Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to review the most effective topical anesthetic methods for reducing pain/discomfort prior to dental local anesthetic needle puncture for dental procedures in children and adolescents.
Methods
A scoping review was conducted. Individual search strategies were developed for each of the bibliographic databases (Cochrane, Embase, LILACS, LIVIVO, Pubmed, Scopus, PsyINFO, Web of Science), and in the gray literature (Google Scholar, Open Gray), comprehensively, without restrictions on language, publication data, or level of socioeconomic development of the country in which the study was conducted. The search was conducted on April 21, 2021 and the updates on May 24, 2024. Randomized controlled studies conducted in patients up to 18 years of age were included. Variables collected: characteristics of the included studies, topical anesthetics evaluated, time and the mode of application.
Results
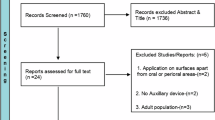
Initially, 8579 studies were retrieved. Then 3127 were identified as eligible, of which (n = 3127), 52 studies were included in the narrative synthesis. The most commonly observed anesthetic methods with the most favorable outcomes were lidocaine, benzocaine, ice cooling, and EMLA. Spray, gel or patch were used, with application times ranging from 1 to 10 min. Mucosal cooling an ice stick was analyzed by eight studies. Only one showed a smaller reduction in pain perception scores than others.
Conclusions
Cooling is a technique with numerous clinical advantages from the clinical point of view, for reduction of pain/discomfort prior to needle puncture of dental local anesthesia in children and adolescents. It is an accessible, inexpensive and pleasant method that does not resemble needles or unpleasant tastes, nor involves systemic toxicity and complications that may be associated with others anesthetics agents. Future randomized controlled studies in accordance with the Consort Statement are needed to further investigate the topic.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that they agree with the availability of data, upon request of the journal, confirming transparence in the presentation of the data.
References
American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Use of local anesthesia for pediatric dental patients. The Reference Manual of Pediatric Dentistry. Chicago, Ill.: American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. 2024:386–93.
Aminah M, Nagar P, Singh P, Bharti M. Comparison of topical anesthetic gel, pre-cooling, vibration and buffered local anesthesia on pain perception of pediatric patients during the administration of local anesthesia in procedures routine dental. Int J Contemp Med Res. 2017;4:77–83.
De Camargo Smolarek P, da Silva LS, Martins PRD, da Cruz Hartman K, Bortoluzzi MC, Chibinski ACR. The influence of distinct techniques of local dental anesthesia in 9- to 12-year-old children: randomized clinical trial on pain and anxiety. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25:3831–43.
Raja S, Carr D, Cohen M, Finnerup N, Flor H, Gibson S, et al. The revised international association for the study of pain definition of pain: concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain. 2020;161:1976–82.
Kaufman E, Epstein J, Naveh E, Gorsky M, Gross A, Cohen G. A survey of pain, pressure, and discomfort induced by commonly used oral local anesthesia injections. Anesth Prog 2005;52:122–7.
Aminabadi NA, Farahani RM. The effect of pre-cooling the injection site on pediatric pain perception during the administration of local anesthesia. J Contemp Dent Pract 2009;10:1–12.
Aravena P, Barrientos C, Troncoso C, Coronado C, Sotelo-Hitschfeld P. Effect of warming anesthetic on pain perception during dental injection: a split-mouth randomized clinical trial. Local Reg Anesth. 2018;22:9–13.
Nair M, Gurunathan D. Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of two anesthetic gels (2% lignocaine and 20% benzocaine) in reducing pain during administration of local anesthesia - a randomized controlled trial. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 2019;35:65–9.
Bågesund M, Tabrizi P. Lidocaine 20% patch vs lidocaine 5% gel for topical anaesthesia of oral mucosa. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2018;18:452–60.
Anantharaj A, Sabu JM, Ramakrishna S, Jagdeesh RB, Praveen P, Shankarappa PR. A comparative evaluation of pain perception following topical application of benzocaine gel, clove-papaya based anesthetic gel and precooling of the injection site before intraoral injections in children. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2020;38:184–9.
