Abstract
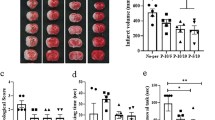
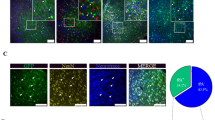
Nuclear translocation of annexin A1 (ANXA1) has recently been reported to participate in neuronal apoptosis after cerebral ischemia. Prevention of the nuclear translocation of ANXA1 should therefore inhibit neuronal apoptosis and protect against cerebral stroke. Here, we found that, in the repeat III domain of ANXA1, the amino-acid residues from R228 to F237 function as a unique nuclear translocation signal (NTS) and are required for nuclear translocation of ANXA1. Intriguingly, we synthesized a cell-penetrating peptide derived by conjugating the trans-activator of transcription (Tat) domain to the NTS sequence. This Tat-NTS peptide specifically blocked the interaction of ANXA1 with importin β and, consequently, the nuclear translocation of ANXA1 without affecting the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of other proteins. The Tat-NTS peptide inhibited the transcriptional activity of p53, decreased Bid expression, suppressed activation of the caspase-3 apoptosis pathway and improved the survival of hippocampal neurons subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion in vitro. Moreover, using a focal brain ischemia animal model, we showed that the Tat-NTS peptide could be efficiently infused into the ischemic hippocampus and cortex by unilateral intracerebroventricular injection. Injection of the Tat-NTS peptide alleviated neuronal apoptosis in the ischemic zone. Importantly, further work revealed that administration of the Tat-NTS peptide resulted in a dramatic reduction in infarct volume and that this was correlated with a parallel improvement in neurological function after reperfusion. Interestingly, the effects of Tat-NTS were injury specific, with little impact on neuronal apoptosis or cognitive function in sham-treated nonischemic animals. In conclusion, based on its profound neuroprotective and cognitive-preserving effects, it is suggested that the Tat-NTS peptide represents a novel and potentially promising new therapeutic candidate for the treatment of ischemic stroke.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hankey GJ. Stroke. Lancet. 2017;389:641.
Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR, Deo R, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135:e146–603.
Khandelwal P, Yavagal DR, Sacco RL. Acute ischemic stroke intervention. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67:2631–44.
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C. The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron. 2010;67:181–98.
Fransen PS, Berkhemer OA, Lingsma HF, Beumer D, La VDB, Yoo AJ, et al. Time to reperfusion and treatment effect for acute ischemic stroke: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2016;73:190.
Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP, Bruno A, Demaerschalk BM, Khatri P, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2013;44:870–947.
Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG. Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2009;40:e331.
Luo Y, Yang X, Zhao S, Wei C, Yin Y, Liu T, et al. Hydrogen sulfide prevents OGD/R-induced apoptosis via improving mitochondrial dysfunction and suppressing an ROS-mediated caspase-3 pathway in cortical neurons. Neurochem Int. 2013;63:826–31.
Solito E, Mcarthur S, Christian H, Gavins F, Buckingham JC, Gillies GE. Annexin A1 in the brain--undiscovered roles? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2008;29:135.
Sugimoto MA, Vago JP, Teixeira MM, Sousa LP. Annexin A1 and the resolution of inflammation: modulation of neutrophil recruitment, apoptosis, and clearance. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:8239258. (2016-1-13) 2016
Yin Z, Xing L, Gong J, Lu L, Chen L, Lu Z, et al. Annexin A1 nuclear translocation induces retinal ganglion cell apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion injury through the p65/IL-1β pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1863:1350–8.
Arora S, Lim W, Bist P, Perumalsamy R, Lukman HM, Li F, et al. Influenza A virus enhances its propagation through the modulation of Annexin-A1 dependent endosomal trafficking and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23:1243.
Gavins FN. Are formyl peptide receptors novel targets for therapeutic intervention in ischaemia-reperfusion injury? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010;31:266–76.
