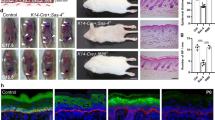
Abstract
Stratification of the epidermis is essential for the barrier function of the skin. However, the molecular mechanisms governing epidermal stratification are not fully understood. Herein, we demonstrate that enkurin domain-containing protein 1 (ENKD1) contributes to epidermal stratification by modulating the cell-division orientation of basal keratinocytes. The epidermis of Enkd1 knockout mice is thinner than that of wild-type mice due to reduced generation of suprabasal cells from basal keratinocytes through asymmetric division. Depletion of ENKD1 impairs proper orientation of the mitotic spindle and delays mitotic progression in cultured cells. Mechanistic investigation further reveals that ENKD1 is a novel microtubule-binding protein that promotes the stability of astral microtubules. Introduction of the microtubule-binding domain of ENKD1 can largely rescue the spindle orientation defects in ENKD1-depleted cells. These findings establish ENKD1 as a critical regulator of astral microtubule stability and spindle orientation that stimulates epidermal stratification in mammalian cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Data availability
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper in the main text or the Supplementary file.
References
Koster MI, Roop DR. Mechanisms regulating epithelial stratification. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:93–113.
Lambrecht BN, Hammad H. The immunology of the allergy epidemic and the hygiene hypothesis. Nat Immunol. 2017;18:1076–83.
Botchkarev VA, Flores ER. p53/p63/p73 in the epidermis in health and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;4:a015248.
Baum S, Sakka N, Artsi O, Trau H, Barzilai A. Diagnosis and classification of autoimmune blistering diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:482–9.
Charruyer A, Fong S, Vitcov GG, Sklar S, Tabernik L, Taneja M, et al. Interleukin-17A-dependent asymmetric stem cell divisions are increased in human psoriasis: a mechanism underlying benign hyperproliferation. Stem Cells. 2017;35:2001–7.
Veltri A, Lang C, Lien WH. Wnt signaling pathways in skin development and epidermal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2018;36:22–35.
Gonzales KAU, Fuchs E. Skin and its regenerative powers: an alliance between stem cells and their niche. Dev Cell. 2017;43:387–401.
Miroshnikova YA, Le HQ, Schneider D, Thalheim T, Rubsam M, Bremicker N, et al. Adhesion forces and cortical tension couple cell proliferation and differentiation to drive epidermal stratification. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:69–80.
Miroshnikova YA, Cohen I, Ezhkova E, Wickstrom SA. Epigenetic gene regulation, chromatin structure, and force-induced chromatin remodelling in epidermal development and homeostasis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2019;55:46–51.
Williams SE, Beronja S, Pasolli HA, Fuchs E. Asymmetric cell divisions promote Notch-dependent epidermal differentiation. Nature. 2011;470:353–8.
Williams SE, Ratliff LA, Postiglione MP, Knoblich JA, Fuchs E. Par3-mInsc and Galphai3 cooperate to promote oriented epidermal cell divisions through LGN. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:758–69.
Xie W, Zhou J. Regulation of mitotic spindle orientation during epidermal stratification. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232:1634–9.
Delgado MK, Cabernard C. Mechanical regulation of cell size, fate, and behavior during asymmetric cell division. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020;67:9–16.
Luo Y, Ran J, Xie S, Yang Y, Chen J, Li S, et al. ASK1 controls spindle orientation and positioning by phosphorylating EB1 and stabilizing astral microtubules. Cell Discov. 2016;2:16033.
Yang Y, Liu M, Li D, Ran J, Gao J, Suo S, et al. CYLD regulates spindle orientation by stabilizing astral microtubules and promoting dishevelled-NuMA-dynein/dynactin complex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:2158–63.
Song X, Yang F, Liu X, Xia P, Yin W, Wang Z, et al. Dynamic crotonylation of EB1 by TIP60 ensures accurate spindle positioning in mitosis. Nat Chem Biol. 2021;17:1314–23.
Stadler C, Rexhepaj E, Singan VR, Murphy RF, Pepperkok R, Uhlen M, et al. Immunofluorescence and fluorescent-protein tagging show high correlation for protein localization in mammalian cells. Nat Methods. 2013;10:315–23.
Hardman MJ, Sisi P, Banbury DN, Byrne C. Patterned acquisition of skin barrier function during development. Development. 1998;125:1541–52.
Sotiropoulou PA, Blanpain C. Development and homeostasis of the skin epidermis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4:a008383.
van Leen EV, di Pietro F, Bellaiche Y. Oriented cell divisions in epithelia: from force generation to force anisotropy by tension, shape and vertices. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020;62:9–16.
di Pietro F, Echard A, Morin X. Regulation of mitotic spindle orientation: an integrated view. EMBO Rep. 2016;17:1106–30.
