Abstract
In hypertensive patients with diabetes, the effectiveness of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors in improving mortality, cardiovascular events, and renal outcomes, compared to other antihypertensive drugs such as calcium channel blockers (CCBs) and diuretics, remains uncertain, particularly in the context of albuminuria. A comprehensive literature search was conducted using PubMed, the Cochrane Library, and the Japan Medical Abstracts Society databases up to October 2024. A meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled trials, including 14,163 patients, was performed. RAS inhibitors showed no significant advantage over CCBs or diuretics for all-cause mortality (relative risk [RR]: 1.00, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.92–1.08, p = 0.98), myocardial infarction (RR: 0.64, 95% CI: 0.32–1.31, p = 0.22), stroke (RR: 1.14, 95% CI: 1.00–1.31, p = 0.05), composite cardiovascular events (RR: 0.93, 95% CI: 0.81–1.07, p = 0.45), or end-stage renal disease (RR: 0.88, 95% CI: 0.72–1.08, p = 0.21). Subgroup analyses stratified by albuminuria status revealed no significant benefits of RAS inhibitors, regardless of albuminuria presence. The findings emphasize the need for cautious interpretation due to limited sample sizes, wide confidence intervals, and low precision. These results highlight the importance of considering not only RAS inhibitors but also other antihypertensive drugs as the first-line choice for blood pressure control in diabetic patients, with careful attention to side effects and other relevant factors.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marx N, Federici M, Schütt K, Müller-Wieland D, Ajjan RA, Antunes MJ, et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes. Eur Heart J. 2023;44:4043–140.
Mancia G, Schumacher H, Redon J, Verdecchia P, Schmieder R, Jennings G, et al. Blood pressure targets recommended by guidelines and incidence of cardiovascular and renal events in the Ongoing telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial (ONTARGET). Circulation. 2011;124:1727–36.
McEvoy JW, McCarthy CP, Bruno RM, Brouwers S, Canavan MD, Ceconi C, et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2024;45:3912–4018.
Mancia G, Kreutz R, Brunström M, Burnier M, Grassi G, Januszewicz A, et al. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension: endorsed by the International Society of Hypertension (ISH) and the European Renal Association (ERA). J Hypertens. 2023;41:1874–2071.
Unger T, Borghi C, Charchar F, Khan NA, Poulter NR, Prabhakaran D, et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2020;75:1334–57.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71:e13–e115.
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–9.
Palmer SC, Mavridis D, Navarese E, Craig JC, Tonelli M, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of blood pressure-lowering agents in adults with diabetes and kidney disease: a network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2015;385:2047–56.
Parving HH, Lehnert H, Bröchner-Mortensen J, Gomis R, Andersen S, Arner P, et al. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:870–8.
Viberti G, Wheeldon NM, MicroAlbuminuria Reduction With VALsartan (MARVAL) Study Investigators. Microalbuminuria reduction with valsartan in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a blood pressure-independent effect. Circulation. 2002;106:672–8.
Schmieder RE, Hilgers KF, Schlaich MP, Schmidt BM. Renin-angiotensin system and cardiovascular risk. Lancet. 2007;369:1208–19.
Cherney DZ, Zinman B, Kennedy CR, Moineddin R, Lai V, Yang S, et al. Long-term hemodynamic and molecular effects persist after discontinued renin-angiotensin system blockade in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 2013;84:1246–53.
Das S, Zhang E, Senapati P, Amaram V, Reddy MA, Stapleton K, et al. A novel angiotensin II-induced long noncoding RNA giver regulates oxidative stress, inflammation, and proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 2018;123:1298–312.
Taal MW, Brenner BM. Renoprotective benefits of RAS inhibition: from ACEI to angiotensin II antagonists. Kidney Int. 2000;57:1803–17.
Kunimura A, Himuro N, Fujiyoshi A, Segawa H, Ohnishi H, Saitoh S. The effects of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on mortality, cardiovascular events, and renal events in hypertensive patients with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hypertens Res. 2019;42:669–80.
Bangalore S, Fakheri R, Toklu B, Messerli FH. Diabetes mellitus as a compelling indication for use of renin angiotensin system blockers: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. BMJ. 2016;352:i438.
Alsalemi N, Sadowski CA, Elftouh N, Louis M, Kilpatrick K, Houle SK, et al. The effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors on continuous and binary kidney outcomes in subgroups of patients with diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. BMC Nephrol. 2022;23:161.
