Abstract
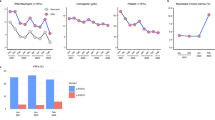
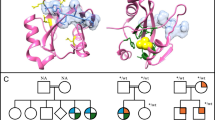
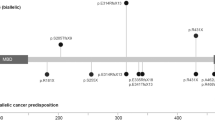
The MCM2-7 helicase is a heterohexameric complex with essential roles as part of both the pre-replication and pre-initiation complexes in the early stages of DNA replication. Meier-Gorlin syndrome, a rare primordial dwarfism, is strongly associated with disruption to the pre-replication complex, including a single case described with variants in MCM5. Conversely, a biallelic pathogenic variant in MCM4 underlies immune deficiency with growth retardation, features also seen in individuals with pathogenic variants in other pre-initiation complex encoding genes such as GINS1, MCM10, and POLE. Through exome and chromium genome sequencing, supported by functional studies, we identify biallelic pathogenic variants in MCM7 and a strong candidate biallelic pathogenic variant in MCM3. We confirm variants in MCM7 are deleterious and through interfering with MCM complex formation, impact efficiency of S phase progression. The associated phenotypes are striking; one patient has typical Meier-Gorlin syndrome, whereas the second case has a multi-system disorder with neonatal progeroid appearance, lipodystrophy and adrenal insufficiency. We provide further insight into the developmental complexity of disrupted MCM function, highlighted by two patients with a similar variant profile in MCM7 but disparate clinical features. Our results build on other genetic findings linked to disruption of the pre-replication and pre-initiation complexes, and the replisome, and expand the complex clinical genetics landscape emerging due to disruption of DNA replication.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evrin C, Clarke P, Zech J, Lurz R, Sun J, Uhle S, et al. A double-hexameric MCM2-7 complex is loaded onto origin DNA during licensing of eukaryotic DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:20240–5.
Remus D, Beuron F, Tolun G, Griffith JD, Morris EP, Diffley JF. Concerted loading of Mcm2-7 double hexamers around DNA during DNA replication origin licensing. Cell. 2009;139:719–30.
Duzdevich D, Warner MD, Ticau S, Ivica NA, Bell SP, Greene EC. The dynamics of eukaryotic replication initiation: origin specificity, licensing, and firing at the single-molecule level. Mol Cell. 2015;58:483–94.
Fu YV, Yardimci H, Long DT, Ho TV, Guainazzi A, Bermudez VP, et al. Selective bypass of a lagging strand roadblock by the eukaryotic replicative DNA helicase. Cell. 2011;146:931–41.
Bicknell LS, Bongers EM, Leitch A, Brown S, Schoots J, Harley ME, et al. Mutations in the pre-replication complex cause Meier-Gorlin syndrome. Nat Genet. 2011;43:356–9.
Bicknell LS, Walker S, Klingseisen A, Stiff T, Leitch A, Kerzendorfer C, et al. Mutations in ORC1, encoding the largest subunit of the origin recognition complex, cause microcephalic primordial dwarfism resembling Meier-Gorlin syndrome. Nat Genet. 2011;43:350–5.
Burrage LC, Charng WL, Eldomery MK, Willer JR, Davis EE, Lugtenberg D, et al. De novo GMNN mutations cause autosomal-dominant Primordial Dwarfism associated with Meier-Gorlin syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;97:904–13.
Fenwick AL, Kliszczak M, Cooper F, Murray J, Sanchez-Pulido L, Twigg SR, et al. Mutations in CDC45, encoding an essential component of the pre-initiation complex, cause Meier-Gorlin syndrome and craniosynostosis. Am J Hum Genet. 2016;99:125–38.
Knapp KM, Sullivan R, Murray J, Gimenez G, Arn P, D’Souza P, et al. Linked-read genome sequencing identifies biallelic pathogenic variants in DONSON as a novel cause of Meier-Gorlin syndrome. J Med Genet. 2020;57:195–202.
Vetro A, Savasta S, Russo Raucci A, Cerqua C, Sartori G, Limongelli I, et al. MCM5: a new actor in the link between DNA replication and Meier-Gorlin syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2017;25:646–50.
