cancer stem-like cells in ESCC: a review of the current knowledge. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1324819.
Mei J, Bachoo R, Zhang CL. MicroRNA-146a inhibits glioma development by targeting Notch1. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31:3584–92.
Li Y, Vandenboom TG 2nd, Wang Z, Kong D, Ali S, Philip PA, et al. miR-146a suppresses invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1486–95.
Katakowski M, Buller B, Zheng X, Lu Y, Rogers T, Osobamiro O, et al. Exosomes from marrow stromal cells expressing miR-146b inhibit glioma growth. Cancer Lett. 2013;335:201–4.
Qiu S, Xie L, Lu C, Gu C, Xia Y, Lv J, et al. Gastric cancer-derived exosomal miR-519a-3p promotes liver metastasis by inducing intrahepatic M2-like macrophage-mediated angiogenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41:296.
Jiao Y, Zhang T, Zhang C, Ji H, Tong X, Xia R, et al. Exosomal miR-30d-5p of neutrophils induces M1 macrophage polarization and primes macrophage pyroptosis in sepsis-related acute lung injury. Crit Care. 2021;25:356.
Chendrimada TP, Gregory RI, Kumaraswamy E, Norman J, Cooch N, Nishikura K, et al. TRBP recruits the Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing. Nature. 2005;436:740–4.
Villarroya-Beltri C, Gutiérrez-Vázquez C, Sánchez-Cabo F, Pérez-Hernández D, Vázquez J, Martin-Cofreces N, et al. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2980.
Teng Y, Ren Y, Hu X, Mu J, Samykutty A, Zhuang X, et al. MVP-mediated exosomal sorting of miR-193a promotes colon cancer progression. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14448.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Shanxi Medical University Key Laboratory of the Ministry of Education for providing us with the Cell physiology equipment platform.
Funding
This work was supported by the Shanxi Province Higher Education “Billion Project” Science and Technology Guidance Project(BYJL027); the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (20210302123292); the Central Guidance on Local Science and Technology Development Fund of Shanxi Province (YDZJSX2021A018); the Shenzhen Project of Science and Technology (JCYJ20190813094203600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaolong Cheng and Ting Yan: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration; Lu Wang: Data curation, Validation, Writing—original draft; Huijuan Liu, Guohui Chen and Qinglu Wu: Supervision, Visualization, revised and edited the manuscript; Songrui Xu, Qichao Zhou, Yadong Zhao, and Qiaorong Wang: Formal analysis, Investigation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Liu, H., Chen, G. et al. TOM1L1 mediated the sort of tumor suppressive miR-378a-3p into exosomes and the excretion out of cells to promote ESCC progression. Cancer Gene Ther 32, 507–520 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-025-00889-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-025-00889-6