Abstract
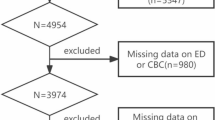
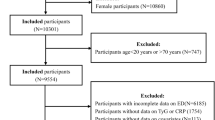
Systemic immune inflammation index (SII) is a global parameter that comprehensively reflects body inflammation, this study aims to assess the correlation between this index and erectile dysfunction (ED). This cross-sectional study incorporated 164 ED patients and 95 healthy adult males. The collection of general demographic information and pertinent hematological data from the participants enabled the computation of corresponding SII values. Statistical analysis, encompassing descriptive statistics as well as normality and logistic regression analyses, was carried out employing SPSS version 26. The findings of the univariate analysis revealed a noteworthy distinction in triglyceride levels (TG) (P = 0.017) and SII (P < 0.001) between ED patients and the healthy population. Subsequent multivariate logistic regression analysis unveiled a significant association between SII (odd ratio (OR):1.012, 95% confidence interval (CI):1.008–1.015; P < 0.001) and the occurrence of ED. Since the impact value is not clearly visible, SII/100 is utilized to magnify the effect value one hundredfold. The regression analysis results indicate that the OR value of SII/100 is 3.171, and the 95% CI is 2.339–4.298 (P < 0.001). The Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis ascertained an AUC of 0.863 (P < 0.001) for SII, with a determined cut-off value of 391.53(109/L), exhibiting a sensitivity of 81.7% and specificity of 83.2%. Moreover, when comparing patients with varying degrees of ED severity, both univariate (P < 0.001) and subsequent multivariate logistic regression analyses (OR: 1.007, 95% CI: 1.004–1.010; P < 0.001) underscored the significance of the SII value. At this point, SII/100 OR: 1.971, 95% CI: 1.508–2.576 (P < 0.001). The ROC curve analysis in this context demonstrated an AUC of 0.799 (P < 0.001), with a determined cut-off value of 746.63(109/L), featuring a sensitivity of 60.6% and specificity of 91.6%. These discerned outcomes affirm a correlation between SII and ED, establishing its potential not only in predicting the onset of ED but also in differentiating among various levels of ED severity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Due to privacy protection, the data of the results of this study have not been published yet. However, if needed, they can be obtained from the corresponding author XSZ.
References
NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA. 1993;270:83–90.
Latini DM, Penson DF, Wallace KL, Lubeck DP, Lue TF. Clinical and psychosocial characteristics of men with erectile dysfunction: baseline data from ExCEED. J Sex Med. 2006;3:1059–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00331.x.
Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994;151:54–61.
Ayta IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ. The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int. 1999;84:50–6. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-410x.1999.00142.x.
Yafi FA, Jenkins L, Albersen M, Corona G, Isidori AM, Goldfarb S, et al. Erectile dysfunction. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16003. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.3.
Özkent MS, Hamarat MB, Taşkapu HH, Kılınç MT, Göger YE, Sönmez MG. Is erectile dysfunction related to self-esteem and depression? A prospective case-control study. Andrologia. 2021;53:e13910. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.13910.
Rust J, Golombok S, Collier J. Marital problems and sexual dysfunction: how are they related. Br J Psychiatry. 1988;152:629–31. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.152.5.629.
Uslu N, Gorgulu S, Alper AT, Eren M, Nurkalem Z, Yildirim A, et al. Erectile dysfunction as a generalized vascular dysfunction. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2006;19:341–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2005.09.017.
Moon DG. Changing men’s health: leading the future. World J Mens Health. 2018;36:1–3. https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.18101.
De Leonardis F, Colalillo G, Finazzi Agrò E, Miano R, Fuschi A, Asimakopoulos AD. Endothelial dysfunction, erectile deficit and cardiovascular disease: an overview of the pathogenetic links. Biomedicines. 2022;10. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081848.
Terentes-Printzios D, Ioakeimidis N, Rokkas K, Vlachopoulos C. Interactions between erectile dysfunction, cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular drugs. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022;19:59–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-021-00593-6.
Liu G, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Wu X, Jiang H, Huang H, et al. Novel predictive risk factor for erectile dysfunction: serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. Andrology. 2022;10:1096–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.13206.
Liao Z, Tang Y, Li X, Li D. The relationship between hematologic parameters and erectile dysfunction. Sex Med. 2021;9:100401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esxm.2021.100401.
Chen JH, Zhai ET, Yuan YJ, Wu KM, Xu JB, Peng JJ, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index for predicting prognosis of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:6261–72. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6261.
