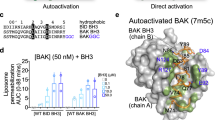
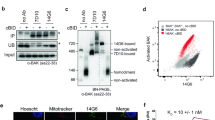
Abstract
It has been widely accepted that mitochondria-dependent apoptosis initiates when select BH3-only proteins (BID, BIM, etc.) directly engage and allosterically activate effector proteins BAX/BAK. Here, through reconstitution of cells lacking all eight pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins, we demonstrate that all BH3-only proteins primarily target the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins BCL-xL/MCL-1, whose simultaneous suppression enables membrane-mediated spontaneous activation of BAX/BAK. BH3-only proteins’ apoptotic activities correlate with affinities for BCL-xL/MCL-1 instead of abilities to directly activate BAX/BAK. Further, BID and BIM do not distinguish BAX from BAK or accelerate BAX/BAK activation following inactivation of BCL-xL/MCL-1. Remarkably, death ligand-induced apoptosis in cells lacking BH3-only proteins and MCL-1 is fully restored by BID mutants capable of neutralizing BCL-xL, but not direct activation of BAX/BAK. Taken together, our findings provide a “Membrane-mediated Permissive” model, in which the BH3-only proteins only indirectly activate BAX/BAK by neutralizing the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins, and thus allowing BAX/BAK to undergo unimpeded, spontaneous activation in the mitochondrial outer membrane milieu, leading to apoptosis initiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adams, J. M. & Cory, S. The BCL-2 arbiters of apoptosis and their growing role as cancer targets. Cell Death Differ. 25, 27–36 (2018).
Youle, R. J. & Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 47–59 (2008).
Chipuk, J. E. & Green, D. R. How do BCL-2 proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization? Trends Cell Biol. 18, 157–164 (2008).
Jiang, X. & Wang, X. Cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73, 87–106 (2004).
Letai, A. et al. Distinct BH3 domains either sensitize or activate mitochondrial apoptosis, serving as prototype cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell 2, 183–192 (2002).
Kim, H. et al. Hierarchical regulation of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by BCL-2 subfamilies. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 1348–1358 (2006).
Czabotar, P. E. et al. Bax crystal structures reveal how BH3 domains activate Bax and nucleate its oligomerization to induce apoptosis. Cell 152, 519–531 (2013).
Kim, H. et al. Stepwise activation of BAX and BAK by tBID, BIM, and PUMA initiates mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol. Cell 36, 487–499 (2009).
Gavathiotis, E. et al. BAX activation is initiated at a novel interaction site. Nature 455, 1076–1081 (2008).
Lovell, J. F. et al. Membrane binding by tBid initiates an ordered series of events culminating in membrane permeabilization by Bax. Cell 135, 1074–1084 (2008).
Czabotar, P. E., Lessene, G., Strasser, A. & Adams, J. M. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 49–63 (2014).
Kuwana, T. et al. BH3 domains of BH3-only proteins differentially regulate Bax-mediated mitochondrial membrane permeabilization both directly and indirectly. Mol. Cell 17, 525–535 (2005).
Kuwana, T. et al. Bid, Bax, and lipids cooperate to form supramolecular openings in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cell 111, 331–342 (2002).
Sarosiek, K. A. et al. BID preferentially activates BAK while BIM preferentially activates BAX, affecting chemotherapy response. Mol. Cell 51, 751–765 (2013).
Du, H. et al. BH3 domains other than Bim and Bid can directly activate Bax/Bak. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 491–501 (2011).
Hockings, C. et al. Bid chimeras indicate that most BH3-only proteins can directly activate Bak and Bax, and show no preference for Bak versus Bax. Cell Death Dis. 6, e1735 (2015).
Chen, H. C. et al. An interconnected hierarchical model of cell death regulation by the BCL-2 family. Nat. Cell Biol. 17, 1270–1281 (2015).
Luna-Vargas, M. P. A. & Chipuk, J. E. Physiological and pharmacological control of BAK, BAX, and beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 26, 906–917 (2016).
Dai, H. et al. Transient binding of an activator BH3 domain to the Bak BH3-binding groove initiates Bak oligomerization. J. Cell Biol. 194, 39–48 (2011).
Willis, S. N. et al. Proapoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev. 19, 1294–1305 (2005).
Willis, S. N. et al. Apoptosis initiated when BH3 ligands engage multiple Bcl-2 homologs, not Bax or Bak. Science 315, 856–859 (2007).
Edlich, F. et al. Bcl-x(L) retrotranslocates Bax from the mitochondria into the cytosol. Cell 145, 104–116 (2011).
O’Neill, K. L., Huang, K., Zhang, J., Chen, Y. & Luo, X. Inactivation of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins activates Bax/Bak through the outer mitochondrial membrane. Genes Dev. 30, 973–988 (2016).
