Abstract
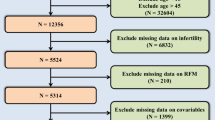
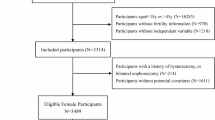
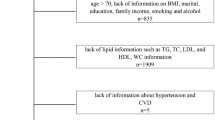
The high prevalence of erectile dysfunction (ED) underscores the critical importance of interventions and preventive measures targeting potential risk factors, among which obesity stands out. Relative fat mass (RFM) emerges as a superior indicator for quantifying body fat compared to traditional metrics like body mass index (BMI) or waist circumference (WC). However, research on the relationship between RFM and ED is extremely limited. A total of 3627 participants from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001-2004 were eligible for analysis. The RFM is calculated using the following formula: RFM = 64-(20×height/WC). Weighted multivariable logistic regression models were utilized to assess the correlation between RFM and ED, supplemented by smooth curve fitting to further explore the linear association. When all potential covariates adjusted, continuous RFM demonstrated a positive association with ED prevalence (odds ratio (OR): 1.11, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.05-1.18, P = 0.002). When RFM was categorized into tertiles (T1-T3), participants in T3 group exhibited a significantly higher likelihood of ED (OR: 2.19, 95% CI: 1.19, 4.05, P = 0.020) compared to those in T1. Subgroup analyses revealed a stronger correlation among participants aged over 60 years, obese individuals, and those with hypertension, while weaker correlations were observed among those with diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD). After sensitivity analysis for severe ED, the aforementioned regression analysis results remained statistically significant. The final ROC analysis demonstrated that the predictive ability of RFM was superior to that of BMI and WC, with an AUC (95% CI) of 0.639 (0.619-0.659). Elevated RFM demonstrated a linear correlation with increased incidence of ED and exhibited strong predictive capability for ED, underscoring the importance of obesity intervention for ED. Future studies with larger clinical samples are necessary to confirm our findings and expand the application value of RFM in assessing ED risk.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original NHANES data were accessible on the NHANES public database, and the processed data for this study are included in this published article. Further requests for our data and the corresponding R code can be made by contacting the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Elterman DS, Bhattacharyya SK, Mafilios M, Woodward E, Nitschelm K, Burnett AL. The Quality of Life and Economic Burden of Erectile Dysfunction. Res Rep Urol. 2021;13:79–86.
Herbenick D, Reece M, Schick V, Sanders SA, Dodge B, Fortenberry JD. Sexual behavior in the United States: results from a national probability sample of men and women ages 14-94. J Sex Med. 2010;7:255–65.
Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994;151:54–61.
NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA. 1993;270:83–90.
Mark KP, Arenella K, Girard A, Herbenick D, Fu J, Coleman E. Erectile dysfunction prevalence in the United States: report from the 2021 National Survey of Sexual Wellbeing. J Sex Med. 2024;21:296–303.
Braun M, Wassmer G, Klotz T, Reifenrath B, Mathers M, Engelmann U. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: results of the ‘Cologne Male Survey. Int J Impot Res. 2000;12:305–11.
Nicolosi A, Glasser DB, Kim SC, Marumo K, Laumann EO. Sexual behaviour and dysfunction and help-seeking patterns in adults aged 40-80 years in the urban population of Asian countries. BJU Int. 2005;95:609–14.
Nicolosi A, Moreira ED Jr, Shirai M, Bin Mohd Tambi MI, Glasser DB. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction in four countries: cross-national study of the prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction. Urology. 2003;61:201–6.
Ayta IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ. The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int. 1999;84:50–6.
Yao FJ, Zhang YD, Wan Z, Li W, Lin H, Deng CH, et al. Erectile dysfunction is associated with subclinical carotid vascular disease in young men lacking widely-known risk factors. Asian J Androl. 2018;20:400–4.
Dong JY, Zhang YH, Qin LQ. Erectile dysfunction and risk of cardiovascular disease: meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:1378–85.
Jiang T, Osadchiy V, Mills JN, Eleswarapu SV. Is It All in My Head? Self-reported Psychogenic Erectile Dysfunction and Depression Are Common Among Young Men Seeking Advice on Social Media. Urology. 2020;142:133–40.
Wang Y, Zhao L, Gao L, Pan A, Xue H. Health policy and public health implications of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9:446–61.
De Lorenzo A, Gratteri S, Gualtieri P, Cammarano A, Bertucci P, Di Renzo L. Why primary obesity is a disease? J Transl Med. 2019;17:169.