Dziedzic EA, Gąsior JS, Tuzimek A, Dąbrowski M, Jankowski P. The association between serum vitamin D concentration and new inflammatory biomarkers-systemic inflammatory index (SII) and systemic inflammatory response (SIRI)-in patients with ischemic heart disease. Nutrients. 2022;14. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194212.
Xu M, Chen R, Liu L, Liu X, Hou J, Liao J, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index and incident cardiovascular diseases among middle-aged and elderly Chinese adults: the Dongfeng-Tongji cohort study. Atherosclerosis. 2021;323:20–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.02.012.
Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD, Lipsky J, Peña BM. Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 1999;11:319–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900472.
Roy N, Rosas SE. Erectile dysfunction and coronary artery calcification in incident dialysis patients. Journal of nephrology. 2021;34:1521–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-021-00994-3.
Huang S, Zhu S, Liu R, Xiong C, Liu L, Huang J, et al. The characteristics of sexual behavior in blind men in Ganzhou, China: a cross-sectional study. Medicine. 2024;103:e37574. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000037574.
Li W, Chen K, Zhang J, Wang X, Xu G, Zhu Y, et al. Association between serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels and erectile dysfunction: a cross-sectional study of Chinese male population. Sci Rep. 2019;9:5929. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42342-3.
Akbas A, Gulpınar MT, Sancak EB, Gunes M, Ucar M, Altok M, et al. The relationship between platelet-lymphocyte ratio and severity of erectile dysfunction. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2016;32:91–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjms.2015.11.002.
Feng X, Mei Y, Wang X, Cui L, Xu R. Association between neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and erectile dysfunction among US males: a population-based cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1192113. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1192113.
Liu G, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Wu X, Huang H, Jiang H, et al. Significance of detailed hematological parameters as markers of arteriogenic erectile dysfunction. Andrology. 2022;10:1556–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.13283.
Sambel M, Kilic M, Demirbas M, Onen E, Oner S, Erdogan A, et al. Relationship between erectile dysfunction and the neutrophil to lymphocyte and platelet to lymphocyte ratios. Int J Impot Res. 2018;30:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-017-0007-1.
Liu C, Gao Y, Ji J, Sun C, Chen M. Association between inflammatory indexes and erectile dysfunction in U.S. adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001-2004. Sex Med. 2023;11:qfad045. https://doi.org/10.1093/sexmed/qfad045.
Zhong L, Zhan X, Luo X. Higher systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with increased risk of erectile dysfunction: result from NHANES 2001-2004. Medicine. 2023;102:e35724. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000035724.
Yaradilmiş RM, Güneylioğlu MM, Öztürk B, Göktuğ A, Aydın O, Güngör A, et al. A novel marker for predicting fulminant myocarditis: systemic immune-inflammation index. Pediatr Cardiol. 2023;44:647–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-022-02988-9.
Tang Y, Zeng X, Feng Y, Chen Q, Liu Z, Luo H, et al. Association of systemic immune-inflammation index with short-term mortality of congestive heart failure: a retrospective cohort study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:753133. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.753133.
Chen CC, Su JS, Yeh HZ, Chang CS, Peng YC, Tseng CW, et al. Association between colonic diverticulosis and erectile dysfunction: a nationwide population-based study. Medicine. 2015;94:e2042. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000002042.
Taskiran M, Dogan K. The efficacy of systemic inflammatory response and oxidative stress in erectile dysfunction through multi-inflammatory index: a prospective cross-sectional analysis. J Sex Med. 2023;20:591–96. https://doi.org/10.1093/jsxmed/qdad037.
Salonia A, Capogrosso P, Clementi MC, Castagna G, Damiano R, Montorsi F. Is erectile dysfunction a reliable indicator of general health status in men. Arab J Urol. 2013;11:203–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aju.2013.07.008.
Sheweita SA, Meftah AA, Sheweita MS, Balbaa ME. Erectile dysfunction drugs altered the activities of antioxidant enzymes, oxidative stress and the protein expressions of some cytochrome P450 isozymes involved in the steroidogenesis of steroid hormones. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0241509. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241509.
Münzel T, Daiber A, Ullrich V, Mülsch A. Vascular consequences of endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling for the activity and expression of the soluble guanylyl cyclase and the cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:1551–7. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000168896.64927.bb.
Vlachopoulos C, Rokkas K, Ioakeimidis N, Stefanadis C. Inflammation, metabolic syndrome, erectile dysfunction, and coronary artery disease: common links. Eur Urol. 2007;52:1590–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2007.08.004.
Kadoglou NPE, Kapetanios D, Korakas E, Valsami G, Tentolouris N, Papanas N, et al. Association of serum levels of osteopontin and osteoprotegerin with adverse outcomes after endovascular revascularisation in peripheral artery disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022;21:171. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-022-01605-6.
