Abstract
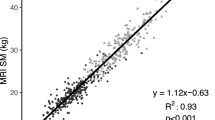
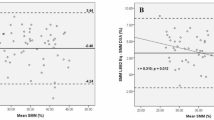
Survivors of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) experience severe muscle wasting. Upper arm anthropometrics can provide a quick, non-invasive estimate of muscle status, but its accuracy is unknown. This study examines the accuracy of upper arm percent muscle area (UAMA) with reference measures of lean mass from dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). Data are from 120 ARDS survivors participating in a multicenter national study. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, by patient sex, demonstrated that UAMA did no better than chance in discriminating low appendicular skeletal muscle mass identified using DXA findings (c-statistics, 6 months: 0.50–0.59, 12 months: 0.54–0.57). Modest correlations of UAMA with DXA measures (whole-body: r = 0.46–0.49, arm-specific: r = 0.50–0.51, p < 0.001) and Bland–Altman plots indicate poor precision. UAMA is not an appropriate screening measure for estimating muscle mass when compared to a DXA reference standard. Alternate screening measures should be evaluated in ARDS survivors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Puthucheary ZA, Rawal J, McPhail M, Connolly B, Ratnayake G, Chan P, et al. Acute skeletal muscle wasting in critical illness. JAMA. 2013;310:1591–600.
Herridge MS, Cheung AM, Tansey CM, Matte-Martyn A, Diaz-Granados N, Al-Saidi F, et al. One-year outcomes in survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:683–93.
Herridge MS, Tansey CM, Matté A, Tomlinson G, Diaz-Granados N, Cooper A, et al. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1293–304.
Pfoh ER, Wozniak AW, Colantuoni E, Dinglas VD, Tellez PAM, Shanholtz C, et al. Physical declines occurring after hospital discharge in ARDS survivors: a 5-year longitudinal study. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42:1557–66.
Fan E, Dowdy DW, Colantuoni E, Mendez-Tellez PA, Sevransky JE, Shanholtz C, et al. Physical complications in acute lung injury survivors: a two-year longitudinal prospective study. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:849–59.
Baumgartner RN, Koehler KM, Gallagher D, Romero L, Heymsfield SB, Ross RR, et al. Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. Am J Epidemiol. 1998;147:755–63.
Frisancho AR. Anthropometric standards for the assessment of growth and nutritional status. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press; 1990.
Guglielmi G, Ponti F, Agostini M, Amadori M, Battista G, Bazzocchi A. The role of DXA in sarcopenia. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2016;28:1047–60.
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing. 2010;39:412–23.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the NHLBI (R24 HL111895, R01HL091760, R01HL091760-02S1, R01HL096504, R01HL88045 and P050HL73994), the Johns Hopkins Institute for Clinical and Translational Research (ICTR) (UL1 TR 000424-06), and the ALTA, EDEN, OMEGA and SAILS trials (contracts for sites participating in this study: HSN268200536170C, HHSN268200536171C, HHSN268200536173C, HHSN268200536174C, HSN268200536175C, and HHSN268200536179C).
Author contributions
KSC, MM and DMN conceived and designed the study. All authors contributed to the analysis plan. MM, CLH, EWE, PEM, ROH, DMN, and VDD acquired the data and LAF performed all analyses. All authors were involved in the interpretation of study results. KSC and MM drafted the manuscript and all authors critically revised it for important intellectual content and approved the final version to be submitted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, K.S., Mourtzakis, M., Aronson Friedman, L. et al. Upper arm anthropometrics versus DXA scan in survivors of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur J Clin Nutr 72, 613–617 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0106-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0106-1