Lopez, H. et al. Perturbation of the Bcl-2 network and an induced Noxa/Bcl-xL interaction trigger mitochondrial dysfunction after DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 15016–15026 (2010).
Zhang, L. et al. Selective involvement of BH3-only proteins and differential targets of Noxa in diverse apoptotic pathways. Cell Death Differ. 18, 864–873 (2011).
Pang, X. et al. The carboxyl-terminal tail of Noxa protein regulates the stability of Noxa and Mcl-1. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 17802–17811 (2014).
Chen, L. et al. Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol. Cell 17, 393–403 (2005).
Li, H., Zhu, H., Xu, C. J. & Yuan, J. Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 94, 491–501 (1998).
Luo, X., Budihardjo, I., Zou, H., Slaughter, C. & Wang, X. Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell 94, 481–490 (1998).
Kotschy, A. et al. The MCL1 inhibitor S63845 is tolerable and effective in diverse cancer models. Nature 538, 477–482 (2016).
Huang, K. et al. Cleavage by caspase 8 and mitochondrial membrane association activate the BH3-only protein bid during TRAIL-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 11843–11851 (2016).
Moldoveanu, T., Follis, A. V., Kriwacki, R. W. & Green, D. R. Many players in BCL-2 family affairs. Trends Biochem. Sci. 39, 101–111 (2014).
Wang, K., Yin, X. M., Chao, D. T., Milliman, C. L. & Korsmeyer, S. J. BID: a novel BH3 domain-only death agonist. Genes Dev. 10, 2859–2869 (1996).
Llambi, F. et al. A unified model of mammalian BCL-2 protein family interactions at the mitochondria. Mol. cell 44, 517–531 (2011).
Walensky, L. D. & Gavathiotis, E. BAX unleashed: the biochemical transformation of an inactive cytosolic monomer into a toxic mitochondrial pore. Trends Biochem. Sci. 36, 642–652 (2011).
Moldoveanu, T. et al. BID-induced structural changes in BAK promote apoptosis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20, 589–597 (2013).
Borner, C. & Andrews, D. W. The apoptotic pore on mitochondria: are we breaking through or still stuck? Cell Death Differ. 21, 187–191 (2014).
Hsu, Y. T. & Youle, R. J. Bax in murine thymus is a soluble monomeric protein that displays differential detergent-induced conformations. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 10777–10783 (1998).
Suzuki, M., Youle, R. J. & Tjandra, N. Structure of Bax: coregulation of dimer formation and intracellular localization. Cell 103, 645–654 (2000).
Fletcher, J. I. et al. Apoptosis is triggered when prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins cannot restrain Bax. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 18081–18087 (2008).
Oltersdorf, T. et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 435, 677–681 (2005).
Greaves, G. et al. BH3-only proteins are dispensable for apoptosis induced by pharmacological inhibition of both MCL-1 and BCL-XL. Cell Death Differ. 26, 1037–1047 (2019).
Pitti, R. M., Marsters, S. A., Ruppert. S., Donahue, C. J., Moore, A., Ashkenazi, A. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 12687–12690 (2019).
George, N. M., Evans, J. J. & Luo, X. A three-helix homo-oligomerization domain containing BH3 and BH1 is responsible for the apoptotic activity of Bax. Genes Dev. 21, 1937–1948 (2007).
Pang, X. et al. Active Bax and Bak are functional holins. Genes Dev. 25, 2278–2290 (2011).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for Keith Johnson and Robert Lewis for helpful discussion and advice. We are also grateful for the UNMC DNA sequencing and flow cytometry facilities for the excellent technical help. This work was supported by a pilot grant from the Nebraska Center for Cellular Signaling (P20-GM103489) and NIH Grants R03CA205496 and R01GM118437 to X.L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.H., K.L.O, and X.L. designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. K.H. and K.L.O. carried out all the experiments. J.L., W.Z., N.H., X.P., W.W., L.S, G.B., Z.L. and L.Z. created some of the cell lines and reagents.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, K., O’Neill, K.L., Li, J. et al. BH3-only proteins target BCL-xL/MCL-1, not BAX/BAK, to initiate apoptosis. Cell Res 29, 942–952 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0231-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0231-y
This article is cited by
-
Parthenolide improves sepsis-induced coagulopathy by inhibiting mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells through BRD4/BCL-xL pathway
Journal of Translational Medicine (2025)
-
Extracellular vesicle-mediated delivery of circp53 suppresses the progression of multiple cancers by activating the CypD/TRAP/HSP90 pathway
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2025)
-
Deciphering molecular specificity in MCL-1/BAK interaction and its implications for designing potent MCL-1 inhibitors
Cell Death & Differentiation (2025)
-
VDAC2 and Bak scarcity in liver mitochondria enables targeting hepatocarcinoma while sparing hepatocytes
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Collaborative orchestration of BH3-only proteins governs Bak/Bax-dependent hepatocyte apoptosis under antiapoptotic protein-deficiency in mice
Cell Death & Differentiation (2025)