Aslan A, Kaya Y, Cirakoglu A, Benli E, Demir EY, Calgin MK. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio could be a marker for erectile dysfunction. Urol J. 2019;16:216–20. https://doi.org/10.22037/uj.v16i2.5011.
Xiang J, He L, Li D, Wei S, Wu Z. Value of the systemic immune-inflammation index in predicting poor postoperative outcomes and the short-term prognosis of heart valve diseases: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e064171. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2022-064171.
Langseth MS, Andersen G, Husebye T, Arnesen H, Zucknick M, Solheim S, et al. Neutrophil extracellular trap components and myocardial recovery in post-ischemic acute heart failure. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0241333. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241333.
Xiu WJ, Yang HT, Zheng YY, Wu TT, Hou XG, Jiang ZH, et al. ALB-dNLR score predicts mortality in coronary artery disease patients after percutaneous coronary intervention. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:709868. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.709868.
Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M. Leukocyte behavior in atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and heart failure. Science. 2013;339:161–6. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1230719.
Charach G, Grosskopf I, Roth A, Afek A, Wexler D, Sheps D, et al. Usefulness of total lymphocyte count as predictor of outcome in patients with chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2011;107:1353–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.12.049.
Markwart R, Condotta SA, Requardt RP, Borken F, Schubert K, Weigel C, et al. Immunosuppression after sepsis: systemic inflammation and sepsis induce a loss of naïve T-cells but no enduring cell-autonomous defects in T-cell function. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e115094. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115094.
Osorio C, Sfera A, Anton JJ, Thomas KG, Andronescu CV, Li E, et al. Virus-induced membrane fusion in neurodegenerative disorders. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:845580. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.845580.
Dindas F, Koyun E, Turkyilmaz E, Abacioglu OO, Yildirim A, Sahin A, et al. Systemic immune inflammation index is a novel marker in predicting the presence and severity of isolated coronary artery ectasia. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023;120:e20220056. https://doi.org/10.36660/abc.20220056.
Chen L, Yan Y, Zhu L, Cong X, Li S, Song S, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index as a useful prognostic indicator predicts survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Manag Res. 2017;9:849–67. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.S151026.
Dai XT, Kong TZ, Zhang XJ, Luan B, Wang Y, Hou AJ. Relationship between increased systemic immune-inflammation index and coronary slow flow phenomenon. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022;22:362. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-022-02798-0.
Cocoş R, Mahler B, Turcu-Stiolica A, Stoichiță A, Ghinet A, Shelby ES, et al. Risk of death in comorbidity subgroups of hospitalized COVID-19 patients inferred by routine laboratory markers of systemic inflammation on admission: a retrospective study. Viruses. 2022;14. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061201.
Ye GL, Chen Q, Chen X, Liu YY, Yin TT, Meng QH, et al. The prognostic role of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute heart failure: a cohort study. Sci Rep. 2019;9:10639. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47143-2.
Akın F, Ayça B, Çelik Ö, Şahin C. Predictors of poor coronary collateral development in patients with stable coronary artery disease: neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelets. Anatol J Cardiol. 2015;15:218–23. https://doi.org/10.5152/akd.2014.5263.
Goldsmith DR, Bekhbat M, Mehta ND, Felger JC. Inflammation-related functional and structural dysconnectivity as a pathway to psychopathology. Biol Psychiatry. 2023;93:405–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2022.11.003.
Ketchem JM, Bowman EJ, Isales CM. Male sex hormones, aging, and inflammation. Biogerontology. 2023;24:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-022-10002-1.
Zou Z, Lin H, Zhang Y, Wang R. The role of nocturnal penile tumescence and rigidity (NPTR) monitoring in the diagnosis of psychogenic erectile dysfunction: a review. Sex Med Rev. 2019;7:442–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sxmr.2018.10.005.
Pathak RA, Broderick GA. Color Doppler duplex ultrasound parameters in men without organic erectile dysfunction. Urology. 2020;135:66–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2019.09.002.
Funding
This study received funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82071637).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: Xiansheng Zhang. Acquisition and interpretation of data: Hui Gao and Xu Wu. Draft and revise the content of the article: Hui Gao, Xu Wu, and Yuyang Zhang. Review and editing, final approval of the completed article: Hui Gao, Guodong Liu, and Xiansheng Zhang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, H., Wu, X., Zhang, Y. et al. Novel predictive factor for erectile dysfunction: systemic immune inflammation index. Int J Impot Res 37, 637–644 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-024-00969-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-024-00969-5