Feeley RJ, Traish AM. Obesity and erectile dysfunction: is androgen deficiency the common link? ScientificWorldJournal. 2009;9:676–84.
Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2020;360:1–8.
Ward ZJ, Bleich SN, Cradock AL, Barrett JL, Giles CM, Flax C, et al. Projected U.S. State-Level Prevalence of Adult Obesity and Severe Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2440–50.
Bacon CG, Mittleman MA, Kawachi I, Giovannucci E, Glasser DB, Rimm EB. A prospective study of risk factors for erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 2006;176:217–21.
Derby CA, Mohr BA, Goldstein I, Feldman HA, Johannes CB, McKinlay JB. Modifiable risk factors and erectile dysfunction: can lifestyle changes modify risk? Urology. 2000;56:302–6.
Donini LM, Pinto A, Giusti AM, Lenzi A, Poggiogalle E. Obesity or BMI Paradox? Beneath the Tip of the Iceberg. Front Nutr. 2020;7:53.
Ness-Abramof R, Apovian CM. Waist circumference measurement in clinical practice. Nutr Clin Pract. 2008;23:397–404.
Mahmoud I, Al-Wandi AS, Gharaibeh SS, Mohamed SA. Concordances and correlations between anthropometric indices of obesity: a systematic review. Public Health. 2021;198:301–6.
Duren DL, Sherwood RJ, Czerwinski SA, Lee M, Choh AC, Siervogel RM, et al. Body composition methods: comparisons and interpretation. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2008;2:1139–46.
Woolcott OO, Bergman RN. Relative fat mass (RFM) as a new estimator of whole-body fat percentage ─ A cross-sectional study in American adult individuals. Sci Rep. 2018;8:10980.
Zhu X, Yue Y, Li L, Zhu L, Cai Y, Shu Y. The relationship between depression and relative fat mass (RFM): A population-based study. J Affect Disord. 2024;356:323–8.
Shen W, Cai L, Wang B, Wang Y, Wang N, Lu Y. Associations of Relative Fat Mass, a Novel Adiposity Indicator, with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: Data from SPECT-China. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023;16:2377–87.
Derby CA, Araujo AB, Johannes CB, Feldman HA, McKinlay JB. Measurement of erectile dysfunction in population-based studies: the use of a single question self-assessment in the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. Int J Impot Res. 2000;12:197–204.
Wu X, Zhang Y, Liu G, Jiang H, Zhang X. Association between severe headache or migraine and erectile dysfunction in American adults: a cross-sectional of data study from the NHANES. Int J Impot Res. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-024-00867-w.
Macdonald EJ, Gaines JM, Kim JI, Paduch DA. Exploring the relationship between socioeconomic status and erectile dysfunction: an analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Int J Impot Res. 2023;35:478–83.
Youcheng L, Xun W, Zhufeng C. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and erectile dysfunction among American Adults from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: a cross-sectional study. Int J Impot Res. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-024-00914-6.
Riedner CE, Rhoden EL, Ribeiro EP, Fuchs SC. Central obesity is an independent predictor of erectile dysfunction in older men. J Urol. 2006;176:1519–23.
Liu Y, Hu X, Xiong M, Li J, Jiang X, Wan Y, et al. Association of BMI with erectile dysfunction: A cross-sectional study of men from an andrology clinic. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1135024.
Janiszewski PM, Janssen I, Ross R. Abdominal obesity and physical inactivity are associated with erectile dysfunction independent of body mass index. J Sex Med. 2009;6:1990–8.
Yassin AA, Nettleship JE, Salman M, Almehmadi Y. Waist circumference is superior to weight and BMI in predicting sexual symptoms, voiding symptoms and psychosomatic symptoms in men with hypogonadism and erectile dysfunction. Andrologia. 2017;49:1–6.
Lin W, Lin ME. Novel anthropometric measures are positively associated with erectile dysfunction: a cross-sectional study. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024;56:855–65.
Eknoyan G. Adolphe Quetelet (1796-1874)-the average man and indices of obesity. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:47–51.
Humphreys S. The unethical use of BMI in contemporary general practice. Br J Gen Pract. 2010;60:696–7.
Grier T, Canham-Chervak M, Sharp M, Jones BH. Does body mass index misclassify physically active young men. Prev Med Rep. 2015;2:483–7.
Batsis JA, Villareal DT. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: aetiology, epidemiology and treatment strategies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14:513–37.
