Fig. 1
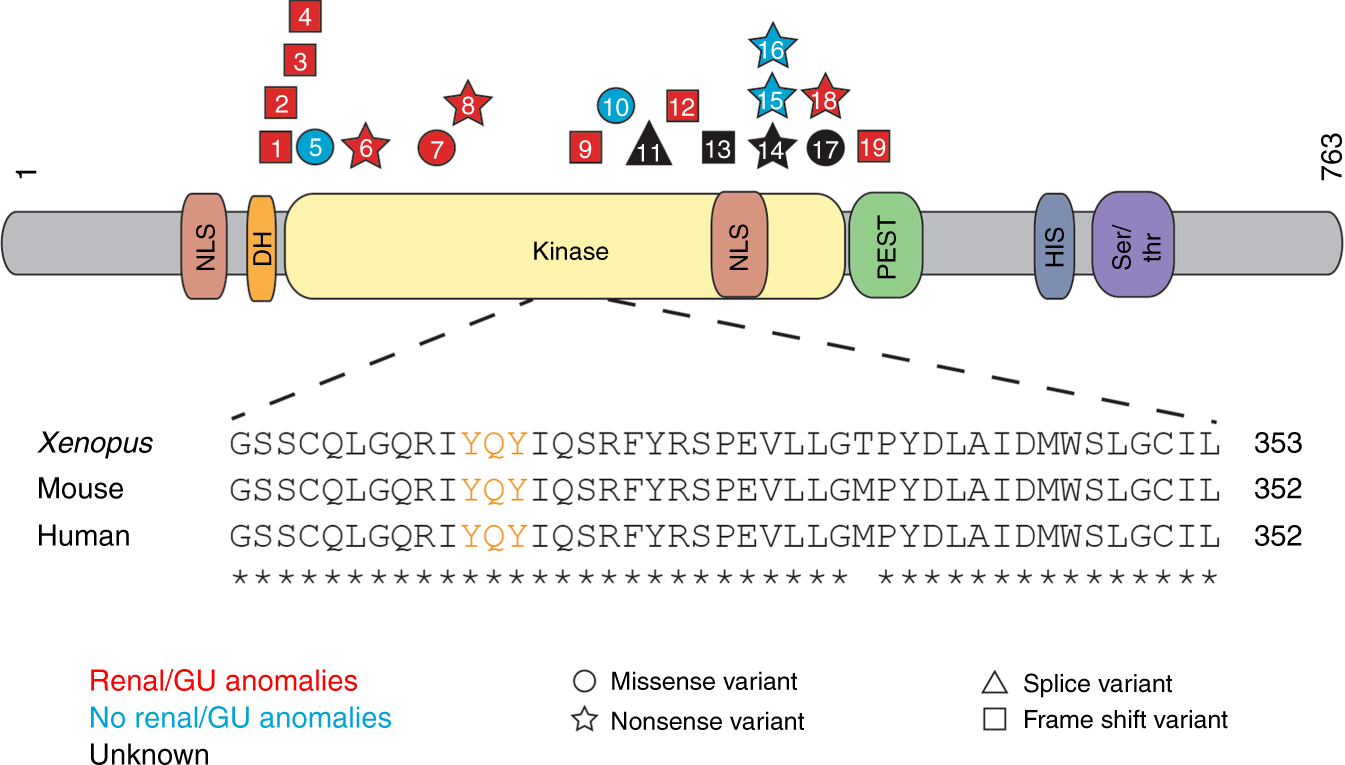
Congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT) associated withDYRK1Avariants in patients withDYRK1A-related intellectual disability syndrome. Schematic shows the DYRK1A protein domains. Shapes, which identify the type of variant (squares = frame shift variants, circles = missense variants, stars = nonsense variants, triangles = splice variants), are positioned where DYRK1A patient variants impact the amino acid sequence. Patient variants are labeled by patient number as listed in Tables 1 and 2. Variants that result in CAKUT are red, those that do not result in CAKUT are blue, and those in which the effects on CAKUT status are unknown are black. Protein domains are abbreviated as follows: DH DYRK homology box; HIS histidine; NLS nuclear localization signal;PEST proline (P), glutamic acid (E), serine (S), and threonine (T); Ser/Thr serine/threonine.Inset shows highly conserved sequence surrounding the activation loop (labeled in orange) of the kinase domain. GU genitourinary.
