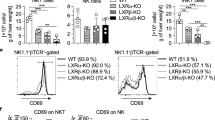
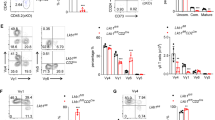
Abstract
Liver X receptors (LXRs) are known as key transcription factors in lipid metabolism and have been reported to play an important role in T-cell proliferation. However, whether LXRs play a role in thymocyte development remains largely unknown. Here, we demonstrated that LXRβ deficiency caused a reduction in single-positive (SP) thymocytes, whereas the transitions from the double-negative to SP stage were normal. Meanwhile, LXRβ-null SP thymocytes exhibited increased apoptosis and impairment of the IL-7Rα-Bcl2 axis. In addition, the LXR agonist T0901317 promoted the survival of SP thymocytes with enhanced IL-7Rα expression in wild-type mice but not in LXRβ-deficient mice. Mechanistically, LXRβ positively regulated the expression of IL-7Rα via direct binding to the Il7r allele in SP thymocytes, and forced expression of IL-7Rα or Bcl2 restored the survival of LXRβ-defective SP thymocytes. Thus, our results indicate that LXRβ functions as an important transcription factor upstream of IL-7Rα to promote the survival of SP thymocytes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taniuchi, I. CD4 helper and CD8 cytotoxic T cell differentiation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 36, 579–601 (2018).
Vacchio, M. S., Ciucci, T. & Bosselut, R. 200 million thymocytes and I: a beginner’s survival guide to T cell development. Methods Mol. Biol. 1323, 3–21 (2016).
Famili, F., Wiekmeijer, A. S. & Staal, F. J. The development of T cells from stem cells in mice and humans. Future Sci. OA 3, FSO186 (2017).
Gascoigne, N. R., Rybakin, V., Acuto, O. & Brzostek, J. TCR signal strength and T cell development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 32, 327–348 (2016).
Barata, J. T., Durum, S. K. & Seddon, B. Flip the coin: IL-7 and IL-7R in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 20, 1584–1593 (2019).
Hong, C., Luckey, M. A. & Park, J. H. Intrathymic IL-7: the where, when, and why of IL-7 signaling during T cell development. Semin Immunol. 24, 151–158 (2012).
Niu, N. & Qin, X. New insights into IL-7 signaling pathways during early and late T cell development. Cell Mol. Immunol. 10, 187–189 (2013).
Zaunders, J. J., Levy, Y. & Seddiki, N. Exploiting differential expression of the IL-7 receptor on memory T cells to modulate immune responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 25, 391–401 (2014).
Tani-ichi, S. et al. Interleukin-7 receptor controls development and maturation of late stages of thymocyte subpopulations. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 612–617 (2013).
Kimura, M. Y. et al. IL-7 signaling must be intermittent, not continuous, during CD8(+) T cell homeostasis to promote cell survival instead of cell death. Nat. Immunol. 14, 143–151 (2013).
Mazzucchelli, R. & Durum, S. K. Interleukin-7 receptor expression: intelligent design. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 144–154 (2007).
Carrette, F. & Surh, C. D. IL-7 signaling and CD127 receptor regulation in the control of T cell homeostasis. Semin Immunol. 24, 209–217 (2012).
Luo, H. et al. Ephrinb1 and Ephrinb2 are associated with interleukin-7 receptor alpha and retard its internalization from the cell surface. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 44976–44987 (2011).
Henriques, C. M., Rino, J., Nibbs, R. J., Graham, G. J. & Barata, J. T. IL-7 induces rapid clathrin-mediated internalization and JAK3-dependent degradation of IL-7Ralpha in T cells. Blood 115, 3269–3277 (2010).
McLeod, I. X., Zhou, X., Li, Q. J., Wang, F. & He, Y. W. The class III kinase Vps34 promotes T lymphocyte survival through regulating IL-7Ralpha surface expression. J. Immunol. 187, 5051–5061 (2011).
Kerdiles, Y. M. et al. Foxo1 links homing and survival of naive T cells by regulating L-selectin, CCR7 and interleukin 7 receptor. Nat. Immunol. 10, 176–184 (2009).
Shi, L. Z. et al. Gfi1-Foxo1 axis controls the fidelity of effector gene expression and developmental maturation of thymocytes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, E67–E74 (2017).
Feng, X. et al. Transcription factor Foxp1 exerts essential cell-intrinsic regulation of the quiescence of naive T cells. Nat. Immunol. 12, 544–550 (2011).
Xue, H. H. et al. GA binding protein regulates interleukin 7 receptor alpha-chain gene expression in T cells. Nat. Immunol. 5, 1036–1044 (2004).
Wang, B. & Tontonoz, P. Liver X receptors in lipid signalling and membrane homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 14, 452–463 (2018).