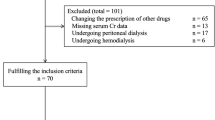
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Tatti P, Pahor M, Byington RP, Di Mauro P, Guarisco R, Strollo G, et al. Outcome results of the fosinopril versus amlodipine cardiovascular Events Randomized Trial (FACET) in patients with hypertension and NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:597–603.
Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Hiatt WR, Biggerstaff SL, Gifford N, Schrier RW. The effect of nisoldipine as compared with enalapril on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes and hypertension. N. Engl J Med. 1998;338:645–52.
Lindholm LH, Hansson L, Ekbom T, Dahlöf B, Lanke J, Linjer E, et al. Comparison of antihypertensive treatments in preventing cardiovascular events in elderly diabetic patients: results from the Swedish Trial in Old Patients with Hypertension-2. STOP Hypertension-2 Study Group. J Hypertens. 2000;18:1671–5.
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:851–60.
Berl T, Hunsicker LG, Lewis JB, Pfeffer MA, Porush JG, Rouleau JL, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes in the irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy Trial of patients with type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:542–9.
Baba S, J-MIND Study Group. Nifedipine and enalapril equally reduce the progression of nephropathy in hypertensive type 2 diabetics. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2001;54:191–201.
Yui Y, Sumiyoshi T, Kodama K, Hirayama A, Nonogi H, Kanmatsuse K, et al. Nifedipine retard was as effective as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in preventing cardiac events in high-risk hypertensive patients with diabetes and coronary artery disease: the Japan Multicenter Investigation for cardiovascular Diseases-B (JMIC-B) subgroup analysis. Hypertens Res. 2004;27:449–56.
Marre M, Puig JG, Kokot F, Fernandez M, Jermendy G, Opie L, et al. Equivalence of indapamide SR and enalapril on microalbuminuria reduction in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes: the NESTOR Study. J Hypertens. 2004;22:1613–22.
Whelton PK, Barzilay J, Cushman WC, Davis BR, Iiamathi E, Kostis JB, et al. Clinical outcomes in antihypertensive treatment of type 2 diabetes, impaired fasting glucose concentration, and normoglycemia: antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:1401–9.
Rahman M, Pressel S, Davis BR, Nwachuku C, Wright JT Jr, Whelton PK, et al. Renal outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients treated with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or a calcium channel blocker vs a diuretic: a report from the antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:936–46.
Nakao K, Hirata M, Oba K, Yasuno S, Ueshima K, Fujimoto A, et al. Role of diabetes and obesity in outcomes of the candesartan antihypertensive survival evaluation in Japan (CASE-J) trial. Hypertens Res. 2010;33:600–6.
Fogari R, Zoppi A, Corradi L, Mugellini A, Lazzari P, Preti P, et al. Long-term effects of ramipril and nitrendipine on albuminuria in hypertensive patients with type II diabetes and impaired renal function. J Hum Hypertens. 1999;13:47–53.
Umemura S, Arima H, Arima S, Asayama K, Dohi Y, Hirooka Y, et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens Res. 2019;42:1235–481.
Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. Lancet. 2000;355:253–9.
Casas JP, Chua W, Loukogeorgakis S, Vallance P, Smeeth L, Hingorani AD, et al. Effect of inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system and other antihypertensive drugs on renal outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2005;366:2026–33.
Wu HY, Huang JW, Lin HJ, Liao WC, Peng YS, Hung KY, et al. Comparative effectiveness of renin-angiotensin system blockers and other antihypertensive drugs in patients with diabetes: systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013;347:f6008.
Saito Y, Yamamoto H, Nakajima H, Takahashi O, Komatsu Y. Incidence of and risk factors for newly diagnosed hyperkalemia after hospital discharge in non-dialysis-dependent CKD patients treated with RAS inhibitors. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0184402.
Strippoli GF, Craig M, Deeks JJ, Schena FP, Craig JC. Effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists on mortality and renal outcomes in diabetic nephropathy: systematic review. BMJ. 2004;329:828.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Editage for providing professional English language editing services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ichikawa, D., Kawarazaki, W., Saka, S. et al. Efficacy of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics in hypertensive patients with diabetes: subgroup analysis based on albuminuria in a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertens Res 48, 1880–1890 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02146-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02146-7
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension 2025 (JSH2025)
Hypertension Research (2026)
-
Key highlights of the Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension 2025 (JSH2025)
Hypertension Research (2025)
-
Comment on: Efficacy of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics in hypertensive patients with diabetes: subgroup analysis based on albuminuria in a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hypertension Research (2025)
-
JSH2025 guidelines new viewpoints
Hypertension Research (2025)
-
The JSH Morning Hypertension Eradication Program Project
Hypertension Research (2025)