Abstract
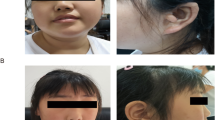
Trio based whole exome sequencing via the Deciphering Developmental Disorders (DDD) study has identified three individuals with de novo frameshift variants in the Suppressor of Variegation, Enhancer of Zeste, and Trithorax (SET) gene. Variants in the SET gene have not previously been recognised to be associated with human developmental disorders. Here we report detailed phenotypic information and propose that SET is a new Intellectual Disability/Developmental Delay (ID/DD) gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Firth HV, Wright CF. The Deciphering Developmental Disorders (DDD) study. Dev Med & Child Neurol. 2011;53:702–3.
Deciphering Developmental Disorders Study. Prevalence and architecture of de novo mutations in developmental disorders. Nature. 2017;542:433–8.
Hamdan FF, Srour M, Capo-Chichi J-M, Daoud H, Nassif C, Patry L, et al. De Novo Mutations in Moderate or Severe Intellectual Disability. PLoS Genet 2014;10:e1004772.
UNIPROT. http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q01105. Accessed 1 Dec. 2016.
Canela N, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Estanyol JM, et al. The SET protein regulates G2/M transition by modulating cyclin B-Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 Activity. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:1158–64.
Miyamoto S, Suzuki T, Muto S, et al. Positive and negative regulation of the cardiovascular transcription factor KLF5 by p300 and the oncogenic regulator SET through interaction and acetylation on the DNA-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:8528–41.
Karetsoua Z, Martica G, Tavoularia S, et al. Prothymosin α associates with the oncoprotein SET and is involved in chromatin decondensation. FEBS Lett. 2004;577:496–500.
Wright CF, Firth HV, Study DDD, et al. Genetic diagnosis of developmental disorders in the DDD study: a scalable analysis of genome-wide research data. Lancet. 2015;385:1305–14.
Ramu A, Noordam MJ, Schwartz RS, et al. DeNovoGear: De novo indel and point mutation discovery and phasing. Nat Methods. 2013;10:985–7.
UK-WHO growth charts. www.rcpch.ac.uk/growthcharts.
Huang N, Lee I, Marcotte EM, Hurles ME. Characterising and predicting haploinsufficiency in the human genome. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1001154.
Firth H, Richards SM, Bevan P, et al. DECIPHER: database of chromosomal imbalance and phenotype in humans using ensembl resources. Am J Human Genet. 2009;84:524–33.
Lek M, Karczewski KJ, Exome Aggregation Consortium, et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature. 2016;536:285–91.
DECIPHER. decipher.sanger.ac.uk. Accessed 20 Mar. 2018.
National Center for Biotechnology Information, Clinvar. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/. Accessed 12 April 2018.
von Lindern, M, van Baal, S, Wiegant, J, Raap, A, Hagemeijer, A, Grosveld, G, ‘Can,’ a putative oncogene associated with myeloid leukemogenesis, may be activated by fusion of its 3-prime half to different genes: characterization of the ‘set’ gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12:3346–55.
Wang D, Kon N, Lasso G, et al. Acetylation-regulated interaction between p53 and SET reveals a widespread regulatory mode. Nature 2016;538:118–22.
Kim DW, KK, Kim JY, Lee KS, Seo SB. Negative regulation of neuronal cell differentiation by INHAT subunit SET/TAF-Iβ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;3:419–25.
Madeira A, Pommet JM, Prochiantz A, Allinquant B. SET protein (TAF1beta, I2PP2A) is involved in neuronal apoptosis induced by an amyloid precursor protein cytoplasmic subdomain. FASEB J. 2005;19:1905–7.
Leung JW, Leitch A, Wood JL, et al. SET nuclear oncogene associates with microcephalin/MCPH1 and regulates chromosome condensation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:21393–400.
Hoischen A, van Bon BW, Gilissen C, et al. De novo mutations of SETBP1 cause Schinzel-Giedion syndrome. Nat Genet. 2010;42:483–5.
Filges I, Shimojima K, Okamoto N, et al. Reduced expression by SETBP1 haploinsufficiency causes developmental and expressive language delay indicating a phenotype distinct from Schinzel-Giedion syndrome. J Med Genet. 2011;48:117–22.
Wang S, Wang Y, Lu Q, et al. The expression and distributions of ANP32A in the developing brain. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:8.
Chai G-S, Feng Q, Wang Z-H, et al. Downregulating ANP32A rescues synapse and memory loss via chromatin remodeling in Alzheimer model. Mol Neurodegener. 2017;12:34.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the families for their participation. The DDD study presents independent research commissioned by the Health Innovation Challenge Fund (grant number HICF-1009-003), a parallel funding partnership between the Wellcome Trust and the Department of Health, and the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute (grant numberWT098051). The views expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the Wellcome Trust or the Department of Health. The study has UK Research Ethics Committee approval (10/H0305/83, granted by the Cambridge South REC, and GEN/284/12 granted by the Republic of Ireland REC). The research team acknowledges the support of the National Institute for Health Research, through the Comprehensive Clinical Research Network.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richardson, R., Splitt, M., Newbury-Ecob, R. et al. SET de novo frameshift variants associated with developmental delay and intellectual disabilities. Eur J Hum Genet 26, 1306–1311 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-018-0199-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-018-0199-y
This article is cited by
-
Identifying SETBP1 haploinsufficiency molecular pathways to improve patient diagnosis using induced pluripotent stem cells and neural disease modelling
Molecular Autism (2024)
-
Whole exome sequencing and transcriptome analysis in two unrelated patients with novel SET mutations
Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
Balanced SET levels favor the correct enhancer repertoire during cell fate acquisition
Nature Communications (2023)