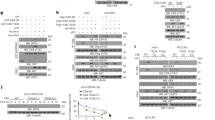
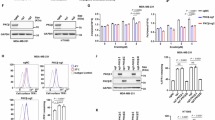
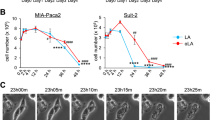
Abstract
GPX4-dependent ferroptosis has emerged as a therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment. Here, we demonstrated that protein kinase A (PKA) participates in the regulation of ferroptosis by controlling the m6A modification of GPX4 in an ALKBH5-dependent manner. Notably, we identified ALKBH5, an m6A demethylase, as a novel target of PKA, which drives phosphorylation-dependent degradation of ALKBH5 protein. Moreover, the deletion of ALKBH5 represses ferroptotic cell death by maintaining GPX4 m6A modification and stability. Thus, by regulating ALKBH5-dependent GPX4 stability, PKA acts as a key regulator of ferroptosis. Our study unveils the involvement of PKA in m6A modification, which could control GPX4-dependent ferroptosis and tumor progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the conclusion in the paper are present in the paper and the supplementary files.
References
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149:1060–72.
Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:266–82.
Stockwell BR. Ferroptosis turns 10: Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications. Cell. 2022;185:2401–21.
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 2017;171:273–85.
Liang D, Minikes AM, Jiang X. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Molecular Cell. 2022;82:2215–27.
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18:280–96.
Stockwell BR, Jiang X, Gu W. Emerging mechanisms and disease relevance of ferroptosis. Trends in Cell Biology. 2020;30:478–90.
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang S-J, Su T, Hibshoosh H, et al. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 2015;520:57–62.
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156:317–31.
Seiler A, Schneider M, Forster H, Roth S, Wirth EK, Culmsee C, et al. Glutathione peroxidase 4 senses and translates oxidative stress into 12/15-lipoxygenase dependent- and AIF-mediated cell death. Cell Metab. 2008;8:237–48.
Ingold I, Berndt C, Schmitt S, Doll S, Poschmann G, Buday K, et al. Selenium utilization by GPX4 is required to prevent hydroperoxide-induced ferroptosis. Cell. 2018;172:409–422 e421.
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Hammond VJ, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:1180–91.
Gaschler MM, Andia AA, Liu H, Csuka JM, Hurlocker B, Vaiana CA, et al. FINO(2) initiates ferroptosis through GPX4 inactivation and iron oxidation. Nat Chem Biol. 2018;14:507–15.
Hangauer MJ, Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Bole D, Eaton JK, Matov A, et al. Drug-tolerant persister cancer cells are vulnerable to GPX4 inhibition. Nature. 2017;551:247–50.
Zou Y, Palte MJ, Deik AA, Li H, Eaton JK, Wang W, et al. A GPX4-dependent cancer cell state underlies the clear-cell morphology and confers sensitivity to ferroptosis. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1617.
Wu K, Yan M, Liu T, Wang Z, Duan Y, Xia Y, et al. Creatine kinase B suppresses ferroptosis by phosphorylating GPX4 through a moonlighting function. Nat Cell Biol. 2023;25:714–25.
Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Dhruv HD, Gill S, Eichhoff OM, Seashore-Ludlow B, et al. Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature. 2017;547:453–7.
Taylor SS, Ilouz R, Zhang P, Kornev AP. Assembly of allosteric macromolecular switches: lessons from PKA. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:646–58.
Tasken K, Aandahl EM. Localized effects of cAMP mediated by distinct routes of protein kinase A. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:137–67.
Cummings DE, Brandon EP, Planas JV, Motamed K, Idzerda RL, McKnight GS. Genetically lean mice result from targeted disruption of the RII beta subunit of protein kinase A. Nature. 1996;382:622–6.
Folkmanaite M, Zaccolo M. Phase separation of protein kinase A: a new paradigm in cardiac regulation? Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024;21:523.
