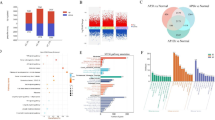
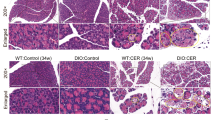
Abstract
Severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) poses significant challenges due to its complex pathophysiology, which includes inflammatory-immune responses that cause considerable damage to both the pancreas and other tissues. In this study, we explored the role of Annexin A1 (Anxa1), a glucocorticoid-regulated protein recognized for its anti-inflammatory properties, in regulating inflammation during acute pancreatitis. Using flow cytometry, single-cell RNA sequencing, and gene expression analysis, we examined how Anxa1 expression is regulated in myeloid cells throughout acute pancreatitis, employing various animal models to evaluate the consequences of modulating Anxa1 on injuries induced by SAP. Our findings revealed dynamic regulation of Anxa1 expression in myeloid cells, with mice lacking Anxa1 exhibiting worsened pancreatic injury and heightened systemic inflammation, resulting in significant damage to extra-pancreatic organs such as the lungs, liver, and kidneys. In contrast, treatment with Ac2-26, a synthetic peptide derived from Anxa1, effectively mitigated both pancreatic and extra-pancreatic inflammation and tissue damage. Overall, this study highlights the critical role of Anxa1 in modulating inflammatory responses during acute pancreatitis. Targeting Anxa1 presents a promising therapeutic strategy to mitigate pancreatic injury and prevent systemic complications associated with severe acute pancreatitis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data underlying the results presented in this study are provided within the manuscript and its supplementary materials. Furthermore, the single-cell RNA-seq data are publically accessible via the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which may be accessed using accession number GSE249349. To access the raw data, please contact the corresponding author with a reasonable request.
Change history
30 July 2025
In the original version of Figure 3, the H&E staining image in panel E (Ac 2-26 Con group) is identical to the image in panel A (WT NaCl group). This error occurred due to an unintentional duplication during the image assembly process. We have re-examined the original experimental data and confirmed the correct H&E staining image for the Ac 2-26 Con group.In Figure 6G, the group labels 'PLA SO' and 'PLA SAP' were incorrect due to a typographical error and should be corrected to 'PBS SO' (PBS-treated sham operation group) and 'PBS SAP' (PBS-treated severe acute pancreatitis group). This mistake arose from confusion between the abbreviations 'PLA' and 'PBS' during data labeling or figure editing.
29 September 2025
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-025-00348-0
References
Mederos MA, Reber HA, Girgis MD. Acute pancreatitis: a review. JAMA. 2021;325:382–90.
Garg PK, Singh VP. Organ failure due to systemic injury in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:2008–23.
Szatmary P, Grammatikopoulos T, Cai W, Huang W, Mukherjee R, Halloran C, et al. Acute pancreatitis: diagnosis and treatment. Drugs. 2022;82:1251–76.
de-Madaria E, Buxbaum JL. Advances in the management of acute pancreatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;20:691–2.
Hines OJ, Pandol SJ. Management of severe acute pancreatitis. BMJ. 2019;367:l6227.
Perretti M, D’Acquisto F. Annexin A1 and glucocorticoids as effectors of the resolution of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:62–70.
Wu L, Liu C, Chang D-Y, Zhan R, Sun J, Cui S-H, et al. Annexin A1 alleviates kidney injury by promoting the resolution of inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2021;100:107–21.
Xu R, Weber M-C, Hu X, Neumann P-A, Kamaly N. Annexin A1 based inflammation resolving mediators and nanomedicines for inflammatory bowel disease therapy. Semin Immunol. 2022;61-64:101664.
Senchenkova EY, Ansari J, Becker F, Vital SA, Al-Yafeai Z, Sparkenbaugh EM, et al. Novel role for the AnxA1-Fpr2/ALX signaling axis as a key regulator of platelet function to promote resolution of inflammation. Circulation. 2019;140:319–35.
Habtezion A, Gukovskaya AS, Pandol SJ. Acute pancreatitis: a multifaceted set of organelle and cellular interactions. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1941–50.
