Abstract
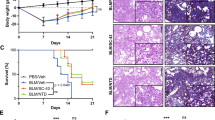
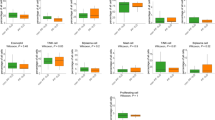
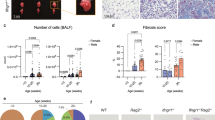
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the most common type of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and has one of the poorest prognosis. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying IPF progression remain largely unknown. In this study, we determined that IL-24, an IL-20 subfamily cytokine member, was increased both in the serum of IPF patients and the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of mice following bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis. As a result, IL-24 deficiency protected mice from BLM-induced lung injury and fibrosis. Specifically, loss of IL-24 significantly attenuated transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) production and reduced M2 macrophage infiltration in the lung of BLM-induced mice. Mechanistically, IL-24 alone did not show a perceptible impact on the induction of M2 macrophages, but it synergized with IL-4 to promote M2 program in macrophages. IL-24 suppressed IL-4-induced expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) and SOCS3, through which it enhanced signal transducer and activator of transcription 6/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (STAT6/PPARγ) signaling, thereby promoting IL-4-induced production of M2 macrophages. Collectively, our data support that IL-24 synergizes with IL-4 to promote macrophage M2 program contributing to the development of pulmonary fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Change history
05 January 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00721-8
References
Hutchinson J, Fogarty A, Hubbard R, McKeever T. Global incidence and mortality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review. Eur Respir J. 2015;46:795–806.
Hopkins RB, Burke N, Fell C, Dion G, Kolb M. Epidemiology and survival of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis from national data in Canada. Eur Respir J. 2016;48:187–95.
Ley B, Collard HR, King TE Jr. Clinical course and prediction of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:431–40.
Desai O, Winkler J, Minasyan M, Herzog EL. The role of immune and inflammatory cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018;5:43.
Richeldi L, Collard HR, Jones MG. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 2017;389:1941–52.
Wynn TA, Vannella KM. Macrophages in tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis. Immunity. 2016;44:450–62.
Pechkovsky DV, Prasse A, Kollert F, Engel KM, Dentler J, Luttmann W, et al. Alternatively activated alveolar macrophages in pulmonary fibrosis-mediator production and intracellular signal transduction. Clin Immunol. 2010;137:89–101.
Toossi Z, Hirsch CS, Hamilton BD, Knuth CK, Friedlander MA, Rich EA. Decreased production of TGF-beta 1 by human alveolar macrophages compared with blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1996;156:3461–8.
Young LR, Gulleman PM, Short CW, Tanjore H, Sherrill T, Qi A, et al. Epithelial-macrophage interactions determine pulmonary fibrosis susceptibility in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. JCI Insight. 2016;1:e88947.
Wang M, Liang P. Interleukin-24 and its receptors. Immunology. 2005;114:166–70.
Poindexter NJ, Walch ET, Chada S, Grimm EA. Cytokine induction of interleukin-24 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;78:745–52.
Menezes ME, Bhatia S, Bhoopathi P, Das SK, Emdad L, Dasgupta S, et al. MDA-7/IL-24: multifunctional cancer killing cytokine. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;818:127–53.
Poindexter NJ, Williams RR, Powis G, Jen E, Caudle AS, Chada S, et al. IL-24 is expressed during wound repair and inhibits TGFalpha-induced migration and proliferation of keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19:714–22.
Shefler I, Pasmanik-Chor M, Kidron D, Mekori YA, Hershko AY. T cell-derived microvesicles induce mast cell production of IL-24: relevance to inflammatory skin diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:e211–3.
Kumari S, Bonnet MC, Ulvmar MH, Wolk K, Karagianni N, Witte E, et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptor signaling in keratinocytes triggers interleukin-24-dependent psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. Immunity. 2013;39:899–911.
McGee HM, Schmidt BA, Booth CJ, Yancopoulos GD, Valenzuela DM, Murphy AJ, et al. IL-22 promotes fibroblast-mediated wound repair in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:1321–9.
