Abstract
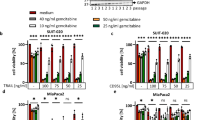
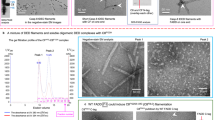
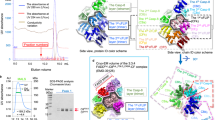
Pharmacological targeting via small molecule-based chemical probes has recently acquired an emerging importance as a valuable tool to delineate molecular mechanisms. Induction of apoptosis via CD95/Fas and TRAIL-R1/2 is triggered by the formation of the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). Caspase-8 activation at the DISC is largely controlled by c-FLIP proteins. However molecular mechanisms of this control have just started to be uncovered. In this study we report the first-in-class chemical probe targeting c-FLIPL in the heterodimer caspase-8/c-FLIPL. This rationally designed small molecule was aimed to imitate the closed conformation of the caspase-8 L2′ loop and thereby increase caspase-8 activity after initial processing of the heterodimer. In accordance with in silico predictions, this small molecule enhanced caspase-8 activity at the DISC, CD95L/TRAIL-induced caspase activation, and subsequent apoptosis. The generated computational model provided further evidence for the proposed effects of the small molecule on the heterodimer caspase-8/c-FLIPL. In particular, the model has demonstrated that boosting caspase-8 activity by the small molecule at the early time points after DISC assembly is crucial for promoting apoptosis induction. Taken together, our study allowed to target the heterodimer caspase-8/c-FLIPL and get new insights into molecular mechanisms of its activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Krammer PH, Arnold R, Lavrik IN. Life and death in peripheral T cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:532–42.
Lavrik IN, Krammer PH. Regulation of CD95/Fas signaling at the DISC. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19:36–41.
Dickens LS, Boyd RS, Jukes-Jones R, Hughes MA, Robinson GL, Fairall L, et al. A death effector domain chain DISC model reveals a crucial role for caspase-8 chain assembly in mediating apoptotic cell death. Mol Cell. 2012;47:291–305.
Schleich K, Warnken U, Fricker N, Ozturk S, Richter P, Kammerer K, et al. Stoichiometry of the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex: experimental and modeling evidence for a death effector domain chain model. Mol Cell. 2012;47:306–19.
Fu TM, Li Y, Lu A, Li Z, Vajjhala PR, Cruz AC, et al. Cryo-EM structure of caspase-8 tandem DED filament reveals assembly and regulation mechanisms of the death-inducing signaling complex. Mol Cell. 2016;64:236–50.
Hughes MA, Harper N, Butterworth M, Cain K, Cohen GM, MacFarlane M. Reconstitution of the death-inducing signaling complex reveals a substrate switch that determines CD95-mediated death or survival. Mol Cell. 2009;35:265–79.
Yu JW, Jeffrey PD, Shi Y. Mechanism of procaspase-8 activation by c-FLIPL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:8169–74.
Golks A, Brenner D, Schmitz I, Watzl C, Krueger A, Krammer PH, et al. The role of CAP3 in CD95 signaling: new insights into the mechanism of procaspase-8 activation. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:489–98.
Hoffmann JC, Pappa A, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN. A new C-terminal cleavage product of procaspase-8, p30, defines an alternative pathway of procaspase-8 activation. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:4431–40.
Ozturk S, Schleich K, Lavrik IN. Cellular FLICE-like inhibitory proteins (c-FLIPs): fine-tuners of life and death decisions. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318:1324–31.
Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Krammer PH, Peter ME. The role of c-FLIP in modulation of CD95-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:1541–8.
Golks A, Brenner D, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN. The c-FLIP-NH2 terminus (p22-FLIP) induces NF-kappaB activation. J Exp Med. 2006;203:1295–305.
Golks A, Brenner D, Fritsch C, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN. c-FLIPR, a new regulator of death receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:14507–13.
Fricker N, Beaudouin J, Richter P, Eils R, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN. Model-based dissection of CD95 signaling dynamics reveals both a pro- and antiapoptotic role of c-FLIPL. J Cell Biol. 2010;190:377–89.
Schleich K, Buchbinder JH, Pietkiewicz S, Kahne T, Warnken U, Ozturk S, et al. Molecular architecture of the DED chains at the DISC: regulation of procaspase-8 activation by short DED proteins c-FLIP and procaspase-8 prodomain. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23:681–94.
Hughes MA, Powley IR, Jukes-Jones R, Horn S, Feoktistova M, Fairall L, et al. Co-operative and hierarchical binding of c-FLIP and caspase-8: a unified model defines how c-FLIP isoforms differentially control cell fate. Mol Cell. 2016;61:834–49.
Chang DW, Xing Z, Pan Y, Algeciras-Schimnich A, Barnhart BC, Yaish-Ohad S, et al. c-FLIP(L) is a dual function regulator for caspase-8 activation and CD95-mediated apoptosis. EMBO J. 2002;21:3704–14.
Micheau O, Thome M, Schneider P, Holler N, Tschopp J, Nicholson DW, et al. The long form of FLIP is an activator of caspase-8 at the Fas death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:45162–71.
Boatright KM, Deis C, Denault JB, Sutherlin DP, Salvesen GS. Activation of caspases-8 and -10 by FLIP(L). Biochemical J. 2004;382:651–7.