Chilakamuri S, Svsg N, Nuvvula S. The effect of pre-cooling versus topical anesthesia on pain perception during palatal injections in children aged 7–9 years: a randomized split-mouth crossover clinical trial. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2020;20:377–86.
Davoudi A, Rismanchian M, Akhavan A, Nosouhian S, Bajoghli F, Haghighat A, et al. A brief review on the efficacy of different possible and nonpharmacological techniques in eliminating discomfort of local anesthesia injection during dental procedures. Anesth Essays Res. 2016;10:13–6.
Hegde KM, R N, Srinivasan I, DR M, Melwani A, Radhakrishna S. Effect of vibration during local anesthesia administration on pain, anxiety, and behavior of pediatric patients aged 6–11 years: a crossover split-mouth study. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2019;19:143–9.
Kwak EJ, Pang NS, Cho JH, Jung BY, Kim KD, Park W. Computer-controlled local anesthetic delivery for painless anesthesia: a literature review. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2016;16:81–8.
Tirupathi SP, Rajasekhar S. Effect of precooling on pain during local anesthesia administration in children: a systematic review. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2020;20:119–27.
Boyce RA, Kirpalani T, Mohan N. Updates of topical and local anesthesia agents. Dent Clin North Am 2016;60:445–71.
Lee HS. Recent advances in topical anesthesia. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2016;16:237–44.
Bagesund M, Tabrizi P. Lidocaine 20% patch vs lidocaine 5% gel for topical anaesthesia of oral mucosa. Int J Paediatr Dent 2008;18:452–60.
Kincheloe JE, Mealiea WL Jr., Mattison GD, Seib K. Psychophysical measurement on pain perception after administration of a topical anesthetic. Quintessence Int 1991;22:311–5.
Malamed SF. Handbook of local anesthesia. St. Louis, Mo: Mosby; 2020.
Primosch RE, Rolland-Asensi G. Comparison of topical EMLA 5% oral adhesive to benzocaine 20% on the pain experienced during palatal anesthetic infiltration in children. Pediatr Dent. 2001;23:11–4.
Paschos E, Huth KC, Benz C, Reeka-Bardschmidt A, Hickel R. Efficacy of intraoral topical anesthetics in children. J Dent. 2006;34:398–404.
Monteiro J, Tanday A, Ashley PF, Parekh S, Alamri H. Interventions for increasing acceptance of local anaesthetic in children and adolescents having dental treatment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;2:CD011024.
Meechan JG. Effective topical anesthetic agents and techniques. Dent Clin North Am. 2002;46:759–66.
Nutter DP. Good clinical pain practice for pediatric procedure pain: target considerations. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2009;37:719–22.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:467–73.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Greenhalgh T, Peacock R. Effectiveness and efficiency of search methods in systematic reviews of complex evidence: audit of primary sources. BMJ. 2005;331:1064–5.
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5:210.
Jessica Gobetti Machado A, Brian Costa ESA, Carolina Goncalves de Oliveira B, Faria Sanglard L, Araujo de Sousa D, Mayrink Goncalves Liberato F, et al. Systematic review of intervention descriptions in randomised controlled trials with injectable agents for temporomandibular disorder using TIDieR and PEDro scales. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024;62:889–98.
Moseley AM, Elkins MR, Van der Wees PJ, Pinheiro MB. Using research to guide practice: the physiotherapy evidence database (PEDro). Braz J Phys Ther. 2020;24:384–91.
PEDro: Physiotherapy evidence database. Centre for evidence-based physiotherapy. [cited 2021 07 November]Available from: https://pedro.org.au/english/resources/pedro-scale.
AmruthaVarshini I, Vinay C, Uloopi KS, RojaRamya KS, Chandrasekhar R, Penmatsa C. Effectiveness of Pre-cooling the injection site, laser biostimulation, and topical local anesthetic gel in reduction of local anesthesia injection pain in children. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021;14:81–3.
Bose S, Garg N, Pathivada L, Yeluri R. Cooling the soft tissue and its effect on perception of pain during infiltration and block anesthesia in children undergoing dental procedures: a comparative study. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospect. 2019;13:159–65.
Dasarraju RK, Svsg N. Comparative efficacy of three topical anesthetics on 7-11-year-old children: a randomized clinical study. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2020;20:29–37.
