Abstract
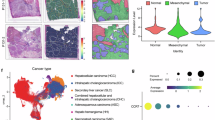
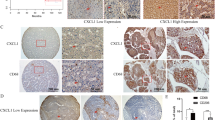
Liver resection is the primary curative treatment for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); however, high recurrence rates remain a major challenge in the absence of effective prognostic and preventive strategies. Here, we identified surgery-induced C-C motif chemokine ligand 11 (CCL11) as a pivotal driver of HCC recurrence through dual mechanisms of immunosuppression and tumor invasiveness. Elevated postoperative circulating CCL11 levels correlated strongly with HCC recurrence and poorer survival, and their integration with clinical parameters enhanced the predictive accuracy of HCC recurrence. Mechanistically, hepatic injury-induced CCL11 recruited immunosuppressive CCR5+CD206+ M2-like macrophages into the residual liver. These macrophages exhibited enhanced PD-L1 expression via activation of the CCL11/IKK/IκB/NF-κB1 axis and promoted regulatory T cell (Treg) induction from naïve CD4+ T cells. Concurrently, CCL11-CCR3 signaling in HCC cells activated PI3K/AKT/MafK to upregulate MMP13, enhancing the invasion ability of HCC cells. In orthotopic models, CCL11 enrichment increased tumor burden and extrahepatic metastases, while post-resection anti-CCL11 therapy reduced HCC recurrence and extended the survival rate of tumor-bearing mice. Our findings unveil CCL11 as a master regulator of the pro-tumorigenic niche post-resection, driving recurrence through coordinated immune evasion and promoting tumor invasiveness. Targeting the CCL11-CCR5/CCR3 axis presents a promising strategy to improve HCC surgical outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting this study are included in the article and its supplementary materials.
References
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12–49.
Zou H, Zhu CZ, Wang C, Wang ZS, Ma X, Han B, et al. Recurrence of barcelona clinic liver cancer stage a hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Am J Med Sci. 2017;354:262–7.
Li CX, Ling CC, Shao Y, Xu A, Li XC, Ng KT-P, et al. CXCL10/CXCR3 signaling mobilized-regulatory T cells promote liver tumor recurrence after transplantation. J Hepatol. 2016;65:944–52.
Jiang J, Ye F, Yang X, Zong C, Gao L, Yang Y, et al. Peri-tumor associated fibroblasts promote intrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by recruiting cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 2017;404:19–28.
Kuang D-M, Peng C, Zhao Q, Wu Y, Chen M-S, Zheng L. Activated monocytes in peritumoral stroma of hepatocellular carcinoma promote expansion of memory T helper 17 cells. Hepatology. 2010;51:154–64.
Liu Q, Zhang H, Jiang X, Qian C, Liu Z, Luo D. Factors involved in cancer metastasis: a better understanding to “seed and soil” hypothesis. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:176.
Fidler IJ, Poste G. The “seed and soil” hypothesis revisited. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:808.
Hughes CE, Nibbs RJB. A guide to chemokines and their receptors. FEBS J. 2018;285:2944–71.
Ozga AJ, Chow MT, Luster AD. Chemokines and the immune response to cancer. Immunity. 2021;54:859–74.
Adar T, Shteingart S, Ben Ya’acov A, Bar-Gil Shitrit A, Goldin E. From airway inflammation to inflammatory bowel disease: eotaxin-1, a key regulator of intestinal inflammation. Clin Immunol. 2014;153:199–208.
Wang J, Man K, Ng KT. Emerging roles of C-C motif ligand 11 (CCL11) in cancers and liver diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2025;26:4662.
Landi A, Weismüller TJ, Lankisch TO, Santer DM, Tyrrell DLJ, Manns MP, et al. Differential serum levels of eosinophilic eotaxins in primary sclerosing cholangitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, and autoimmune hepatitis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014;34:204–14.
Kong M, Dong W, Kang A, Kuai Y, Xu T, Fan Z, et al. Regulatory role and translational potential of CCL11 in liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 2023;78:120–35.
Fan Z, Sun X, Chen X, Liu H, Miao X, Guo Y, et al. C–C motif chemokine CCL11 is a novel regulator and a potential therapeutic target in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. JHEP Rep. 2023;5:100805.
Ng KT, Liu J, Yeung OW, Pang L, Shiu HC, Liu H, et al. Post-transplant inflammatory cytokine signature adds value for predicting tumor recurrence after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int. 2023;17:1596–609.
Ng KT, Pang L, Wang JQ, She WH, Tsang SH, Lo CM, et al. Indications of pro-inflammatory cytokines in laparoscopic and open liver resection for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary & pancreatic diseases international. HBPD INT. 2024;23:257–64.
Ng KT, Xu A, Cheng Q, Guo DY, Lim ZX, Sun CK, et al. Clinical relevance and therapeutic potential of angiopoietin-like protein 4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:196.
Pang L, Yeung OWH, Ng KTP, Liu H, Zhu J, Liu J, et al. Postoperative plasmacytoid dendritic cells secrete IFNα to promote recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and drive hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Cancer Res. 2022;82:4206–18.