Manohar M, Jones EK, Rubin SJS, Subrahmanyam PB, Swaminathan G, Mikhail D, et al. Novel circulating and tissue monocytes as well as macrophages in pancreatitis and recovery. Gastroenterology. 2021;161:2014–29.e14.
Zhao Q, Wei Y, Pandol SJ, Li L, Habtezion A. STING signaling promotes inflammation in experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:1822–35.e2.
Sharif R, Dawra R, Wasiluk K, Phillips P, Dudeja V, Kurt-Jones E, et al. Impact of toll-like receptor 4 on the severity of acute pancreatitis and pancreatitis-associated lung injury in mice. Gut. 2009;58:813–9.
Niederau C, Lüthen R, Niederau MC, Grendell JH, Ferrell LD. Acute experimental hemorrh agic-necrotizing pancreatitis induced by feeding a choline-deficient, ethionine-supplemented diet. Methodol Stand Eur Surg Res. 1992;24 Suppl 1:40–54.
Laukkarinen JM, Van Acker GJD, Weiss ER, Steer ML, Perides G. A mouse model of acute biliary pancreatitis induced by retrograde pancreatic duct infusion of Na-taurocholate. Gut. 2007;56:1590–8.
Hou Z, Lu F, Lin J, Wu Y, Chen L, Fang H, et al. Loss of Annexin A1 in macrophages restrains efferocytosis and remodels immune microenvironment in pancreatic cancer by activating the cGAS/STING pathway. J Immunotherapy Cancer. 2024;12:e009318.
Yu X, Pan Y, Fei Q, Lin X, Chen Z, Huang H. Serum soluble PD-1 plays a role in predicting infection complications in patients with acute pancreatitis. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2021;9:310–8.
Pan Y, Fang H, Lu F, Pan M, Chen F, Xiong P, et al. Ulinastatin ameliorates tissue damage of severe acute pancreatitis through modulating regulatory T cells. J Inflamm (Lond). 2017;14:7.
Zhao K, Qian C, Qi L, Li Q, Zhao C, Zhang J, et al. Modified acid polysaccharide derived from Salvia przewalskii with excellent wound healing and enhanced bioactivity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;263:129803.
Pan Y, Fei Q, Xiong P, Yang J, Zhang Z, Lin X, et al. Synergistic inhibition of pancreatic cancer with anti-PD-L1 and c-Myc inhibitor JQ1. Oncoimmunology. 2019;8:e1581529.
Zhao K, Qi L, Li Q, Wang Y, Qian C, Shi Z. Self-absorbing multilayer skin-like composite with Phyllostachys nigra polysaccharides promotes wound healing. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater. 2024;7:225.
Pan Y, Li Y, Gao L, Tong Z, Ye B, Liu S, et al. Development of a novel model of hypertriglyceridemic acute pancreatitis in mice. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40799.
Eltzschig HK, Bratton DL, Colgan SP. Targeting hypoxia signalling for the treatment of ischaemic and inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13:852–69.
Pan Y, Gao J, Lin J, Ma Y, Hou Z, Lin Y, et al. High-dimensional single-cell analysis unveils distinct immune signatures of peripheral blood in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1181538.
Hou Z, Lin J, Ma Y, Fang H, Wu Y, Chen Z, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing revealed subclonal heterogeneity and gene signatures of gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic cancer. Front Pharm. 2023;14:1193791.
Pan Y, Lu F, Fei Q, Yu X, Xiong P, Yu X, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals compartmental remodeling of tumor-infiltrating immune cells induced by anti-CD47 targeting in pancreatic cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:124.
Zhang D, Wang M, Zhang Y, Xia C, Peng L, Li K, et al. Novel insight on marker genes and pathogenic peripheral neutrophil subtypes in acute pancreatitis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:964622.
Liu X, Luo W, Chen J, Hu C, Mutsinze RN, Wang X, et al. USP25 deficiency exacerbates acute pancreatitis via up-regulating TBK1-NF-κB signaling in macrophages. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;14:1103–22.
Jabłońska B, Mrowiec S. Nutritional support in patients with severe acute pancreatitis-current standards. Nutrients. 2021;13:1498.