H A, Rao A, Natarajan S, Yarmunja Mahabala K, Nayak A. Efficacy of an external cold and vibrating device in reducing discomfort during the administration of an inferior alveolar nerve block in children: a split-mouth randomised crossover study. F1000Res. 2023;12:984.
Deepika A, Rao CR, Vinay C, Uloopi KS, Rao VV. Effectiveness of two flavored topical anesthetic agents in reducing injection pain in children: a comparative study. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2012;37:15–8.
Deulkar PV, Rathi NV, Thosar N, Bane SP, Deshpande MA. Comparative evaluation of electronic acupuncture pen and 2% lignocaine gel as an intraoral topical anesthetic agent in children. Cureus. 2023;15:e47652.
Dhawan P, Dhawan G. Topical anesthetics: how effective are they. Int Dent Clin. 2011;3:11–3.
Dhingra N, Mathur S, Malik M. Effectiveness of cryotherapy, sucrose solution and a combination therapy for pain control during local anesthesia in children: a split mouth study. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022;46:1–5.
Fathima HM, Mathew MG. Comparative evaluation of two topical anaesthetic gels to reduce pain during local anaesthesia administration. Biosc Biotech Res Comm. 2020;13:354–9.
Hameed NN, Sargod SS, Bhat SS, Hegde SK, Bava MM. Effectiveness of precooling the injection site using tetrafluorethane on pain perception in children. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2018;36:296–300.
Jain N, Juneja P, Masih U, Bhushan AKB, Bhaduaria US, Badjatya K. Efficacy of external cold and a vibrating device in reducing pain and anxiety during local anaesthesia. J Family Med Prim Care. 2021;10:4017–22.
Joshi P, Baliga S, Rathi N, Thosar N. Comparative evaluation of pricking pain response, behavioural response, heart rate and blood pressure response to prilido cream and lignocad gel prior to local anesthesia administration in children. IOSR-JPBS. 2015;10:37–41.
Khan BS, Setty JV, Srinivasan I, Kibriya S, Anu S, Radhakrishna S, et al. Low-level laser therapy to alleviate pain of local anesthesia injection in children: a randomized control trial. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023;16(Suppl 3):283–7.
Lakshmanan L, Ravindran V. Efficacy of cryotherapy application on the pain perception during intraoral injection: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021;14:616–20.
Mohite VA, Baliga S, Thosar N, Rathi N, Khobragade P, Srivastava R. Comparative evaluation of a novel herbal anesthetic gel and 2% lignocaine gel as an intraoral topical anesthetic agent in children: bilateral split-mouth, single-blind, crossover in vivo study. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2020;38:177–83.
Mohiuddin I, Setty JV, Srinivasan I, Ahmed JD. Topical application of local anaesthetic gel vs. ice in pediatric patients for infiltration anaesthesia. J Evol Med Dent Sci. 2015;4:12934–40.
Pooja B, Kamatham R, Anchala K, Avisa P. Effectiveness of low-level laser therapy in reducing pain perception of children during dental local anesthetic administration using laser acupuncture pen on the LI4 point: a randomized clinical trial. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2023;24:219–27.
Sandhyarani B, Pawar RR, Patil AT, Kevadia MV. Effect of low-level laser on LI4 acupoint in pain reduction during local anesthesia in children. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021;14:462–6.
Shehab LA, Basheer B, Baroudi K. Effectiveness of lidocaine Denti patch(R) system versus lidocaine gel as topical anesthetic agent in children. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2015;33:285–90.
Singh R, Gupta N, Gambhir N. Comparative evaluation of reduction in pain perception using 5% topical LA vs freezed cone as a preparatory agent for intraoral injection in children and effect of VRD as distraction technique. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022;15:558–63.
Soni HK, Saha R, Prajapati R, Pathak S. The effectiveness of pre-cooling the injection site in alleviating the pain of oral injections in pediatric subjects. Acta Sci Dent Sci. 2020;4:51–5.
Sruthi MA, Jeevanandan G. Emla in the management of needle prick pain in children. J Res Med Dent Sci. 2020;8:186–92.