Pop C, Oberst A, Drag M, Van Raam BJ, Riedl SJ, Green DR, et al. FLIP(L) induces caspase 8 activity in the absence of interdomain caspase 8 cleavage and alters substrate specificity. Biochem J. 2011;433:447–57.
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT, et al. Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem. 2004;47:1739–49.
Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, et al. Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J Med Chem. 2006;49:6177–96.
Sastry GM, Adzhigirey M, Day T, Annabhimoju R, Sherman W. Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J Comput-Aided Mol Des. 2013;27:221–34.
Irwin JJ, Sterling T, Mysinger MM, Bolstad ES, Coleman RG. ZINC: a free tool to discover chemistry for biology. J Chem Inf Model. 2012;52:1757–68.
Neumann L, Pforr C, Beaudouin J, Pappa A, Fricker N, Krammer PH, et al. Dynamics within the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex decide life and death of cells. Mol Syst Biol. 2010;6:352.
Schmidt JH, Pietkiewicz S, Naumann M, Lavrik IN. Quantification of CD95-induced apoptosis and NF-kappaB activation at the single cell level. J Immunol Methods. 2015;423:12–7.
Pietkiewicz S, Eils R, Krammer PH, Giese N, Lavrik IN. Combinatorial treatment of CD95L and gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells induces apoptotic and RIP1-mediated necroptotic cell death network. Exp Cell Res. 2015;339:1–9.
Hillert LK, Bettermann-Bethge K, Nimmagadda SC, Fischer T, Naumann M, Lavrik IN. Targeting RIPK1 in AML cells carrying FLT3-ITD. Int J Cancer. 2019;145:1558–69.
Pietkiewicz S, Schmidt JH, Lavrik IN. Quantification of apoptosis and necroptosis at the single cell level by a combination of imaging flow cytometry with classical annexin V/propidium iodide staining. J Immunol Methods. 2015;423:99–103.
Raue A, Kreutz C, Maiwald T, Bachmann J, Schilling M, Klingmuller U, et al. Structural and practical identifiability analysis of partially observed dynamical models by exploiting the profile likelihood. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1923–9.
Vickers CJ, Gonzalez-Paez GE, Litwin KM, Umotoy JC, Coutsias EA, Wolan DW. Selective inhibition of initiator versus executioner caspases using small peptides containing unnatural amino acids. ACS Chem Biol. 2014;9:2194–8.
Spencer SL, Sorger PK. Measuring and modeling apoptosis in single cells. Cell. 2011;144:926–39.
Lavrik IN. Systems biology of death receptor networks: live and let die. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1259.
Kallenberger SM, Beaudouin J, Claus J, Fischer C, Sorger PK, Legewie S, et al. Intra- and interdimeric caspase-8 self-cleavage controls strength and timing of CD95-induced apoptosis. Sci Signal. 2014;7:ra23.
Hardy JA, Lam J, Nguyen JT, O’Brien T, Wells JA. Discovery of an allosteric site in the caspases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:12461–6.
Scheer JM, Romanowski MJ, Wells JA. A common allosteric site and mechanism in caspases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:7595–600.
Bucur O, Gaidos G, Yatawara A, Pennarun B, Rupasinghe C, Roux J, et al. A novel caspase 8 selective small molecule potentiates TRAIL-induced cell death. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9893.
Schoeberl B, Kudla A, Masson K, Kalra A, Curley M, Finn G, et al. Systems biology driving drug development: from design to the clinical testing of the anti-ErbB3 antibody seribantumab (MM-121). NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2017;3:16034.
Roux J, Hafner M, Bandara S, Sims JJ, Hudson H, Chai D, et al. Fractional killing arises from cell-to-cell variability in overcoming a caspase activity threshold. Mol Syst Biol. 2015;11:803.
Roberts AW, Davids MS, Pagel JM, Kahl BS, Puvvada SD, Gerecitano JF, et al. Targeting BCL2 with Venetoclax in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:311–22.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the center of dynamic systems, funded by the EU-programme European Regional Development Fund, Volkswagen Foundation (VW 90315), Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung (2017.008.01), DFG (LA 2386), and Russian Science Foundation 14-44-00011 for supporting our work. We thank Dr Sabine Pietkiewicz, Claudia Arndt, and Dr Nastya Shunaeva-Zotova for the experimental help. We acknowledge Prof. Peter H. Krammer (DKFZ, Heidelberg) for providing us with anti-APO-1, C15, NF6, and 1C4 antibodies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LH performed experiments and contributed to the manuscript text. NI performed computational modeling and worked a lot on the manuscript text. DB, CK, and JE contributed experimentally. SP and NK contributed to the theoretical design. VI and IL designed a study and wrote a manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by S. Fulda
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hillert, L.K., Ivanisenko, N.V., Busse, D. et al. Dissecting DISC regulation via pharmacological targeting of caspase-8/c-FLIPL heterodimer. Cell Death Differ 27, 2117–2130 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-0489-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-0489-0
This article is cited by
-
Research landscape of photodynamic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Hotspots and Prospects from 2012 to 2025
Hereditas (2025)
-
Pharmacological targeting of caspase-8/c-FLIPL heterodimer enhances complex II assembly and elimination of pancreatic cancer cells
Communications Biology (2025)
-
Non-apoptotic caspase-8 is critical for orchestrating exaggerated inflammation during severe SARS-CoV-2 infection
Nature Communications (2025)
-
The role of cell death in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
cFLIP downregulation is an early event required for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in tumor cells
Cell Death & Disease (2022)