Rutz S, Wang X, Ouyang W. The IL-20 subfamily of cytokines–from host defence to tissue homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:783–95.
Garn H, Schmidt A, Grau V, Stumpf S, Kaufmann A, Becker M, et al. IL-24 is expressed by rat and human macrophages. Immunobiology. 2002;205:321–34.
Cui Z, Liao J, Cheong N, Longoria C, Cao G, DeLisser HM, et al. The receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility (CD168) promotes inflammation and fibrosis after acute lung injury. Matrix Biol. 2019;78:255–71.
Sun P, Li L, Zhao C, Pan M, Qian Z, Su X. Deficiency of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor attenuates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Mol Med. 2017;23:34–49.
Burgy O, Wettstein G, Bellaye PS, Decologne N, Racoeur C, Goirand F, et al. Deglycosylated bleomycin has the antitumor activity of bleomycin without pulmonary toxicity. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:326ra20.
Gordon S, Martinez FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. 2010;32:593–604.
Lu J, Xie L, Liu C, Zhang Q, Sun S. PTEN/PI3k/AKT regulates macrophage polarization in emphysematous mice. Scand J Immunol. 2017;85:395–405.
Vergadi E, Ieronymaki E, Lyroni K, Vaporidi K, Tsatsanis C. Akt signaling pathway in macrophage activation and M1/M2 polarization. J Immunol. 2017;198:1006–14.
Hao J, Hu Y, Li Y, Zhou Q, Lv X. Involvement of JNK signaling in IL4-induced M2 macrophage polarization. Exp cell Res. 2017;357:155–62.
Shan M, Qin J, Jin F, Han X, Guan H, Li X, et al. Autophagy suppresses isoprenaline-induced M2 macrophage polarization via the ROS/ERK and mTOR signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;110:432–43.
Kawano A, Ariyoshi W, Yoshioka Y, Hikiji H, Nishihara T, Okinaga T. Docosahexaenoic acid enhances M2 macrophage polarization via the p38 signaling pathway and autophagy. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:12604–17.
Steinert A, Linas I, Kaya B, Ibrahim M, Schlitzer A, Hruz P, et al. The stimulation of macrophages with TLR ligands supports increased IL-19 expression in inflammatory bowel disease patients and in colitis models. J Immunol. 2017;199:2570–84.
Hashimoto D, Chow A, Noizat C, Teo P, Beasley MB, Leboeuf M, et al. Tissue-resident macrophages self-maintain locally throughout adult life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes. Immunity. 2013;38:792–804.
Zhang L, Wang Y, Wu G, Xiong W, Gu W, Wang CY. Macrophages: friend or foe in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Respir Res. 2018;19:170.
Noskovicova N, Heinzelmann K, Burgstaller G, Behr J, Eickelberg O. Cub domain-containing protein 1 negatively regulates TGF-beta signaling and myofibroblast differentiation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018;314:695–707.
Yao Y, Wang Y, Zhang Z, He L, Zhu J, Zhang M, et al. Chop deficiency protects mice against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by attenuating M2 macrophage production. Mol Ther. 2016;24:915–25.
Yu X, Buttgereit A, Lelios I, Utz SG, Cansever D, Becher B, et al. The cytokine TGF-beta promotes the development and homeostasis of alveolar macrophages. Immunity. 2017;47:903–12.
Lepparanta O, Sens C, Salmenkivi K, Kinnula VL, Keski-Oja J, Myllarniemi M, et al. Regulation of TGF-beta storage and activation in the human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis lung. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;348:491–503.
Martinez FJ, Collard HR, Pardo A, Raghu G, Richeldi L, Selman M, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2017;3:1–19.
Celada LJ, Kropski JA, Herazo-Maya JD, Luo W, Creecy A, Abad AT, et al. PD-1 up-regulation on CD4+ T cells promotes pulmonary fibrosis through STAT3-mediated IL-17A and TGF-β1 production. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10:eaar8356.
Wei Q, Sha Y, Bhattacharya A, Abdel Fattah E, Bonilla D, Jyothula SS, et al. Regulation of IL-4 receptor signaling by STUB1 in lung inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189:16–29.