Pushpasanthy M, Ephraim R, Ayilliath A, Dhanya KB. Effectiveness of aculief acupressure device on pain perception during local anesthesia in children: a double-blinded study. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2023;41:309–15.
Petluru H, Nirmala S, Nuvvula S. A comparative evaluation of peppermint oil and lignocaine spray as topical anesthetic agents prior to local anesthesia in children: a randomized clinical trial. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2024;24:119–28.
Davangere Padmanabh SK, Gangurde VB, Jhamb V, Gori N. Effect of cryoanesthesia and sweet tasting solution in reducing injection pain in pediatric patients aged 7–10 years: a randomized controlled trial. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2024;24:37–45.
Nayak R, Sudha P. Evaluation of three topical anaesthetic agents against pain: a clinical study. Indian J Dent Res. 2006;17:155–60.
Bagherian A, Sheikhfathollahi M. Children’s behavioral pain reactions during local anesthetic injection using cotton-roll vibration method compared with routine topical anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. Dent Res J 2016;13:272–7.
Ghaderi F, Banakar S, Rostami S. Effect of pre-cooling injection site on pain perception in pediatric dentistry: “A randomized clinical trial”. Dent Res J. 2013;10:790–4.
Omidpanah N, Shahrzad N, Safari R. The effect of topical anesthetic gel versus relaxation exercise in controlling the pain of anterior maxillary injection. Open Dent J. 2020;14:752–6.
Shekarchi F, Nokhbatolfoghahaei H, Chiniforush N, Mohaghegh S, Haeri Boroojeni HS, Amini S, et al. Evaluating the preemptive analgesic effect of photo-biomodulation therapy on pain perception during local anesthesia injection in children: a split-mouth triple-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Photochem Photobiol. 2022;98:1195–200.
Vafaei A, Rahbar M, Dadkhah R, Ranjkesh B, Erfanparast L. Children’s pain perception and behavioral feedback during local anesthetic injection with four injection site preparation methods. Maedica. 2019;14:343–9.
Yildirim S, Tokuc M, Aydin MN. The effect of pre-anesthesia with a needle-free system versus topical anesthesia on injection pain of the inferior alveolar nerve block: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24:4355–61.
Kreider KA, Stratmann RG, Milano M, Agostini FG, Munsell M. Reducing children’s injection pain: lidocaine patches versus topical benzocaine gel. Pediatr Dent. 2001;23:19–23.
Lathwal G, Pandit IK, Gugnani N, Gupta M. Efficacy of different precooling agents and topical anesthetics on the pain perception during intraoral injection: a comparative clinical study. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2015;8:119–22.
Stecker SS, Swift JQ, Hodges JS, Erickson PR. Should a mucoadhesive patch (DentiPatch) be used for gingival anesthesia in children? Anesth Prog. 2002;49:3–8.
Wu SJ, Julliard K. Children’s preference of benzocaine gel versus the lidocaine patch. Pediatr Dent. 2003;25:401–5.
Atabek D, Cinar C, Sillelioglu H, Bani M, Kip G. Comparison of topical 10 percent lidocaine and a local anesthetic system in pediatric dental patients. J Dent Child. 2015;82:91–6.
Bilsin E, Gungormus Z, Gungormus M. The efficacy of external cooling and vibration on decreasing the pain of local anesthesia injections during dental treatment in children: a randomized controlled study. J Perianesth Nurs. 2020;35:44–7.
Alanazi KJ, Pani S, AlGhanim N. Efficacy of external cold and a vibrating device in reducing discomfort of dental injections in children: a split mouth randomised crossover study. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2019;20:79–84.
AlHareky M, AlHumaid J, Bedi S, El Tantawi M, AlGahtani M, AlYousef Y. Effect of a vibration system on pain reduction during injection of dental anesthesia in children: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Dent. 2021;2021:8896408.
Maldonado-Ramírez MA, Issasi-Hernández H, Trejo-Tejeda S, Morales-Sánchez LA. Efficacy of two topical anesthetics for dental use in pediatric. Acta Pediatr Mex. 2017;38:83–90.
Diab HM, El-Malt MA, Mourad YO. Evaluation of the effectiveness of photobiomodulation therapy as an alternative method to local anesthesia injection in pediatric dentistry. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2023;41:222–7.
