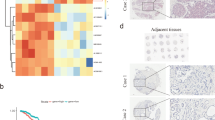
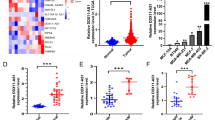
Abstract
Breast cancer (BC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality, largely due to its aggressive proliferation and metastatic potential. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as key regulators in tumor development and progression. This study explored the functional role and mechanism of Lnc-PRSS23-AS1 in BC. We assessed Lnc-PRSS23-AS1 expression and localization using fluorescence in situ hybridization, qRT-PCR, and Western blotting in BC tissues and cell lines. Binding interactions between Lnc-PRSS23-AS1, miR-3176, and Y-box binding protein 1 (YBX1) were validated through dual-luciferase reporter assays, RNA pulldown, and RNA immunoprecipitation. Lnc-PRSS23-AS1 was significantly upregulated in BC and predominantly localized in the cytoplasm. Silencing Lnc-PRSS23-AS1 or overexpressing miR-3176 suppressed BC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and in vivo. Conversely, miR-3176 inhibition or YBX1 overexpression reversed these effects. Mechanistically, Lnc-PRSS23-AS1 promoted YBX1 protein expression by acting as a molecular sponge for miR-3176. These findings highlight the Lnc-PRSS23-AS1/miR-3176/YBX1 axis as a driver of BC progression and suggest Lnc-PRSS23-AS1 as a potential therapeutic target for breast cancer treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harbeck N, Gnant M. Breast cancer. Lancet. 2017;389:1134–1150.
Xu H, Xu B. Breast cancer: epidemiology, risk factors and screening. Chin J Cancer Res. 2023;35:565–583.
Burstein HJ, Curigliano G, Thürlimann B, Weber WP, Poortmans P, Regan MM, et al. Customizing local and systemic therapies for women with early breast cancer: the St. Gallen International Consensus Guidelines for treatment of early breast cancer 2021. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:1216–1235.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48.
Bi Z, Wang Y. Advances in regional nodal management of early-stage breast cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 2024;36:215–225.
Castaneda M, den Hollander P, Kuburich NA, Rosen JM, Mani SA. Mechanisms of cancer metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;87:17–31.
Fonseca VC, Sidiropoulou Z. Geriatric breast cancer: staging, molecular surrogates, and treatment. a review & meta-analysis. Aging Dis. 2024;15:1602–1618.
Schmitt AM, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:452–463.
Liu SJ, Dang HX, Lim DA, Feng FY, Maher CA. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21:446–460.
Tang Y, Cheung BB, Atmadibrata B, Marshall GM, Dinger ME, Liu PY, et al. The regulatory role of long noncoding RNAs in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;391:12–19.
Winkle M, El-Daly SM, Fabbri M, Calin GA. Noncoding RNA therapeutics - challenges and potential solutions. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20:629–651.
Wei L, Sun J, Zhang N, Zheng Y, Wang X, Lv L, et al. Noncoding RNAs in gastric cancer: implications for drug resistance. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:62.
Wei L, Wang X, Lv L, Liu J, Xing H, Song Y, et al. The emerging role of microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:147.
Zhang Y, Dong X, Guo X, Li C, Fan Y, Liu P, et al. LncRNA-BC069792 suppresses tumor progression by targeting KCNQ4 in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2023;22:41.
Jiang T, Zhu J, Jiang S, Chen Z, Xu P, Gong R, et al. Targeting lncRNA DDIT4-AS1 sensitizes triple negative breast cancer to chemotherapy via suppressing of autophagy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10:e2207257.
Meng Z, Zhang R, Wu X, Piao Z, Zhang M, Jin T. LncRNA HAGLROS promotes breast cancer evolution through miR-135b-3p/COL10A1 axis and exosome-mediated macrophage M2 polarization. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15:633.
Lin X, Zhuang S, Chen X, Du J, Zhong L, Ding J, et al. lncRNA ITGB8-AS1 functions as a ceRNA to promote colorectal cancer growth and migration through integrin-mediated focal adhesion signaling. Mol Ther. 2022;30:688–702.
Zhang Y, Luo M, Cui X, O’Connell D, Yang Y. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes ferroptosis by modulating the miR-362-3p/MIOX axis as a ceRNA. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29:1850–1863.
Xue ST, Zheng B, Cao SQ, Ding JC, Hu GS, Liu W, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00680 functions as a ceRNA to promote esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the miR-423-5p/PAK6 axis. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:69.
Wang X, Li X, Lin F, Sun H, Lin Y, Wang Z, et al. The lnc-CTSLP8 upregulates CTSL1 as a competitive endogenous RNA and promotes ovarian cancer metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40:151.