Yeung OWH, Lo C-M, Ling C-C, Qi X, Geng W, Li C-X, et al. Alternatively activated (M2) macrophages promote tumour growth and invasiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2015;62:607–16.
Pang L, Ng KT-P, Liu J, Yeung W-HO, Zhu J, Chiu T-LS, et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells recruited by HIF-1α/eADO/ADORA1 signaling induce immunosuppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2021;522:80–92.
Li X, Yao W, Yuan Y, Chen P, Li B, Li J, et al. Targeting of tumour-infiltrating macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 signalling as a therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2015;66:157–67.
Hao Q, Vadgama JV, Wang P. CCL2/CCR2 signaling in cancer pathogenesis. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18:82.
Korbecki J, Kojder K, Siminska D, Bohatyrewicz R, Gutowska I, Chlubek D, et al. CC Chemokines in a tumor: a review of pro-cancer and anti-cancer properties of the ligands of receptors CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, and CCR4. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:8412.
Jöhrer K, Zelle-Rieser C, Perathoner A, Moser P, Hager M, Ramoner R, et al. Up-regulation of functional chemokine receptor CCR3 in human renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2459–65.
Bekaert S, Rocks N, Vanwinge C, Noel A, Cataldo D. Asthma-related inflammation promotes lung metastasis of breast cancer cells through CCL11-CCR3 pathway. Respir Res. 2021;22:61.
Blank S, Nienhüser H, Dreikhausen L, Sisic L, Heger U, Ott K, et al. Inflammatory cytokines are associated with response and prognosis in patients with esophageal cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:47518–32.
Nevola R, Ruocco R, Criscuolo L, Villani A, Alfano M, Beccia D, et al. Predictors of early and late hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. World J Gastroenterol. 2023;29:1243–60.
Zhuang H, Cao G, Kou C, Liu T. CCL2/CCR2 axis induces hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro through activation of the Hedgehog pathway. Oncol Rep. 2018;39:21–30.
Wu J, Chan YT, Lu Y, Wang N, Feng Y. The tumor microenvironment in the postsurgical liver: mechanisms and potential targets of postoperative recurrence in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Res Rev. 2023;43:1946–73.
Xu H-X, Zhu X-D, Zhuang P-Y, Zhang J-B, Zhang W, Kong L-Q, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of placental growth factor in hepatocellular carcinoma and peritumoral liver tissue. Int J Cancer. 2011;128:1559–69.
Lefranc F, Brotchi J, Kiss R. Possible future issues in the treatment of glioblastomas: special emphasis on cell migration and the resistance of migrating glioblastoma cells to apoptosis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2411–22.
Winkler F, Kienast Y, Fuhrmann M, von Baumgarten L, Burgold S, Mitteregger G, et al. Imaging glioma cell invasion in vivo reveals mechanisms of dissemination and peritumoral angiogenesis. Glia. 2009;57:1306–15.
Jaruga B, Hong F, Sun R, Radaeva S, Gao B. Crucial role of IL-4/STAT6 in T cell-mediated hepatitis: up-regulating eotaxins and IL-5 and recruiting leukocytes. J Immunol. 2003;171:3233–44.
Miyamasu M, Misaki Y, Yamaguchi M, Yamamoto K, Morita Y, Matsushima K, et al. Regulation of human eotaxin generation by Th1-/Th2-derived cytokines. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000;122:54–58.
Simson L, Ellyard JI, Dent LA, Matthaei KI, Rothenberg ME, Foster PS, et al. Regulation of carcinogenesis by IL-5 and CCL11: a potential role for eosinophils in tumor immune surveillance. J Immunol. 2007;178:4222–9.
Ivanovska M, Abdi Z, Murdjeva M, Macedo D, Maes A, Maes M. CCL-11 or eotaxin-1: an immune marker for ageing and accelerated ageing in neuro-psychiatric disorders. Pharmaceuticals. 2020;13:230.
Kalluri R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:582–98.
Shiga K, Hara M, Nagasaki T, Sato T, Takahashi H, Takeyama H. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: their characteristics and their roles in tumor growth. Cancers. 2015;7:2443–58.
Xu M, Wang Y, Xia R, Wei Y, Wei X. Role of the CCL2-CCR2 signalling axis in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. Cell Prolif. 2021;54:e13115.
Guo Y, Xie Y-Q, Gao M, Zhao Y, Franco F, Wenes M, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of terminally exhausted CD8+ T cells by IL-10 enhances anti-tumor immunity. Nat Immunol. 2021;22:746–56.
Ling CC, Ng KT, Shao Y, Geng W, Xiao JW, Liu H, et al. Post-transplant endothelial progenitor cell mobilization via CXCL10/CXCR3 signaling promotes liver tumor growth. J Hepatol. 2014;60:103–9.
Liu H, Ling CC, Yeung WHO, Pang L, Liu J, Zhou J, et al. Monocytic MDSC mobilization promotes tumor recurrence after liver transplantation via CXCL10/TLR4/MMP14 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:489.
Shao Y, Lo CM, Ling CC, Liu XB, Ng KT, Chu AC, et al. Regulatory B cells accelerate hepatocellular carcinoma progression via CD40/CD154 signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2014;355:264–72.