Zhao Y, Wang J, Jiang H, Yu Z, Li X, Shi J. Following OGD/R, annexin 1 nuclear translocation and subsequent induction of apoptosis in neurons are assisted by myosin IIA in a TRPM7 kinase-dependent manner. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51:729.
Li X, Zhao Y, Xia Q, Zheng L, Liu L, Zhao B, et al. Nuclear translocation of annexin 1 following oxygen-glucose deprivation|[ndash]|reperfusion induces apoptosis by regulating Bid expression via p53 binding. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2356.
Soderholm JF, Bird SL, Kalab P, Sampathkumar Y, Hasegawa K, Uehara-Bingen M, et al. Importazole, a small molecule inhibitor of the transport receptor importin-β. ACS Chem Biol. 2011;6:700–8.
Song H, Kim W, Kim SH, Kim KT. VRK3-mediated nuclear localization of HSP70 prevents glutamate excitotoxicity-induced apoptosis and Aβ accumulation via enhancement of ERK phosphatase VHR activity. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38452.
Herhaus L, Perezoliva AB, Cozza G, Gourlay R, Weidlich S, Campbell DG, et al. Casein kinase 2 (CK2) phosphorylates the deubiquitylase OTUB1 at Ser16 to trigger its nuclear localization. Sci Signal. 2015;8:ra35.
Dowdy SF. Transducible TAT-HA fusogenic peptide enhances escape of TAT-fusion proteins after lipid raft macropinocytosis. Nat Med. 2004;10:310.
Guidotti G, Brambilla L, Rossi D. Cell-penetrating peptides: from basic research to clinics. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017;38:406–24.
Hill MD, Martin RH, Mikulis D, Wong JH, Silver FL, Terbrugge KG, et al. Safety and efficacy of NA-1 in patients with iatrogenic stroke after endovascular aneurysm repair (ENACT): a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11:942–50.
El ZI, Touchard E, Berdugo M, Abadie C, Kowalczuk L, Deloche C, et al. Subconjunctival injection of XG-102, a c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor peptide, in the treatment of endotoxin-induced uveitis in rats. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2015;31:17–24.
Aghazadeh Y, Martinez-Arguelles DB, Fan J, Culty M, Papadopoulos V. Induction of androgen formation in the male by a TAT-VDAC1 fusion peptide blocking 14-3-3varepsilon protein adaptor and mitochondrial VDAC1 interactions. Mol Ther. 2014;22:1779–91.
Shin MJ, Kim DW, Jo HS, Cho SB, Park JH, Lee CH, et al. Tat-PRAS40 prevent hippocampal HT-22 cell death and oxidative stress induced animal brain ischemic insults. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;97:250–62.
Boudhraa Z, Bouchon B, Viallard C, D’Incan M, Degoul F. Annexin A1 localization and its relevance to cancer. Clin Sci. 2016;130:205.
Rosengarth A, Gerke V, Luecke H. X-ray structure of full-length annexin 1 and implications for membrane aggregation. J Mol Biol. 2001;306:489–98.
Jeong SA, Kim K, Lee JH, Cha JS, Khadka P, Cho HS, et al. Akt-mediated phosphorylation increases the binding affinity of hTERT for importin α to promote nuclear translocation. J Cell Sci. 2015;128:2287–301.
Shin HY, Reich NC. Dynamic trafficking of STAT5 depends on an unconventional nuclear localization signal. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(Pt 15):3333–43.
Soniat M, Chook YM. Nuclear localization signals for four distinct karyopherin-beta nuclear import systems. Biochem J. 2015;468:353–62.
Yan W, Li R, He J, Du J, Hou J. Importin beta1 mediates nuclear factor-kappaB signal transduction into the nuclei of myeloma cells and affects their proliferation and apoptosis. Cell Signal. 2015;27:851–9.
Yu H, Shi L, Qi G, Zhao S, Gao Y, Li Y. Gypenoside protects cardiomyocytes against ischemia-reperfusion injury via the inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase mediated nuclear factor kappa B pathway in vitro and in vivo. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:148.