Zhang X, Bian H, Wei W, Wang Q, Chen J, Hei R, et al. DLX5 promotes osteosarcoma progression via activation of the NOTCH signaling pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 2021;11:3354–74.
Zhang T, Deng L, Ji Y, Cheng G, Su D, Qiu B. Novel long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) panel as biomarkers for prognosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma via competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network analysis. Transl Cancer Res. 2021;10:393–405.
Lyabin DN, Eliseeva IA, Ovchinnikov LP. YB-1 protein: functions and regulation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014;5:95–110.
Zhang H, Yu H, Ren D, Sun Y, Guo F, Cai H, et al. CBX3 regulated By YBX1 promotes smoking-induced pancreatic cancer progression via inhibiting SMURF2 expression. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18:3484–3497.
Evdokimova V, Tognon C, Ng T, Ruzanov P, Melnyk N, Fink D, et al. Translational activation of snail1 and other developmentally regulated transcription factors by YB-1 promotes an epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:402–415.
Jayavelu AK, Schnöder TM, Perner F, Herzog C, Meiler A, Krishnamoorthy G, et al. Splicing factor YBX1 mediates persistence of JAK2-mutated neoplasms. Nature. 2020;588:157–163.
Zhang Y, Huang YX, Wang DL, Yang B, Yan HY, Lin LH, et al. LncRNA DSCAM-AS1 interacts with YBX1 to promote cancer progression by forming a positive feedback loop that activates FOXA1 transcription network. Theranostics. 2020;10:10823–10837.
Kong X, Li J, Li Y, Duan W, Qi Q, Wang T, et al. A novel long non-coding RNA AC073352.1 promotes metastasis and angiogenesis via interacting with YBX1 in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:670.
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U, Sahu A, Hosono Y, et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat Genet. 2015;47:199–208.
Bai Y, Gotz C, Chincarini G, Zhao Z, Slaney C, Boath J, et al. YBX1 integration of oncogenic PI3K/mTOR signalling regulates the fitness of malignant epithelial cells. Nat Commun. 2023;14:1591.
Huarte M. The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nat Med. 2015;21:1253–61.
Huang Z, Zhou JK, Peng Y, He W, Huang C. The role of long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:77.
Karreth FA, Pandolfi PP. ceRNA cross-talk in cancer: when ce-bling rivalries go awry. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:1113–21.
Lin J, Liao S, Liu Z, Li E, Wu X, Zeng W. LncRNA FGD5-AS1 accelerates cell proliferation in pancreatic cancer by regulating miR-520a-3p/KIAA1522 axis. Cancer Biol Ther. 2021;22:257–266.
Pan X, Chen S, Ye L, Xu S, Wang L, Sun Y. Long non-coding RNA DLGAP1-AS1 modulates the development of non-small-cell lung cancer via the microRNA-193a-5p/DTL axis. Lab Invest. 2022;102:1182–1191.
Berger AC, Korkut A, Kanchi RS, Hegde AM, Lenoir W, Liu W, et al. A comprehensive pan-cancer molecular study of gynecologic and breast cancers. Cancer Cell. 2018;33:690–705.
Ma W, Zhao F, Yu X, Guan S, Suo H, Tao Z, et al. Immune-related lncRNAs as predictors of survival in breast cancer: a prognostic signature. J Transl Med. 2020;18:442.
Chen LL. Linking long noncoding RNA localization and function. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016;41:761–72.
Statello L, Guo CJ, Chen LL, Huarte M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:96–118.
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature. 2014;505:344–352.
Wu H, Liu B, Chen Z, Li G, Zhang Z. MSC-induced lncRNA HCP5 drove fatty acid oxidation through miR-3619-5p/AMPK/PGC1α/CEBPB axis to promote stemness and chemo-resistance of gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:233.
Liu S, Chen W, Hu H, Zhang T, Wu T, Li X, et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes breast cancer proliferation and metastasis by binding miR-128-3p and UPF1. Breast Cancer Res. 2021;23:115.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all laboratory members for their discussion of this manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HY and FM conducted the molecular biology analyses, participated in designing the study and collecting clinical specimens, and drafted the manuscript. WM, JY, and WM collected clinical specimens, participated in data analysis, and performed statistical analyses. CZ and WM conceived and designed the study, participated in data analysis and coordination, and assisted in drafting the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study received approval from the Sixth Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital (Beijing, China) and adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki. All procedures involving animal care and use were approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of the Beijing Geneline Bioscience Biotechnology Company and followed the National Policy on the Use of Laboratory Animals.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to this publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Feng, M., Jiang, Y. et al. Long non-coding RNA PRSS23-AS1 as ceRNA promotes breast cancer progression by regulating EMT via miR-3176 /YBX1 axis. Cancer Gene Ther 32, 1018–1029 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-025-00943-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-025-00943-3