Schmandt M, Glowka TR, Kreyer S, Muders T, Muenster S, Theuerkauf NU, et al. Secondary ARDS following acute pancreatitis: is extracorporeal membrane oxygenation feasible or futile? J Clin Med. 2021;10:1000.
Hu H, Zhang W, Zhou Y, Zhao K, Kuang J, Liu X, et al. Engineered mitochondrial ROS scavenger nanocomplex to enhance lung biodistribution and reduce inflammation for the treatment of ARDS. Adv Comp Hybrid Mater. 2024;7:1–15.
Ricci E, Ronchetti S, Pericolini E, Gabrielli E, Cari L, Gentili M, et al. Role of the glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper gene in dexamethasone-induced inhibition of mouse neutrophil migration via control of annexin A1 expression. FASEB J. 2017;31:3054–65.
Paszt A, Eder K, Szabolcs A, Tiszlavicz L, Lázár G, Duda E, et al. Effects of glucocorticoid agonist and antagonist on the pathogenesis of L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis in rat. Pancreas. 2008;36:369–76.
Aney KJ, Jeong W-J, Vallejo AF, Burdziak C, Chen E, Wang A, et al. Novel approach for pancreas transcriptomics reveals the cellular landscape in homeostasis and acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2024;166:1100–13.
Hu F, Lou N, Jiao J, Guo F, Xiang H, Shang D. Macrophages in pancreatitis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110693.
Ganguly D, Haak S, Sisirak V, Reizis B. The role of dendritic cells in autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:566–77.
Veglia F, Sanseviero E, Gabrilovich DI. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the era of increasing myeloid cell diversity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21:485–98.
Bruschi M, Petretto A, Vaglio A, Santucci L, Candiano G, Ghiggeri GM. Annexin A1 and autoimmunity: from basic science to clinical applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:1348.
Butcher MJ, Galkina EV. wRAPping up early monocyte and neutrophil recruitment in atherogenesis via Annexin A1/FPR2 signaling. Circ Res. 2015;116:774–7.
Patel HB, Kornerup KN, Sampaio ALF, D’Acquisto F, Seed MP, Girol AP, et al. The impact of endogenous annexin A1 on glucocorticoid control of inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:1872–80.
Chen J, Norling LV, Mesa JG, Silva MDP, Burton SE, Reutelingsperger C, et al. Annexin A1 attenuates cardiac diastolic dysfunction in mice with inflammatory arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118:e2020385118.
Li C, Zhao Y, Cheng J, Guo J, Zhang Q, Zhang X, et al. A Proresolving Peptide Nanotherapy for Site-Specific Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease by Regulating Proinflammatory Microenvironment and Gut Microbiota. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6:1900610.
Funding
This study was funded by the Excellent Young Scholars Cultivation Project of Fujian Medical University Union Hospital (2022XH025), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82103310), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2021J01774), the Joint Funds of the Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Fujian Province (2020Y9081), the Fujian Provincial Health Technology Project (2020GGA029), and the Youth Research Project of the Fujian Provincial Health Commission Science and Technology Project (2023QN01010127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YP and HF conceived and designed the studies. SL, CC, YW, FL, JL, HF, ZH, and YP conducted the experiments. SL, CC, YW, and FL obtained and assessed the data. Written by YP’s hand, the first draft of the work. SL, CC, and HH worked on editing and reviewing the manuscript. Throughout its entirety, the study was supervised by YP. All authors have read and approved the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This research involving human materials and data was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study protocol received approval from the Committee for the Ethical Review of Research at Fujian Medical University Union Hospital (Approval No. 2021KJT084). Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study. The animal experiments in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Fujian Medical University (FJMUA2021025). All animal experiments were conducted in compliance with institutional guidelines and the ARRIVE guidelines, ensuring ethical treatment of animals and adherence to proper protocols.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, S., Liang, F., Chen, C. et al. Annexin A1 regulates inflammatory-immune response and reduces pancreatic and extra- pancreatic injury during severe acute pancreatitis. Genes Immun 26, 124–136 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-025-00321-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-025-00321-x