Odegaard JI, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Goforth MH, Morel CR, Subramanian V, Mukundan L, et al. Macrophage-specific PPARgamma controls alternative activation and improves insulin resistance. Nature. 2007;447:1116–20.
Inomata M, Into T, Nakashima M, Noguchi T, Matsushita K. IL-4 alters expression patterns of storage components of vascular endothelial cell-specific granules through STAT6- and SOCS-1-dependent mechanisms. Mol Immunol. 2009;46:2080–9.
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:788–824.
Wang J, Hu B, Zhao Z, Zhang H, Zhang H, Zhao Z, et al. Intracellular XBP1-IL-24 axis dismantles cytotoxic unfolded protein response in the liver. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:17.
Liu P, Miao K, Zhang L, Mou Y, Xu Y, Xiong W, et al. Curdione ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by repressing TGF-beta-induced fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. Respir Res. 2020;21:58.
Wang Q, Yu J, Hu Y, Chen X, Zhang L, Pan T, et al. Indirubin alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice by suppressing fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110715.
Miao K, Pan T, Mou Y, Zhang L, Xiong W, Xu Y, et al. Scutellarein inhibits BLM-mediated pulmonary fibrosis by affecting fibroblast differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2020;11:2040622320940185.
Wang Y, Zhu J, Zhang L, Zhang Z, He L, Mou Y, et al. Role of C/EBP homologous protein and endoplasmic reticulum stress in asthma exacerbation by regulating the IL-4/signal transducer and activator of transcription 6/transcription factor EC/IL-4 receptor alpha positive feedback loop in M2 macrophages. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:1550–61.
Schwegmann A, Guler R, Cutler AJ, Arendse B, Horsnell WG, Flemming A, et al. Protein kinase C delta is essential for optimal macrophage-mediated phagosomal containment of Listeria monocytogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:16251–6.
Guo YC, Zhang M, Wang FX, Pei GC, Sun F, Zhang Y, et al. Macrophages regulate unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal lymphangiogenesis through C-C motif chemokine receptor 2-dependent phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT-mechanistic target of rapamycin signaling and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha/vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression. Am J Pathol. 2017;187:1736–49.
Hu Y, Yu J, Wang Q, Zhang L, Chen X, Cao Y, et al. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5/ACP5 interacts with p53 to control the expression of SMAD3 in lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020;16:272–88.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81530024, 91749207, 81920108009, 81770823, 81760008, 81800068, and 81670929), the Ministry of Science and Technology (2016YFC1305002 and 2017YFC1309603), NHC Drug Discovery Program (2017ZX09304022-07), the Department of Science and Technology of Hubei State (2017ACA096), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Program (2018GXNSFDA281041), the Integrated Innovative Team for Major Human Disease Programs of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and the Innovative Funding for Translational Research from Tongji Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by M. Bianchi
The original online version of this article was revised: In the “Acknowledgments” part, the funding number “9174927” (in the second line) should be corrected to “91749207”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, LZ., Wang, Y., Zhang, L. et al. IL-24 deficiency protects mice against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by repressing IL-4-induced M2 program in macrophages. Cell Death Differ 28, 1270–1283 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00650-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00650-6
This article is cited by
-
Synergistic regulation of TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling and inflammatory pathways via SA/NAC-based nanoplatforms: a novel strategy to enhance anti-fibrotic therapeutic outcomes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2026)
-
Rubiadin-1-methyl ether alleviates bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis
Scientific Reports (2026)
-
CILP attenuates pulmonary fibrosis through the TGF-β1/SMAD3 pathway
European Journal of Medical Research (2025)
-
Intranasal delivery of hMSC-derived supernatant for treatment of ischemic stroke by inhibiting the pro-inflammatory polarization of neutrophils
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2025)
-
RTN3 regulates collagen biosynthesis and profibrotic macrophage differentiation to promote pulmonary fibrosis via interacting with CRTH2
Molecular Medicine (2025)