Zhang JZ, Lu T-W, Stolerman LM, Tenner B, Yang JR, Zhang J-F, et al. Phase Separation of a PKA Regulatory Subunit Controls cAMP Compartmentation and Oncogenic Signaling. Cell. 2020;182:1531–44.
Taylor SS, Zhang P, Steichen JM, Keshwani MM, Kornev AP. PKA: lessons learned after twenty years. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1834:1271–8.
Ramms DJ, Raimondi F, Arang N, Herberg FW, Taylor SS, Gutkind JS. Galphas-protein kinase A (PKA) pathway signalopathies: the emerging genetic landscape and therapeutic potential of human diseases driven by aberrant galphas-PKA signaling. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73:155–97.
Iglesias-Bartolome R, Torres D, Marone R, Feng X, Martin D, Simaan M, et al. Inactivation of a Galpha(s)-PKA tumour suppressor pathway in skin stem cells initiates basal-cell carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17:793–803.
Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, He C. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18:31–42.
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature. 2014;505:117–20.
Zaccara S, Ries RJ, Jaffrey SR. Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:608–24.
Deng X, Qing Y, Horne D, Huang H, Chen J. The roles and implications of RNA m(6)A modification in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20:507–26.
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P, Huang CM, Li CJ, et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell. 2013;49:18–29.
Zhao X, Nedvetsky P, Stanchi F, Vion AC, Popp O, Zühlke K, et al. Endothelial PKA activity regulates angiogenesis by limiting autophagy through phosphorylation of ATG16L1. Elife. 2019;8:e46380.
Song H, Liu D, Wang L, Liu K, Chen C, Wang L, et al. Methyltransferase like 7B is a potential therapeutic target for reversing EGFR-TKIs resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. Molecular Cancer. 2022;21:43.
Ye F, Wu J, Zhang F. METTL16 epigenetically enhances GPX4 expression via m6A modification to promote breast cancer progression by inhibiting ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;638:1–6.
Sapio L, Di Maiolo F, Illiano M, Esposito A, Chiosi E, Spina A, et al. Targeting protein kinase A in cancer therapy: an update. EXCLI J. 2014;13:843–55.
Wu Y, Sun Y, Xu B, Yang M, Wang X, Zhao X. SCARNA10 regulates p53 acetylation-dependent transcriptional activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;669:38–45.
Wang X, Zha M, Zhao X, Jiang P, Du W, Tam AY, et al. Siva1 inhibits p53 function by acting as an ARF E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1551.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Pavel I Nedvetsky (University Hospital Münster, Germany) for kindly suggestion. This work was supported by the grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (82200438, 82200271, 82311530688), the Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2022A1515011946), the Guangdong Zhujiang Talent Program (0920220203), Shenzhen Key Laboratory (ZDSYS20230626091402006) Shenzhen Clinical Research Center for Gastroenterology (LCYSSQ20220823091203008), Natural Science Funds of Zhejiang Province (LQ22H020010) and Leading Innovation and Entrepreneurship Team of Zhejiang Province (2023R01005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and experimental design: XZ, YS, XW. Methodology and data acquisition: YS, XZ, JZ, XW. Analysis and interpretation of data: XZ, YS, JZ, YW, MH, HK, GL, HG, WG, YZ, MS, XW. Manuscript writing: XZ, YZ, MS, XW.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All experiments with animals were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), Sun Yat-sen University (Approve number: SYSU-IACUC-2024-000478) and performed according to the relevant ethical guidelines and regulations. This research did not involve human subject study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Sun, Y., Zou, J. et al. Protein kinase A regulates ferroptosis by controlling GPX4 m6A modification through phosphorylation of ALKBH5. Cell Death Differ 32, 1058–1070 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-025-01453-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-025-01453-3
This article is cited by
-
Epigenetic and post-translational regulatory networks of ferroptosis in the tumor immune microenvironment
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2026)
-
Emerging Dual Roles of ALKBH5 in Ischemia-reperfusion Injury: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2025)
-
Post-translational modifications in hepatocellular carcinoma: mechanisms and therapeutic potential
Medical Oncology (2025)