Abstract
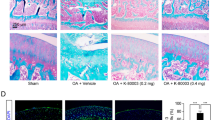
Osteoarthritis (OA), a prevalent joint disorder, can lead to disability, with no effective treatment available. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) plays a crucial role in the progression of OA, and its receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra), a natural IL-1 inhibitor, represents a promising therapeutic target by obstructing the IL-1 signaling pathway. This study delivered IL-1Ra via adeno-associated virus (AAV), a gene therapy vector enabling long-term protein expression, to treat knee osteoarthritis (KOA) in animal models. scAAV-oIL-1Ra-I1/2 injected directly into the joint in both MMT/ACLT-induced KOA model rat improved abnormal gait (increasing footprint area and pressure), subchondral bone lesions, and significantly reduced cartilage wear and pathological scores. In the MMT-induced KOA rabbit model, weight-bearing asymmetry (indicating pain) improved after 8 weeks of scAAV-oIL-1Ra-I1/2 administration, and X-ray showed decreased K-L scores (severity grade), reduced cartilage loss, and lower pathology scores compared to untreated animals. Additionally, sex-determining region Y-type high mobility group box 9 (SOX9) was co-delivered with IL-1Ra via AAV in ACLT + MMT-induced KOA rats. The combined treatment significantly alleviated subchondral bone lesions, cartilage destruction, synovial inflammation, and pathological scores, demonstrating superior efficacy compared to either treatment administered alone. Co-delivering IL-1Ra and SOX9 inhibited IL-1 mediated inflammatory signaling, maintained cartilage homeostasis, and promoted its repair in KOA models, suggesting potential for clinical use.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors, Dr. Wu or Dr. Xiao, upon reasonable request.
References
Chen D. Osteoarthritis: a complicated joint disease requiring extensive studies with multiple approaches. J Orthop Translat. 2022;32:130.
Li Y, Xie W, Xiao W, Dou D. Progress in osteoarthritis research by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. Bone Res. 2022;10:41.
Austine J, Nair S, Mirza K. Perspective of orthopedists on pain management in osteoarthritis: a qualitative study. Indian J Palliat Care. 2016;22:410–5.
Chen D, Shen J, Zhao W, Wang T, Han L, Hamilton JL, et al. Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res. 2017;5:16044.
Vincent TL, Alliston T, Kapoor M, Loeser RF, Troeberg L, Little CB. Osteoarthritis pathophysiology: therapeutic target discovery may require a multifaceted approach. Clin Geriatr Med. 2022;38:193–219.
Martel-Pelletier J, Barr AJ, Cicuttini FM, Conaghan PG, Cooper C, Goldring MB, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
Kapoor M, Martel-Pelletier J, Lajeunesse D, Pelletier JP, Fahmi H. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:33–42.
Jenei-Lanzl Z, Meurer A, Zaucke F. Interleukin-1β signaling in osteoarthritis - chondrocytes in focus. Cell Signal. 2019;53:212–23.
Qian M, Shi Y, Lu W. LINC00707 knockdown inhibits IL-1β-induced apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of osteoarthritis chondrocytes by the miR-330-5p/FSHR axis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44:671–81.
Mehta S, Akhtar S, Porter RM, Önnerfjord P, Bajpayee AG. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) is more effective in suppressing cytokine-induced catabolism in cartilage-synovium co-culture than in cartilage monoculture. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21:238.
Iqbal I, Fleischmann R. Treatment of osteoarthritis with anakinra. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2007;9:31–35.
Wang JH, Gessler DJ, Zhan W, Gallagher TL, Gao G. Adeno-associated virus as a delivery vector for gene therapy of human diseases. Signal Transduction Targeted Therapy. 2024;9:78.
Naso MF, Tomkowicz B, Perry WL 3rd, Strohl WR. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) as a vector for gene therapy. BioDrugs. 2017;31:317–34.
Evans CH, Gouze JN, Gouze E, Robbins PD, Ghivizzani SC. Osteoarthritis gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2004;11:379–89.
Candela ME, Yasuhara R, Iwamoto M, Enomoto-Iwamoto M. Resident mesenchymal progenitors of articular cartilage. Matrix Biol. 2014;39:44–49.
