Abstract
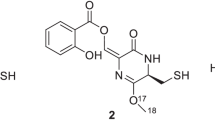
A new piperazine derivative designated helvamide was isolated as a pair of rotamers (1 and 2) from the culture broth of the fungus Aspergillus nidulans BF-0142 along with a known helvafuranone (3). The structures of 1 and 2 were elucidated based on spectroscopic analyses by the interpretation of one-dimensional and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance data, ROESY (rotational Overhauser effect spectroscopy) correlations, and a chemical method. Helvamide existed as a rotameric mixture (1 and 2) in dimethyl sulfoxide. Helvamide inhibited sterol O-acyltransferases 1 and 2 (SOAT1 and SOAT2) in enzyme-based and cell-based assays using SOAT1-expressing and SOAT2-expressing Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kang HK, Seo CH, Park Y. Marine peptides and their anti-infective activities. Mar Drugs. 2015;13:618–54.
Newman DJ, Cragg GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2010. J Nat Prod. 2012;75:311–35.
Debbab A, Aly AH, Lin WH, Proksch P. Bioactive compounds from marine bacteria and fungi. Microb Biotechnol. 2010;3:544–63.
Trzoss L, Fukuda T, Costa-Lotufo LV, Jimenez P, La Clair JJ, Fenical W. Seriniquinone, a selective anticancer agent, induces cell death by autophagocytosis, targeting the cancer-protective protein dermcidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:14687–92.
Fukuda T, Takahashi M, Nagai K, Harunari E, Imada C, Tomoda H. Isomethoxyneihumicin, a new cytotoxic agent produced by marine Nocardiopsis alba KM6-1. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2017;70:590–4.
Fukuda T, Shinkai M, Sasaki E, Nagai K, Kurihara Y, Kanamoto A, Tomoda H. Graphiumins, new thiodiketopiperazines from the marine-derived fungus Graphium sp. OPMF00224. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2015;68:620–7.
Fukuda T, Nagai K, Kurihara Y, Kanamoto A, Tomoda H. Graphiumins I and J, new thiodiketopiperazines from the marine-derived fungus Graphium sp. OPMF00224. Natural Product. Sciences. 2015;21:251–60.
Furukawa T, Fukuda T, Nagai K, Uchida R, Tomoda H. Helvafuranone produced by the fungus Aspergillus nidulans BF142 isolated from hot spring-derived soil. Nat Prod Commun. 2016;11:1001–3.
Fujita T, Hayashi H. New brasiliamide congeners, brasiliamides C, D and E, from Penicillium brasilianum batista JV-379. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2004;68:820–6.
Shin C-G, Kato H, Yonezawa Y, Hayakawa M, Yoshimura J. Synthesis and structural assignment of naturally occurring 3-benzyl-6-benzylidene-2,5-piperazinedione. Heterocycles. 1980;14:1767–70.
Ohshiro T, Tomoda H. Isoform-specific inhibitors of ACATs: recent advances and promising developments. Fut Med Chem. 2011;3:2039–61.
Sekiya T, et al. Syntheses and pharmacological activities of novel optically active inhibitors of Acyl-CoA: cholesterol O-acyltransferase: EAB-309((R)-N-2-(1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl)heptyl-N’-2,6-diisopropylphenylurea) and its enantiomer. Chem Pharm Bull. 1994;42:586–91.
Matsuda D, et al. Molecular target of piperine in the inhibition of lipid droplet accumulation in macrophages. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008;31:1063–6.
Ohishi K, et al. Inhibitory effects of N-(3,5-dimethoxy-4-n-octyloxycinnamoyl)-N-(3,4- dimethylphenyl)piperazine (YIC-C8-434), an acyl-CoA:cholesterol O-acyltransferase inhibitor, on cholesterol esterification in the intestine and liver. Biol Pharm Bull. 2003;26:1125–8.
Lada AT, et al. Identification of ACAT1- and ACAT2-specific inhibitors using a novel, cell-based fluorescence assay: individual ACAT uniqueness. J Lipid Res. 2004;45:378–86.
Ohshiro T, Rudel LL, Ōmura S, Tomoda H. Selectivity of microbial acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitors toward isozymes. J Antibiot. 2007;60:43–51.
Bligh EG, Dyer W. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959;37:911–7.
Field FJ, Cooper AD, Erickson SK. Regulation of rabbit intestinal acyl coenzyme A-cholesterol acyltransferase in vivo and in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1982;83:873–80.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Noriko Sato (School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kitasato University) for the measurements of NMR spectra and Prof. LL Rudel (Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, NC, USA) for kindly providing SOAT1-CHO and SOAT2-CHO cells. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 15K07417 (to TF), JSPS KAKENHI Grant number JP26253009 (to HT), and the Takeda Science Foundation (to HT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuda, T., Furukawa, T., Kobayashi, K. et al. Helvamide, a new inhibitor of sterol O-acyltransferase produced by the fungus Aspergillus nidulans BF-0142. J Antibiot 72, 8–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-018-0101-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-018-0101-8
This article is cited by
-
New piperazine derivatives helvamides B–C from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium velutinum ZK-14 uncovered by OSMAC (One Strain Many Compounds) strategy
Natural Products and Bioprospecting (2024)