Chen M, Cao Y, Dong D, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Chen J, et al. Regulation of mitotic spindle orientation by phosphorylation of end binding protein 1. Exp Cell Res. 2019;384:111618.
Stout JR, Yount AL, Powers JA, LeBlanc C, Ems-McClung SC, Walczak CE, et al. Kif18B interacts with EB1 and controls astral microtubule length during mitosis. Mol Biol Cell. 2011;22:3070–80.
Rognoni E, Watt FM. Skin cell heterogeneity in development, wound healing, and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28:709–22.
Blanpain C, Fuchs E. Epidermal homeostasis: a balancing act of stem cells in the skin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:207–17.
Amini-Nik S, Dolp R, Eylert G, Datu AK, Parousis A, Blakeley C, et al. Stem cells derived from burned skin—The future of burn care. EBioMedicine. 2018;37:509–20.
Bauer JW, Koller J, Murauer EM, De Rosa L, Enzo E, Carulli S, et al. Closure of a large chronic wound through transplantation of gene-corrected epidermal stem cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:778–81.
Razmi TM, Kumar R, Rani S, Kumaran SM, Tanwar S, Parsad D. Combination of follicular and epidermal cell suspension as a novel surgical approach in difficult-to-treat vitiligo: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:301–8.
Song T, Zhou P, Sun C, He N, Li H, Ran J, et al. Enkurin domain containing 1 (ENKD1) regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajco.13550.
Dimitracopoulos A, Srivastava P, Chaigne A, Win Z, Shlomovitz R, Lancaster OM, et al. Mechanochemical crosstalk produces cell-intrinsic patterning of the cortex to orient the mitotic spindle. Curr Biol. 2020;30:3687–96.
Lechler T, Mapelli M. Spindle positioning and its impact on vertebrate tissue architecture and cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:691–708.
Yan S, Guo C, Hou G, Zhang H, Lu X, Williams JC, et al. Atomic-resolution structure of the CAP-Gly domain of dynactin on polymeric microtubules determined by magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:14611–6.
D’Alessandro M, Hnia K, Gache V, Koch C, Gavriilidis C, Rodriguez D, et al. Amphiphysin 2 orchestrates nucleus positioning and shape by linking the nuclear envelope to the actin and microtubule cytoskeleton. Dev Cell. 2015;35:186–98.
Sutton KA, Jungnickel MK, Wang Y, Cullen K, Lambert S, Florman HM. Enkurin is a novel calmodulin and TRPC channel binding protein in sperm. Dev Biol. 2004;274:426–35.
Jungnickel MK, Sutton KA, Baker MA, Cohen MG, Sanderson MJ, Florman HM. The flagellar protein Enkurin is required for mouse sperm motility and for transport through the female reproductive tract. Biol Reprod. 2018;99:789–97.
Denda M, Tsutsumi M. Roles of transient receptor potential proteins (TRPs) in epidermal keratinocytes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;704:847–60.
Sigg MA, Menchen T, Lee C, Johnson J, Jungnickel MK, Choksi SP, et al. Evolutionary proteomics uncovers ancient associations of cilia with signaling pathways. Dev Cell. 2017;43:744–62.
Gao J, Sun L, Huo L, Liu M, Li D, Zhou J. CYLD regulates angiogenesis by mediating vascular endothelial cell migration. Blood. 2010;115:4130–7.
Hergovich A, Lisztwan J, Barry R, Ballschmieter P, Krek W. Regulation of microtubule stability by the von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor protein pVHL. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:64–70.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Drs. Huijie Zhao, Xueliang Zhu, and Rutao Cui for discussion. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31730050, 31871347, 32170829, 32070708, 32000490, and 32000870) and the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFA0503502 and 2021YFA1101001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TZ and XW performed experiments and analyzed data; WX, XL, TS, SS, YL, DL and ML performed experiments; SX and JZ supervised the project and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical statement
All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. The use of mice was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Shandong Normal University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by M Hardwick
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, T., Wu, X., Xie, W. et al. ENKD1 promotes epidermal stratification by regulating spindle orientation in basal keratinocytes. Cell Death Differ 29, 1719–1729 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-022-00958-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-022-00958-5
This article is cited by
-
HDAC6 deacetylates ENKD1 to regulate mitotic spindle behavior and corneal epithelial homeostasis
EMBO Reports (2025)
-
CFAP100 couples microtubule glutamylation to spindle pole integrity in keratinocytes to promote epidermal development
Nature Communications (2025)
-
MiR-760 protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced septic acute kidney injury by targeting ENKD1
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (2025)
-
CEP78 regulates the proliferation and angiogenesis of endothelial cells by mediating microtubule stabilization via p150glued
Journal of Molecular Histology (2025)
-
Anthropogenic events and responses to environmental stress are shaping the genomes of Ethiopian indigenous goats
Scientific Reports (2024)