Gugjoo MB, Fazili MR, Gayas MA, Ahmad RA, Dhama K. Animal mesenchymal stem cell research in cartilage regenerative medicine - a review. Vet Q. 2019;39:95–120.
Zhang X, Wu S, Zhu Y, Chu CQ. Long-term durable repaired cartilage induced by SOX9 in situ with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18:1399–405.
Lange C, Madry H, Venkatesan JK, Schmitt G, Speicher-Mentges S, Zurakowski D, et al. rAAV-mediated sox9 overexpression improves the repair of osteochondral defects in a clinically relevant large animal model over time in vivo and reduces perifocal osteoarthritic changes. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49:3696–707.
Jotanovic Z, Mihelic R, Sestan B, Dembic Z. Emerging pathways and promising agents with possible disease-modifying effect in osteoarthritis treatment. Curr Drug Targets. 2014;15:635–61.
Chen B, Qin J, Wang H, Magdalou J, Chen L. Effects of adenovirus-mediated bFGF, IL-1Ra, and IGF-1 gene transfer on human osteoarthritic chondrocytes and osteoarthritis in rabbits. Exp Mol Med. 2010;42:684–95.
Tao K, Rey-Rico A, Frisch J, Venkatesan JK, Schmitt G, Madry H, et al. rAAV-mediated combined gene transfer and overexpression of TGF-β and SOX9 remodels human osteoarthritic articular cartilage. J Orthop Res. 2016;34:2181–90.
Yang L, Jiang J, Drouin LM, Agbandje-McKenna M, Chen C, Qiao C, et al. A myocardium tropic adeno-associated virus (AAV) evolved by DNA shuffling and in vivo selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:3946–51.
Xiao X, Li J, Samulski RJ. Production of high-titer recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors in the absence of helper adenovirus. J Virol. 1998;72:2224–32.
Kimmerling KA, Gomoll AH, Farr J, Mowry KC. Amniotic suspension allograft improves pain and function in a rat meniscal tear-induced osteoarthritis model. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24:63.
Brenneis C, Menges S, Westhof A, Lindemann S, Thudium CS, Kleinschmidt-Doerr K. Colony housing promotes structural and functional changes during surgically induced osteoarthritis in rats. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2020;2:100100.
Huang K, Cai HL, Zhang PL, Wu LD. Comparison between two rabbit models of posttraumatic osteoarthritis: a longitudinal tear in the medial meniscus and anterior cruciate ligament transection. J Orthop Res. 2020;38:2721–30.
Swearingen CA, Chambers MG, Lin C, Marimuthu J, Rito CJ, Carter QL, et al. A short-term pharmacodynamic model for monitoring aggrecanase activity: injection of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) in rats and assessment of aggrecan neoepitope release in synovial fluid using novel ELISAs. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18:1159–66.
Hernandez-Garcia CM, Chiera JM, Finer JJ. Robotics and dynamic image analysis for studies of gene expression in plant tissues. J Vis Exp. 2010;39:1733.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Conaghan PG, Cook AD, Hamilton JA, Tak PP. Therapeutic options for targeting inflammatory osteoarthritis pain. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15:355–63.
Lefebvre V, Angelozzi M, Haseeb A. SOX9 in cartilage development and disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019;61:39–47.
Lamandé SR, Bateman JF. Genetic disorders of the extracellular matrix. Anat Rec. 2020;303:1527–42.
Grol MW, Lee BH. Gene therapy for repair and regeneration of bone and cartilage. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018;40:59–66.
Bucher K, Rodríguez-Bocanegra E, Dauletbekov D, Fischer MD. Immune responses to retinal gene therapy using adeno-associated viral vectors - Implications for treatment success and safety. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021;83:100915.
Yoon DS, Lee KM, Cho S, Ko EA, Kim J, Jung S, et al. Cellular and tissue selectivity of AAV serotypes for gene delivery to chondrocytes and cartilage. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18:3353–60.
Chen Q, Luo H, Zhou C, Yu H, Yao S, Fu F, et al. Comparative intra-articular gene transfer of seven adeno-associated virus serotypes reveals that AAV2 mediates the most efficient transduction to mouse arthritic chondrocytes. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0243359.