Ross R, Neeland IJ, Yamashita S, Shai I, Seidell J, Magni P, et al. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: a Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16:177–89.
Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Ascherio A, Spiegelman D, Colditz GA, et al. Body size and fat distribution as predictors of coronary heart disease among middle-aged and older US men. Am J Epidemiol. 1995;141:1117–27.
Vazquez G, Duval S, Jacobs DR Jr, Silventoinen K. Comparison of body mass index, waist circumference, and waist/hip ratio in predicting incident diabetes: a meta-analysis. Epidemiol Rev. 2007;29:115–28.
Wang J, Guan J, Huang L, Li X, Huang B, Feng J, et al. Sex differences in the associations between relative fat mass and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A population-based prospective cohort study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2024;34:738–54.
Guzmán-León AE, Velarde AG, Vidal-Salas M, Urquijo-Ruiz LG, Caraveo-Gutiérrez LA, Valencia ME. External validation of the relative fat mass (RFM) index in adults from north-west Mexico using different reference methods. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0226767.
Yu P, Huang T, Hu S, Yu X. Predictive value of relative fat mass algorithm for incident hypertension: a 6-year prospective study in Chinese population. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e038420.
Suthahar N, Wang K, Zwartkruis VW, Bakker SJL, Inzucchi SE, Meems LMG, et al. Associations of relative fat mass, a new index of adiposity, with type-2 diabetes in the general population. Eur J Intern Med. 2023;109:73–8.
Efe S, Karagoz A, Dogan C, Bayram Z, Kalkan S, Altıntas MS, et al. Relative Fat Mass Index can be solution for obesity paradox in coronary artery disease severity prediction calculated by SYNTAX Score. Postgrad Med J. 2021;97:434–41.
Caiano LM, Costanzo S, Panzera T, Di Castelnuovo A, de Gaetano G, Donati MB, et al. Association between body mass index, waist circumference, and relative fat mass with the risk of first unprovoked venous thromboembolism. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021;31:3122–30.
Zhang M, Wang Z, Liu W, Wang M, Wu H, An R. Association between the recommended volume of leisure-time physical activity and erectile dysfunction: A cross-sectional analysis of the national health and nutrition examination survey, 2001-2004. Heliyon. 2024;10:e32884.
Zhou H, Xu M, Xu Z, Li M, Ren C, Chen X, et al. The association of various physical activities with erectile dysfunction: NHANES 2001-2004. Sex Med. 2023;11:qfad036.
Huangfu Z, Gan X, Yang Y, Pang Q, Zhu B, Zhang X, et al. A Mendelian randomization study on causal effects of leisure sedentary behavior on the risk of erectile dysfunction. Andrology. 2024;12:1841–50.
Xi YJ, Feng YG, Bai YQ, Wen R, Zhang HY, Su QY, et al. Genetic prediction of modifiable lifestyle factors for erectile dysfunction. Sex Med. 2024;12:qfae010.
Tucker J, Salas J, Secrest S, Scherrer JF. Erectile dysfunction associated with undiagnosed prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in young adult males: A retrospective cohort study. Prev Med. 2023;174:107646.
Liu Q, Zhang Y, Wang J, Li S, Cheng Y, Guo J, et al. Erectile Dysfunction and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Sex Med. 2018;15:1073–82.
Chen G, Huang L, Lai M, Ran J. Association between erectile dysfunction and the prevalence and prognosis of hyperglycemia in adults in the USA based on NHANES 2001-2004. Sci Rep. 2024;14:17663.
Acknowledgements
We extend our gratitude to all NHANES participants and staff for their outstanding work and substantial data contributions. We also thank the Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University for their support.
Funding
This work received support from the Changzhou Health Commission’s Youth Talent Science and Technology Project (Grant No. QN202109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xingliang Feng, Nuo Ji, Bo Zhang, Yiming Chen: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review & editing; Xingliang Feng, Nuo Ji and Wei Xia: data curation, formal analysis, writing- original draft preparation; Xingliang Feng, Nuo Ji, Yiming Chen: validation, supervision, writing—review & editing, funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics
The study protocols were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) (Protocol #98-12), and all participants provided written informed consent. The NHANES database is publicly accessible; therefore, a second ethical review of this study by our institution was exempt. Additionally, all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
All authors have given their consent for publication
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, X., Ji, N., Zhang, B. et al. Association of relative fat mass with prevalence of erectile dysfunction in US men: an analysis of NHANES 2001-2004. Int J Impot Res 37, 645–654 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-024-01003-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-024-01003-4