Wang L, Lan J, Tang J, Luo N. MCP-1 targeting: shutting off an engine for tumor development. Oncol Lett. 2022;23:26.
Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, Sica A, Locati M. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J Pathol. 2013;229:176–85.
Chaudhary B, Elkord E. Regulatory T cells in the tumor microenvironment and cancer progression: role and therapeutic targeting. Vaccines. 2016;4:28.
Yuan A, Chen JJ, Yao PL, Yang PC. The role of interleukin-8 in cancer cells and microenvironment interaction. Front Biosci. 2005;10:853–65.
Lin X, Kang K, Chen P, Zeng Z, Li G, Xiong W, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 in cancers. Mol Cancer. 2024;23:108.
Dammeijer F, van Gulijk M, Mulder EE, Lukkes M, Klaase L, van den Bosch T, et al. The PD-1/PD-L1-checkpoint restrains T cell immunity in tumor-draining lymph nodes. Cancer Cell. 2020;38:685–700 e688.
Cai J, Wang D, Zhang G, Guo X. The role of PD-1/PD-L1 axis in Treg development and function: implications for cancer immunotherapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:8437–45.
Que Y, Xiao W, Guan YX, Liang Y, Yan SM, Chen HY, et al. PD-L1 expression is associated with FOXP3+ regulatory T-cell infiltration of soft tissue sarcoma and poor patient prognosis. J Cancer. 2017;8:2018–25.
Levina V, Nolen BM, Marrangoni AM, Cheng P, Marks JR, Szczepanski MJ, et al. Role of eotaxin-1 signaling in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:2647–56.
Wang R, Huang K. CCL11 increases the proportion of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg cells and the production of IL‑2 and TGF‑β by CD4+ T cells via the STAT5 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21:2522–32.
Lin S, Zhang X, Huang G, Cheng L, Lv J, Zheng D, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote lung cancer metastasis by CCL11 to activate ERK and AKT signaling and induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor cells. Oncogene. 2021;40:1476–89.
Ogilvie P, Bardi G, Clark-Lewis I, Baggiolini M, Uguccioni M. Eotaxin is a natural antagonist for CCR2 and an agonist for CCR5. Blood. 2001;97:1920–4.
Li S, Pritchard DM, Yu LG. Regulation and function of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancers. 2022;14:3263.
Mustafa S, Koran S, AlOmair L. Insights into the role of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer and its various therapeutic aspects: a review. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:896099.
Main S, Handy R, Wilton J, Smith S, Williams L, Du Fou L, et al. A potent human anti-eotaxin1 antibody, CAT-213: isolation by phage display and in vitro and in vivo efficacy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;319:1395–404.
Humbles AA, Conroy DM, Marleau S, Rankin SM, Palframan RT, Proudfoot AE, et al. Kinetics of eotaxin generation and its relationship to eosinophil accumulation in allergic airways disease: analysis in a guinea pig model in vivo. J Exp Med. 1997;186:601–12.
Nolen BM, Lokshin AE. Targeting CCL11 in the treatment of ovarian cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010;14:157–67.
Zimmermann N, Hershey GK, Foster PS, Rothenberg ME. Chemokines in asthma: cooperative interaction between chemokines and IL-13. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111:227–42; quiz 243.
Lu LC, Cheng AL, Poon RT. Recent advances in the prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Semin Liver Dis. 2014;34:427–34.
Zhu W-J, Huang C-Y, Li C, Peng W, Wen T-F, Yan L-N, et al. Risk factors for early recurrence of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma meeting milan criteria after curative resection. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:7101–6.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Surgical Tissue Bank and staff, Dr. Wan-Ching Yu and Miss Fion Sin for preparing the clinical samples, and Dr. Jana Yim Hung Wo and Dr. Hoi Chung Shiu for assisting the animal and cell experiments, respectively.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program of Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission (JCYJ20240813113042055, JCYJ20210324114403010) and the Theme-based Research Scheme of the Research Grant Council of Hong Kong (TRS: T12-703/19 R).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: J Wang, K Man, and K Ng; Acquisition of data: J Wang, O Yeung, and W Qiu; Analysis and interpretation of data: J Wang, O Yeung, L Pang, X Yang, T Ding, J Liu, and K Ng; Statistical analysis: J Wang, J Liu, T Cheung, Z Hu, and K Ng; Drafting of the manuscript: J Wang and K Ng; Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: J Wang, O Yeung, W Qiu, L Pang, J Liu, X Yang, S Zeng, T Ding, Z Wang, Z Hu, T Cheung, K Man, and K Ng; Administrative, technical, or material support: T Cheung, K Man and K Ng; Final approval of the version to be submitted: J Wang, O Yeung, W Qiu, L Pang, J Liu, X Yang, S Zeng, T Ding, Z Wang, Z Hu, T Cheung, K Man, and K Ng.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by Professor Yufang Shi
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Yeung, O.WH., Qiu, W. et al. CCL11 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after surgery by potentiating immunosuppressive CCR5 + CD206 + M2-like macrophages and promoting tumor invasiveness. Cell Death Dis (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-026-08508-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-026-08508-4