Reynolds JJ, Bicknell LS, Carroll P, Higgs MR, Shaheen R, Murray JE, et al. Mutations in DONSON disrupt replication fork stability and cause microcephalic dwarfism. Nat Genet. 2017;49:537–49.
de Munnik SA, Otten BJ, Schoots J, Bicknell LS, Aftimos S, Al-Aama JY, et al. Meier-Gorlin syndrome: growth and secondary sexual development of a microcephalic primordial dwarfism disorder. Am J Med Genet A. 2012;158A:2733–42.
de Munnik SA, Hoefsloot EH, Roukema J, Schoots J, Knoers NV, Brunner HG, et al. Meier-Gorlin syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10:114.
Casey JP, Nobbs M, McGettigan P, Lynch S, Ennis S. Recessive mutations in MCM4/PRKDC cause a novel syndrome involving a primary immunodeficiency and a disorder of DNA repair. J Med Genet. 2012;49:242–5.
Hughes CR, Guasti L, Meimaridou E, Chuang CH, Schimenti JC, King PJ, et al. MCM4 mutation causes adrenal failure, short stature, and natural killer cell deficiency in humans. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:814–20.
Gineau L, Cognet C, Kara N, Lach FP, Dunne J, Veturi U, et al. Partial MCM4 deficiency in patients with growth retardation, adrenal insufficiency, and natural killer cell deficiency. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:821–32.
Wang X, Ishimi Y. Function of the amino-terminal region of human MCM4 in helicase activity. J Biochem. 2018;164:449–60.
Sheu YJ, Stillman B. Cdc7-Dbf4 phosphorylates MCM proteins via a docking site-mediated mechanism to promote S phase progression. Mol Cell. 2006;24:101–13.
Cottineau J, Kottemann MC, Lach FP, Kang YH, Vely F, Deenick EK, et al. Inherited GINS1 deficiency underlies growth retardation along with neutropenia and NK cell deficiency. J Clin Invest. 2017;127:1991–2006.
Frugoni F, Dobbs K, Felgentreff K, Aldhekri H, Al Saud BK, Arnaout R, et al. A novel mutation in the POLE2 gene causing combined immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:635–8 e1.
Logan CV, Murray JE, Parry DA, Robertson A, Bellelli R, Tarnauskaite Z, et al. DNA polymerase Epsilon deficiency causes IMAGe syndrome with variable immunodeficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;103:1038–44.
Mace EM, Paust S, Conte MI, Baxley RM, Schmit MM, Patil SL, et al. Human NK cell deficiency as a result of biallelic mutations in MCM10. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:5272–86.
Pachlopnik Schmid J, Lemoine R, Nehme N, Cormier-Daire V, Revy P, Debeurme F, et al. Polymerase epsilon1 mutation in a human syndrome with facial dysmorphism, immunodeficiency, livedo, and short stature (“FILS syndrome”). J Exp Med. 2012;209:2323–30.
Starokadomskyy P, Wilton KM, Krzewski K, Lopez A, Sifuentes-Dominguez L, Overlee B, et al. NK cell defects in X-linked pigmentary reticulate disorder. JCI Insight. 2019;4:21.
Thiffault I, Saunders C, Jenkins J, Raje N, Canty K, Sharma M, et al. A patient with polymerase E1 deficiency (POLE1): clinical features and overlap with DNA breakage/instability syndromes. BMC Med Genet. 2015;16:31.
Kortum F, Caputo V, Bauer CK, Stella L, Ciolfi A, Alawi M, et al. Mutations in KCNH1 and ATP6V1B2 cause Zimmermann-Laband syndrome. Nat Genet. 2015;47:661–7.
Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, et al. SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:W296–W303.
Yuan Z, Riera A, Bai L, Sun J, Nandi S, Spanos C, et al. Structural basis of Mcm2-7 replicative helicase loading by ORC-Cdc6 and Cdt1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017;24:316–24.
Tocilj A, On KF, Yuan Z, Sun J, Elkayam E, Li H, et al. Structure of the active form of human origin recognition complex and its ATPase motor module. Elife. 2017;6:e20818.
Sobreira N, Schiettecatte F, Valle D, Hamosh A. GeneMatcher: a matching tool for connecting investigators with an interest in the same gene. Hum Mutat. 2015;36:928–30.
Schwacha A, Bell SP. Interactions between two catalytically distinct MCM subgroups are essential for coordinated ATP hydrolysis and DNA replication. Mol Cell. 2001;8:1093–104.