Shetty A, Naik SS, Patil RB, Valke PS, Mali S, Patil D. Effectiveness of an extraoral cold and vibrating device in reducing pain perception during deposition of local anesthesia in pediatric patients aged 3–12 years: a split-mouth crossover study. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2023;23:317–25.
Amitai Y, Whitesell L, Lovejoy FH Jr. Death following accidental lidocaine overdose in a child. N. Engl J Med. 1986;314:182–3.
Hess GP, Walson PD. Seizures secondary to oral viscous lidocaine. Ann Emerg Med. 1988;17:725–7.
Spiller HA, Russell JL, Casavant MJ, Ho RY, Gerona RR. Identification of N-Hydroxy-para-aminobenzoic acid in a cyanotic child after benzocaine exposure. Clin Toxicol. 2014;52:976–9.
Bittmann S, Kruger C. Benzocaine-induced methaemoglobinaemia: a case study. Br J Nurs. 2011;20:168–70.
Logan BK, Gordon AM. Death of an infant involving benzocaine. J Forensic Sci. 2005;50:1486–8.
Berg J. Topical anesthetic before primary molar buccal anesthesia is not better than placebo in reducing child’s pain perception. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2007;7:116–7.
Wambier LM, Gonzaga CC, Chibinski A, Wambier DS, Farago PV, Loguercio AD, et al. Efficacy of a light-cured tetracaine-based anesthetic gel for rubber dam clamp placement: a triple-blind randomized clinical trial. Oper Dent. 2020;45:E57–E65.
Sanglard LF, Oliveira LB, Massignan C, Polmann H, De Luca Canto G. Evaluating pain, fear, anxiety or stress/distress using children’s drawings in paediatric dentistry: a scoping review. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022;23:199–222.
DeSantana J, Perissinotti D, Oliveira Junior J, Correia L, Oliveira C, Fonseca P. Definition of pain revised after four decades. BrJP. 2020;3:197–8.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Practice & Ambulatory Medicine. 2024 Recommendations for Preventive Pediatric Health Care: Policy Statement. Pediatrics. 2024;154:e2024067201.
Amrollahi N, Rastghalam N, Faghihian R. Effect of pre-cooling on pain associated with dental injections in children: a systematic review. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2021;21:101588.
Funding
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest amongst our research team.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Luciana Faria Sanglard1 contributed with the conception, design, acquired data and/or played an important role in interpreting the results, analysis and interpretation, drafted the initial manuscript, critically reviewed the manuscript, approved of the final version to be published. Is responsible for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved; and for communicating with the journal during the submission process. Luana da Silva Paiva2 contributed with the conception, acquired data and drafted the initial manuscript, played an important role in interpreting the results, approval of the final version to be published; agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. Isabel Cristina Quaresma Rego3 contributed with drafted the initial manuscript, approval of the final version to be published; agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. Amanda Vieira Barollo4 contributed with on data collection, with approval of the final version to be published and responsible for all aspects of the work; agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. Mariana Pires Feletti5 contributed with the conception, on data collection and analysis and drafted the initial manuscript, approval of the final version to be published; agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. Daniela Nascimento Silva6 contributed with the conception, on data collection and drafted the initial manuscript, played an important role in interpreting the results, approval of the final version to be published; agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. Juliana Cama Ramacciato7 contributed with the conception, on data collection, drafted the initial manuscript and critical review of the manuscript, played an important role in interpreting the results, approval of the final version to be published; agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. Luciana Butini Oliveira8 contributed to the conception, design, data collection, played an important role in analysis and interpretation, drafted the initial manuscript and critical review of the manuscript, approval of the final version to be published and responsible for all aspects of the work; agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The corresponding author guarantees that the article has not been published and is not being considered for publication elsewhere. This study is a scoping review and IRB approval was not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sanglard, L.F., da Silva Paiva, L., Rego, I.C.Q. et al. Topical anesthetics methods used to reduce needle pain/discomfort prior to local anesthesia in children and adolescents: a scoping review. Evid Based Dent 26, 65 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41432-025-01106-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41432-025-01106-x