Kyostio-Moore S, Berthelette P, Cornell CS, Nambiar B, Figueiredo MD. Hyaluronic acid synthase-2 gene transfer into the joints of Beagles by use of recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors. Am J Vet Res. 2018;79:505–17.
Vrouwe JPM, Meulenberg JJM, Klarenbeek NB, Navas-Cañete A, Reijnierse M, Ruiterkamp G, et al. Administration of an adeno-associated viral vector expressing interferon-β in patients with inflammatory hand arthritis, results of a phase I/II study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30:52–60.
Miller RE, Miller RJ, Malfait AM. Osteoarthritis joint pain: the cytokine connection. Cytokine. 2014;70:185–93.
Mailhot B, Christin M, Tessandier N, Sotoudeh C, Bretheau F, Turmel R, et al. Neuronal interleukin-1 receptors mediate pain in chronic inflammatory diseases. J Exp Med. 2020;217:e20191430.
Fiocco U, Vezzù M, Cozzi L, Todesco S. IL-1Ra (recombinant human IL-1 receptor antagonist) in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: the efficacy. Reumatismo. 2004;56:62–73.
Watson Levings RS, Smith AD, Broome TA, Rice BL, Gibbs EP, Myara DA, et al. Self-complementary adeno-associated virus-mediated interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene delivery for the treatment of osteoarthritis: test of efficacy in an equine model. Hum Gene Ther Clin Dev. 2018;29:101–12.
Migliorini F, Giorgino R, Mazzoleni MG, Schäfer L, Bertini FA, Maffulli N. Intra-articular injections of ozone versus hyaluronic acid for knee osteoarthritis: a level I meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024;35:20.
Yang J, Wang X, Zhang Y, He R, Fu Z, Wang R, et al. Intra-articular injection of interleukin-8 neutralizing monoclonal antibody effectively attenuates osteoarthritis progression in rabbits. Cartilage. 2024 Mar 25:19476035241240361.
Cucchiarini M, Terwilliger EF, Kohn D, Madry H. Remodelling of human osteoarthritic cartilage by FGF-2, alone or combined with Sox9 via rAAV gene transfer. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13:2476–88.
Grässel S, Muschter D. Recent advances in the treatment of osteoarthritis. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev–325.
Stone A, Grol MW, Ruan MZC, Dawson B, Chen Y, Jiang MM, et al. Combinatorial Prg4 and Il-1ra gene therapy protects against hyperalgesia and cartilage degeneration in post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Hum Gene Ther. 2019;30:225–35.
Zhang Q, Ji Q, Wang X, Kang L, Fu Y, Yin Y, et al. SOX9 is a regulator of ADAMTSs-induced cartilage degeneration at the early stage of human osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23:2259–68.
Zhang X, Wu S, Zhu Y, Chu CQ. Exploiting joint-resident stem cells by exogenous SOX9 for cartilage regeneration for therapy of osteoarthritis. Front Med. 2021;8:622609.
Hunziker EB, Rosenberg LC. Repair of partial-thickness defects in articular cartilage: cell recruitment from the synovial membrane. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78:721–33.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFC2700803).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, WX and XX, Methodology, ZKY, WX, and XX; Investigation, ZKY, YM, and SJB; Writing—Original Draft, ZKY; Writing—Review & Editing, ZKY, LXT, and WX; Funding Acquisition, WX, and XX.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
We declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
C57BL/6 J mice were obtained from Gempharmatech Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were purchased from Weitong Lihua Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). New Zealand rabbits were purchased from Aoshima Kangda Aibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd. All experimental procedures involving mouse and rat animals were approved by the Ethical Committee of Shanghai Model Organisms Center, Inc. All experimental procedures involving rabbit animals were approved by the Ethical Committee of PharmaLegacy Laboratories (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. And all experimental procedures involving non-human primates were approved by the Ethical Committee of Kunming Medical University. No. SCXK (Yunnan) K2020-0006, Animal Ethics Code: kmmu20221596. All experiments conformed to relevant regulatory standards.
Consent for Publication
All the listed authors have participated in the study, and have seen and approved the submitted manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, K., Yuan, M., Sun, J. et al. Co-delivery of IL-1Ra and SOX9 via AAV inhibits inflammation and promotes cartilage repair in surgically induced osteoarthritis animal models. Gene Ther 32, 211–222 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-025-00515-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-025-00515-y