Abstract
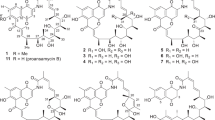
Emericellopsic acid (1), the first B/C ring-rearranged fusidane-type antibiotic possessing a 6/5/7/5-fused ring framework, together with seven known helvolic acid derivatives, was isolated from the sponge-associated fungus Emericellopsis maritima IMB18-123 cultivated with autoclaved Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The structure of 1 was determined by extensive spectroscopic data analysis combined with ECD calculation. Compound 1 exhibited moderate antimicrobial activities against Staphylococcus aureus and S. epidermidis with the minimum inhibition concentration of 4−8 μg ml−1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Godtfredsen WO, Jahnsen S, Lorck H, Roholt K, Tybring L. Fusidic acid: a new antibiotic. Nature. 1962;193:987.
Chain E, Florey HW, Jennings MA, Williams TI. Helvolic acid, an antibiotic produced by Aspergillus fumigatus, mut. helvola Yuill. Br J Exp Pathol. 1943;24:108–19.
Burton HS, Abraham EP. Isolation of antibiotics from a species of Cephalosporium. cephalosporins P1, P2, P3, P4, and P5. Biochem J. 1951;50:168–74.
von Daehne W, Godtfredsen WO, Rasmussen PR. Structure-activity relationships in fusidic acid-type antibiotics. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1979;25:95–146.
Fernandes P. Fusidic acid: a bacterial elongation factor inhibitor for the oral treatment of acute and chronic staphylococcal infections. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016;6:a025437.
Williamson DA, Carter GP, Howden BP. Current and emerging topical antibacterials and antiseptics: agents, action, and resistance patterns. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2017;30:827–60.
Marian E, Tita B, Duteanu N, Vicas L, Ciocan S, Jurca T, et al. Antimicrobial activity of fusidic acid inclusion complexes. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;101:65–73.
Zhao M, Gödecke T, Gunn J, Duan JA, Che CT. Protostane and fusidane triterpenes: a mini-review. Molecules. 2013;18:4054–80.
Cao Z-Q, Lv J-M, Liu Q, Qin S-Y, Chen G-D, Dai P, et al. Biosynthetic study of cephalosporin P1 reveals a multifunctional P450 enzyme and a site-selective acetyltransferase. ACS Chem Biol. 2020;15:44–51.
The compound name given in the reference with 29-nordammarane as the parent structure should be corrected by 29-norprotostane, Kong FD, Huang XL, Ma QY, Xie QY, Wang P, Chen PW, et al. Helvolic acid derivatives with antibacterial activities against Streptococcus agalactiae from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus HNMF0047. J Nat Prod. 2018;81:1869–76.
Afiyatullov S, Zhuravleva OI, Antonov AS, Kalinovsky AI, Pivkin MV, Menchinskaya ES, et al. New metabolites from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nat Prod Commun. 2012;7:497–500.
Tian C, Gao H, Peng XP, Li G, Lou HX. Fusidic acid derivatives from the endophytic fungus Acremonium pilosum F47. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2021;23:1148–55.
Zhang ZB, Du SY, Ji B, Ji CJ, Xiao YW, Yan RM, et al. New helvolic acid derivatives with antibacterial activities from Sarocladium oryzae DX-THL3, an endophytic fFungus from Dongxiang Wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Molecules. 2021;26:1828.
Zhang B, Zhang T, Xu J, Lu J, Qiu P, Wang T, et al. Marine sponge-associated fungi as potential novel bioactive natural product sources for drug discovery: a review. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020;20:1966–2010.
Hao X, Li S, Ni J, Wang G, Li F, Li Q, et al. Acremopeptaibols A–F, 16-residue peptaibols from the sponge-derived Acremonium sp. IMB18-086 cultivated with heat-killed Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Nat Prod. 2021;84:2990–3000.
Li J, Chen M, Hao X, Li S, Li F, Yu L, et al. Structural revision and absolute configuration of burnettramic acid A. Org Lett. 2020;22:98–101.
Li S, Li Y, Yu T, Wei X, Zhang Y, Chen B, et al. Discovery of potent antiosteoporotic cyclic depsipeptides with an unusual nitrile hydroxy acid from Microascus croci. Bioorg Chem. 2025;155:108133.
Zaman KAU, Hu Z, Wu X, Hou S, Saito J, Kondratyuk TP, et al. NF-κB inhibitory and antibacterial helvolic and fumagillin derivatives from Aspergillus terreus. J Nat Prod. 2020;83:730–7.
Godtfredsen WO, Rastrup-Andersen N, Vangedal S, Ollis WD. Metabolites of fusidium coccineum. Tetrahedron. 1979;35:2419–31.
Ratnaweera PB, Williams DE, de Silva ED, Wijesundera RL, Dalisay DS, Andersen RJ. Helvolic acid, an antibacterial nortriterpenoid from a fungal endophyte, Xylaria sp. of orchid Anoectochilus setaceus endemic to Sri Lanka. Mycology. 2014;5:23–8.
Song X, Lv J, Cao Z, Huang H, Chen G, Awakawa T, et al. Extensive expansion of the chemical diversity of fusidane-type antibiotics using a stochastic combinational strategy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11:1676–85.
Lv J-M, Hu D, Gao H, Kushiro T, Awakawa T, Chen G-D, et al. Biosynthesis of helvolic acid and identification of an unusual C-4-demethylation process distinct from sterol biosynthesis. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1644.
Mitsuguchi H, Seshime Y, Fujii I, Shibuya M, Ebizuka Y, Kushiro T. Biosynthesis of steroidal antibiotic fusidanes: functional analysis of oxidosqualene cyclase and subsequent tailoring enzymes from Aspergillus fumigatus. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:6402–11.
Fujimoto H, Negishi E, Yamaguchi K, Nishi N, Yamazaki M. Isolation of new tremorgenic metabolites from an ascomycete, Corynascus setosus. Chem Pharm Bull. 1996;44:1843–8.
Lee SY, Kinoshita H, Ihara F, Igarashi Y, Nihira T. Identification of novel derivative of helvolic acid from Metarhizium anisopliae grown in medium with insect component. J Biosci Bioeng. 2008;105:476–80.
Molecular operating environment (moe), 2019.01. Chemical Computing Group Inc. 1010 Sherbooke St. West, Suite #910, Montreal, QC, Canada, H3A 2R7, 2019.
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, et al. Gaussian 09, Revision A.1. Wallingford CT: Gaussian, Inc.; 2009.
Bruhn T, Schaumlöffel A, Hemberger Y, Bringmann G. SpecDis: Quantifying the Comparison of Calculated and Experimental Electronic Circular Dichroism Spectra. Chirality. 2013;25:243–9.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 82273830), CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS, 2021-I2M-1-055 and 2024-I2M-TS-016), and National Key R&D Program of China (Grant no. 2024YFC2309604).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Hao, X., Li, Y. et al. Emericellopsic acid, a helvolic acid derivative with a 6/5/7/5 tetracyclic skeleton from sponge-derived Emericellopsis maritima. J Antibiot 78, 580–585 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-025-00852-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-025-00852-5