Lu T, Bao Z, Wang Y, Yang L, Lu B, Yan K, et al. Karyopherinbeta1 regulates proliferation of human glioma cells via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;478:1189–97.
Zhang J, Zhang J, Qi C, Yang P, Chen X, Liu Y. Activation of Wnt3alpha/beta-catenin signal pathway attenuates apoptosis of the cerebral microvascular endothelial cells induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490:71–77.
Kaufmann T, Strasser A, Jost PJ. Fas death receptor signalling: roles of Bid and XIAP. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19:42–50.
Culmsee C, Krieglstein J. Ischaemic brain damage after stroke: new insights into efficient therapeutic strategies. International Symposium on Neurodegeneration and Neuroprotection. EMBO Rep. 2007;8:129–33.
Bolhassani A, Jafarzade BS, Mardani G. In vitro and in vivo delivery of therapeutic proteins using cell penetrating peptides. Peptides. 2017;87:50–63.
Zhou HH, Tang Y, Zhang XY, Luo CX, Gao LY, Wu HY, et al. Delayed administration of Tat-HA-NR2B9c promotes recovery after stroke in rats. Stroke. 2015;46:1352–8.
Teves LM, Cui H, Tymianski M. Efficacy of the PSD95 inhibitor Tat-NR2B9c in mice requires dose translation between species. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015;36:0271678X15612099.
Cook DJ, Teves L, Tymianski M. A translational paradigm for the preclinical evaluation of the stroke neuroprotectant Tat-NR2B9c in gyrencephalic nonhuman primates. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:154ra133.
Brooks H, Lebleu B, Vivès E. Tat peptide-mediated cellular delivery: back to basics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57:559–77.
Rossi D, Gaidano G. Messengers of cell death: apoptotic signaling in health and disease. Haematologica. 2003;88:212–8.
Ansari S, Azari H, Mcconnell DJ, Afzal A, Mocco J. Intraluminal middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model for ischemic stroke with laser doppler flowmetry guidance in mice. J Vis Exp. 2011;51:e2879–e2879.
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Dávalos A, Guidetti D, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 h after acute ischemic stroke. New Engl J Med. 2008;359:1317–29.
Xie XQ, Zhang P, Tian B, Chen XQ. Downregulation of NAD-dependent deacetylase SIRT2 protects mouse brain against ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54:7251–61.
Fan X, Zhao F, Wang X, Wu G. Doxorubicin-triggered self-assembly of native amphiphilic peptides into spherical nanoparticles. Oncotarget. 2016;7:58445–58.
Lei P, Shan W, Jin H, Bi L, Na W, Yan H, et al. A novel mechanism of spine damages in stroke via DAPK1 and Tau. Cereb Cortex. 2015;25:4559–71.
Acknowledgements
The current studies were supported by funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31771126, 31471015), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (no. 2017M620310).
Author contributions
JS, XL, and YZ conceived and designed the project; XL, LZ, and QX performed the experiments; LL, MM, and HJZ gave much valuable advice and conducted the data analysis; JS and XL wrote the manuscript with approval from all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by M. Piacentini.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zheng, L., Xia, Q. et al. A novel cell-penetrating peptide protects against neuron apoptosis after cerebral ischemia by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of annexin A1. Cell Death Differ 26, 260–275 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0116-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0116-5
This article is cited by
-
Gain-of-function PPM1D mutations attenuate ischemic stroke
Cell Death & Differentiation (2025)
-
Phosphorylation of GABAA receptor β3 subunit at Ser408–409 is essential for contextual learning at hippocampal CA1 synapses
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Annexin-A1 tripeptide enhances functional recovery and mitigates brain damage in traumatic brain injury by inhibiting neuroinflammation and preventing ANXA1 nuclear translocation in mice
Metabolic Brain Disease (2024)
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH1 reduces inflammation and pyroptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via PCSK9 downregulation
Mammalian Genome (2024)
-
NRXN1 depletion in the medial prefrontal cortex induces anxiety-like behaviors and abnormal social phenotypes along with impaired neurite outgrowth in rat
Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders (2023)