Abstract
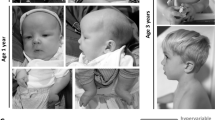
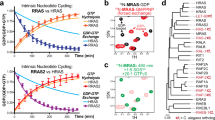
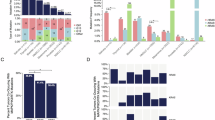
Specific activating missense HRAS variants cause Costello syndrome (CS), a RASopathy with recognizable facial features. The majority of these dominant disease causing variants affect the glycine residues in position 12 or 13. A clinically suspected CS diagnosis can be confirmed through identification of a dominant pathogenic HRAS variant. A novel HRAS variant predicting p.(Glu62_Arg68dup) was identified in an individual with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Chiari 1 malformation and ectodermal findings consistent with a RASopathy. Functional studies showed that the p.Glu62_Arg68dup alteration affects HRAS interaction with effector protein PIK3CA (catalytic subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase) and the regulator neurofibromin 1 (NF1) GTPase-activating protein (GAP). HRASGlu62_Arg68dup binding with effectors rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (RAF1), RAL guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator (RALGDS) and phospholipase C1 (PLCE1) was enhanced. Accordingly, p.Glu62_Arg68dup increased steady-state phosphorylation of MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 downstream of RAF1, whereas AKT phosphorylation downstream of PI3K was not significantly affected. Growth factor stimulation revealed that expression of HRASGlu62_Arg68dup abolished the HRAS’ capacity to modulate downstream signaling. Our data underscore that different qualities of dysregulated HRAS-dependent signaling dynamics determine the clinical severity in CS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gripp KW, Morse LA, Axelrad M, Chatfield KC, Chidekel A, Dobyns W, et al. Costello syndrome: clinical phenotype, genotype and management guidelines. Am J Med Genet. 2019;179:1725–44.
Grant AR, Cushman BJ, Cavé H, Dillon MW, Gelb BD, Gripp KW, et al. Assessing the gene-disease association of 19 genes with the RASopathies using the ClinGen gene curation framework. Hum Mutat. 2018;39:1485–93.
Sol-Church K, Gripp KW The molecular basis of Costello syndrome. In: Zenker M (editor) Noonan syndrome and related disorders—a matter of deregulated Ras signaling. Monographs in human genetics, vol 17, Basel: Karger; 2009. p. 94–103
Xu F, Wang HJ, Lin ZM, Yu B. Recurrent duplication mutation in HRAS causing mild Costello syndrome in a Chinese patient. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:404–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/ced.12571
Lorenz S, Lissewski C, Simsek-Kiper PO, Alanay Y, Boduroglu K, Zenker M, et al. Functional analysis of a duplication (p.E63_D69dup) in the switch II region of HRAS: new aspects of the molecular pathogenesis underlying Costello syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22:1643–53. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt014
Gremer L, De Luca A, Merbitz-Zahradnik T, Dallapiccola B, Morlot S, Tartaglia M, et al. Duplication of Glu37 in the switch I region of HRAS impairs effector/GAP binding and underlies Costello syndrome by promoting enhanced growth factor-dependent MAPK and AKT activation. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19:790–802. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddp548
Gripp KW, Bifeld E, Stabley DL, Hopkins E, Meien S, Vinette K, et al. A novel HRAS substitution (c.266C>G; p.S89C) resulting in decreased downstream signaling suggests a new dimension of RAS pathway dysregulation in human development. Am J Med Genet A. 2012;158A:2106–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.35449
Gurovich Y, Hanani Y, Bar O, Nadav G, Fleischer N, Gelbman D, et al. Identifying facial phenotypes of genetic disorders using deep learning. Nat Med. 2019;25:60–64.
Scheffzek K, Ahmadian MR, Kabsch W, Wiesmuller L, Lautwein A, Schmitz F, et al. The Ras-RasGAP complex: structural basis for GTPase activation and its loss in oncogenic Ras mutants. Science. 1997;277:333–8.
Boriack-Sjodin PA, Margarit SM, Bar-Sagi D, Kuriyan J. The structural basis of the activation of Ras by Sos. Nature. 1998;394:337–43.
Vetter IR, Wittinghofer A. The guanine nucleotide-binding switch in three dimensions. Science. 2001;294:1299–304.
Gripp KW, Kolbe V, Brandenstein LI, Rosenberger G. Attenuated phenotype of Costello syndrome and early death in a patient with an HRAS mutation (c.179G>T; p.Gly60Val) affecting signalling dynamics. Clin Genet. 2017;92:332–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.12980
Ahmadian MR, Kiel C, Stege P, Scheffzek K. Structural fingerprints of the Ras-GTPase activating proteins neurofibromin and p120GAP. J Mol Biol. 2003;329:699–710.
Pacold ME, Suire S, Perisic O, Lara-Gonzalez S, Davis CT, Walker EH, et al. Crystal structure and functional analysis of Ras binding to its effector phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma. Cell. 2000;103:931–43.
Walker EH, Perisic O, Ried C, Stephens L, Williams RL. Structural insights into phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalysis and signalling. Nature. 1999;402:313–20.
Moodie SA, Paris M, Villafranca E, Kirshmeier P, Willumsen BM, Wolfman A. Different structural requirements within the switch II region of the Ras protein for interactions with specific downstream targets. Oncogene. 1995;11:447–54.
Bunney TD, Harris R, Gandarillas NL, Josephs MB, Roe SM, Sorli SC, et al. Structural and mechanistic insights into ras association domains of phospholipase C epsilon. Mol Cell. 2006;21:495–507.
Gripp KW, Sol-Church K, Smpokou P, Graham GE, Stevenson DA, Hanson H, et al. An attenuated phenotype of Costello syndrome in three unrelated individuals with a HRAS c.179G>A (p.Gly60Asp) mutation correlates with uncommon functional consequences. Am J Med Genet A. 2015;167A:2085–97.
Acknowledgements
We thank the family for allowing us to share this information.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF, GeNeRARe, TP6 to GR, funding code 01GM1902E).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
KWG is the CMO for FDNA, the company providing the Face2Gene application.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gripp, K.W., Baker, L., Robbins, K.M. et al. The novel duplication HRAS c.186_206dup p.(Glu62_Arg68dup): clinical and functional aspects. Eur J Hum Genet 28, 1548–1554 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0662-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0662-4
This article is cited by
-
A novel HRAS c.466C>T p.(Phe156Leu) variant in two patients with attenuated features of Costello syndrome
European Journal of Human Genetics (2022)