Lee JK, Hurwitz J. Isolation and characterization of various complexes of the minichromosome maintenance proteins of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:18871–8.
Sherman DA, Forsburg SL. Schizosaccharomyces pombe Mcm3p, an essential nuclear protein, associates tightly with Nda4p (Mcm5p). Nucleic Acids Res. 1998;26:3955–60.
Frigola J, Remus D, Mehanna A, Diffley JF. ATPase-dependent quality control of DNA replication origin licensing. Nature. 2013;495:339–43.
Ryu S, Holzschuh J, Erhardt S, Ettl AK, Driever W. Depletion of minichromosome maintenance protein 5 in the zebrafish retina causes cell-cycle defect and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:18467–72.
Yao L, Chen J, Wu X, Jia S, Meng A. Zebrafish cdc6 hypomorphic mutation causes Meier-Gorlin syndrome-like phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26:4168–80.
Bellelli R, Boulton SJ. Spotlight on the replisome: aetiology of DNA replication-associated genetic diseases. Trends Genet. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2020.09.008.
Lessel D, Hisama FM, Szakszon K, Saha B, Sanjuanelo AB, Salbert BA, et al. POLD1 germline mutations in patients initially diagnosed with Werner syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2015;36:1070–9.
Weedon MN, Ellard S, Prindle MJ, Caswell R, Lango Allen H, Oram R, et al. An in-frame deletion at the polymerase active site of POLD1 causes a multisystem disorder with lipodystrophy. Nat Genet. 2013;45:947–50.
Li N, Zhai Y, Zhang Y, Li W, Yang M, Lei J, et al. Structure of the eukaryotic MCM complex at 3.8 A. Nature. 2015;524:186–91.
Kang S, Warner MD, Bell SP. Multiple functions for Mcm2-7 ATPase motifs during replication initiation. Mol Cell. 2014;55:655–65.
Coster G, Frigola J, Beuron F, Morris EP, Diffley JF. Origin licensing requires ATP binding and hydrolysis by the MCM replicative helicase. Mol Cell. 2014;55:666–77.
Lewis EMA, Sankar S, Tong C, Patterson ES, Waller LE, Gontarz P, et al. Geminin is required for Hox gene regulation to pattern the developing limb. Dev Biol. 2020;464:11–23.
Tamayo-Orrego L, Gallo D, Racicot F, Bemmo A, Mohan S, Ho B, et al. Sonic hedgehog accelerates DNA replication to cause replication stress promoting cancer initiation in medulloblastoma. Nat Cancer. 2020;1:840–54.
Cole TJ. The LMS method for constructing normalized growth standards. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1990;44:45–60.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the families for their involvement in this study. Thank you to Katie Young for assistance with flow cytometry and Anna Pawluchin for assistance with Sanger sequencing.
Funding
KK is supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (KU 1240/6-2 and KU 1240/10-1). This research, KMK and LSB are supported by the Marsden Fund; LSB is supported by a Rutherford Discovery Fellowship, both administered by the Royal Society of New Zealand. DEJ is supported by the Neurological Foundation of New Zealand and RS is supported by the Health Research Council of New Zealand; both awarded to LSB.
Sources of support
Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (KU 1240/6-2 and KU 1240/10-1). Marsden Fund; Rutherford Discovery Fellowship, both administered by the Royal Society of New Zealand; Neurological Foundation of New Zealand; Health Research Council of New Zealand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knapp, K.M., Jenkins, D.E., Sullivan, R. et al. MCM complex members MCM3 and MCM7 are associated with a phenotypic spectrum from Meier-Gorlin syndrome to lipodystrophy and adrenal insufficiency. Eur J Hum Genet 29, 1110–1120 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-021-00839-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-021-00839-4
This article is cited by
-
The genetic basis of human height
Nature Reviews Genetics (2025)
-
The expanding genetic and clinical landscape associated with Meier-Gorlin syndrome
European Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
Comment on: “The expanding genetic and clinical landscape associated with Meier-Gorlin syndrome” by Nielsen-Dandoroff et al.
European Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
Unwinding the Role of the CMG Helicase in Inborn Errors of Immunity
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2023)
-
De novo MCM6 variants in neurodevelopmental disorders: a recognizable phenotype related to zinc binding residues
Human Genetics (2023)