Repa, J. J. et al. Regulation of mouse sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c gene (SREBP-1c) by oxysterol receptors, LXRalpha and LXRbeta. Genes Dev. 14, 2819–2830 (2000).
Hong, C. & Tontonoz, P. Liver X receptors in lipid metabolism: opportunities for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Disco. 13, 433–444 (2014).
Pascual-Garcia, M. & Valledor, A. F. Biological roles of liver X receptors in immune cells. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 60, 235–249 (2012).
Joseph, S. B. et al. LXR-dependent gene expression is important for macrophage survival and the innate immune response. Cell 119, 299–309 (2004).
Bensinger, S. J. et al. LXR signaling couples sterol metabolism to proliferation in the acquired immune response. Cell 134, 97–111 (2008).
Alberti, S. et al. Hepatic cholesterol metabolism and resistance to dietary cholesterol in LXRbeta-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 107, 565–573 (2001).
Liu, Z. et al. Cutting edge: transcription factor BCL6 is required for the generation, but not maintenance, of memory CD8(+) T cells in acute viral infection. J. Immunol. 203, 323–327 (2019).
Xu, L. et al. The transcription factor TCF-1 initiates the differentiation of TFH cells during acute viral infection. Nat. Immunol. 16, 991–999 (2015).
Yang, W. et al. Potentiating the antitumour response of CD8(+) T cells by modulating cholesterol metabolism. Nature 531, 651–655 (2016).
Guo, X. et al. Lipid-dependent conformational dynamics underlie the functional versatility of T-cell receptor. Cell Res. 27, 505–525 (2017).
Fink, P. J. The biology of recent thymic emigrants. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 31, 31–50 (2013).
Li, C. S. et al. Trap1a is an X-linked and cell-intrinsic regulator of thymocyte development. Cell Mol. Immunol. 14, 685–692 (2017).
Repa, J. J. et al. Regulation of absorption and ABC1-mediated efflux of cholesterol by RXR heterodimers. Science 289, 1524–1529 (2000).
Houck, K. A. et al. T0901317 is a dual LXR/FXR agonist. Mol. Genet. Metab. 83, 184–187 (2004).
Bock, F. J. & Tait, S. W. G. Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 85–100 (2020).
Wang, Y., Viscarra, J., Kim, S. J. & Sul, H. S. Transcriptional regulation of hepatic lipogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 678–689 (2015).
de la Rosa, J. V., Ramon-Vazquez, A., Tabraue, C. & Castrillo, A. Analysis of LXR nuclear receptor cistrome through ChIP-seq data bioinformatics. Methods Mol. Biol. 1951, 99–109 (2019).
Ito, A. et al. LXRs link metabolism to inflammation through Abca1-dependent regulation of membrane composition and TLR signaling. eLife 4, e08009 (2015).
Heinz, S. et al. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol. Cell 38, 576–589 (2010).
Pehkonen, P. et al. Genome-wide landscape of liver X receptor chromatin binding and gene regulation in human macrophages. BMC Genomics 13, 50 (2012).
Park, J. H. et al. Signaling by intrathymic cytokines, not T cell antigen receptors, specifies CD8 lineage choice and promotes the differentiation of cytotoxic-lineage T cells. Nat. Immunol. 11, 257–264 (2010).
Park, J. H. et al. Suppression of IL7Ralpha transcription by IL-7 and other prosurvival cytokines: a novel mechanism for maximizing IL-7-dependent T cell survival. Immunity 21, 289–302 (2004).
Ligons, D. L. et al. CD8 lineage-specific regulation of interleukin-7 receptor expression by the transcriptional repressor Gfi1. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 34386–34399 (2012).
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr J.Å. Gustafsson (Karolinska Institutet) for providing LXRα- and LXRβ-deficient mice. We thank Dr H.H. Xue (University of Iowa) for providing retroviral vectors. We thank the core facility center of Third Military Medical University for cell sorting. This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFA0502203 to X.Z. and No. 2016YFA0502204 to Y.W.), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81571537 to T.Z., No. 31770949 to X.Z., No. 31770972 to Z.X., and No. 81571604 to J.Z.), and the Chongqing Basic and Frontier Research Project (No. cstc2015jcyjBX0086 to H.He.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.Hu., X.W., and D.M. performed the experiments and analyzed the data with assistance from Y.F., L.Z., Z.L., S.T., X.L., and Y.Ca. X.Z., Y.W., T.Z., H.He., Z.X., and J.Z. procured several grants. Y.Ch. provided LXRα- and LXRβ-deficient mice. X.Z., H.Hu., and T.Z. designed the study. X.Z. and H.Hu. wrote the paper. X.Z., Y.W., and T.Z. supervised the study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Wu, X., Meng, D. et al. Liver X receptor β is required for the survival of single-positive thymocytes by regulating IL-7Rα expression. Cell Mol Immunol 18, 1969–1980 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-00546-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-00546-y