Abstract
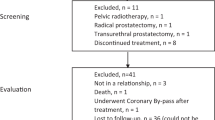
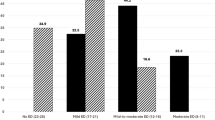
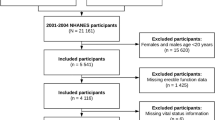
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common male sexual disorder. Vitamin D (VD) deficiency is frequent in ED patients and has been associated with greater disease severity, but its role in predicting treatment response remains unclear. In this prospective cohort study, 202 ED patients were initially enrolled, and after excluding 30 ineligible cases, 172 were included in the final analysis at Chengdu University of TCM Affiliated Hospital (September 2023–August 2024). ED severity was evaluated using the International Index of Erectile Function-5 (IIEF-5) during a 1-month follow-up, with 152 patients (88.4%) reporting symptomatic improvement after daily tadalafil 5 mg treatment. Patients with VD ≥ 20 ng/mL showed faster responses. Multivariate Cox regression demonstrated a significant positive association between baseline VD levels and treatment outcomes (adjusted hazard ratio = 1.60 per 1 ng/mL increase; 95% confidence interval: 1.31–1.95). Restricted Cubic Spline analysis revealed a nonlinear relationship, with the strongest effect observed at VD ≤ 19.6 ng/mL, representing a data-driven inflection point. Interaction analyses further confirmed consistent benefits across all age groups. These findings indicate that baseline VD is an independent prognostic factor for tadalafil efficacy in ED, highlighting its potential clinical utility for risk stratification and individualized treatment decisions in ED.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset generated during the current study was available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Zhang X, Yang B, Li N, Li H. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in chinese adult males. J Sex Med. 2017;14:1201–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsxm.2017.08.009.
NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH consensus development panel on impotence. JAMA. 1993;270:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1993.03510010089036.
McCabe MP, Sharlip ID, Lewis R, Atalla E, Balon R, Fisher AD, et al. Incidence and prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women and men: a consensus statement from the fourth international consultation on sexual medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13:144–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsxm.2015.12.034.
Ayta IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ. The likely worldwide increase in erectile Dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int. 1999;84:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-410x.1999.00142.x.
Sheng Z. Psychological consequences of erectile dysfunction. Trends Urol Mens Health. 2021;12:19–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/tre.827.
Delrue C, Speeckaert MM. Vitamin D and Vitamin D-binding protein in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:4642 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054642.
DeLuca HF. Vitamin D endocrinology. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85:367–77. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-85-3-367.
Farag YMK, Guallar E, Zhao D, Kalyani RR, Blaha MJ, Feldman DI, et al. Vitamin D deficiency is independently associated with greater prevalence of erectile dysfunction: the national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES) 2001-4. Atherosclerosis. 2016;252:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.07.921.
Horsanalı MO, Eren H, Dil E, Caglayan A, Erdogan O, Ekren F. Novel predictive risk factor of erectile dysfunction: Serum 25‐hydroxy vitamin D. Andrologia. 2020;52:e13767 https://doi.org/10.1111/and.13767.
Crafa A, Cannarella R, Condorelli RA, La Vignera S, Calogero AE. Is there an association between vitamin D deficiency and erectile dysfunction? a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2020;12:1411 https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051411.
Duarte Romero B, Waterhouse M, Baxter C, McLeod DSA, English DR, Armstrong BK, et al. The effect of three years of vitamin D supplementation on erectile dysfunction: results from the randomized placebo-controlled D-Health Trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2024;60:109–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2024.01.011.
Elshahid AR, Zaky AM, Goda YMH, Ismail NF. Relationship between vitamin D receptors gene polymorphism and arteriogenic erectile dysfunction. Urologia. 2024;91:592–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/03915603241241430.
Crafa A, Cannarella R, Barbagallo F, Leanza C, Palazzolo R, Flores HA, et al. Mechanisms suggesting a relationship between vitamin D and erectile dysfunction: an overview. Biomolecules. 2023;13:930 https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13060930.
Wang R, Zheng T, Zhang TB, Li R, Wang ZL, Yang F, et al. Efficacy and safety of sildenafil citrate in treatment of erectile dysfunction. Natl J Androl. 2019;25:603–7. https://doi.org/10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2019.07.005. Article in Chinese].
Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD, Lipsky J, Peña BM. Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 1999;11:319–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900472.
Chinese Urological Association. Diagnosis and treatment guidelines for erectile dysfunction. Chin J Androl. 2022;28:722–55. https://doi.org/10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2022.08.009. Article in Chinese].
Vermeulen A, Verdonck L, Kaufman JM. A critical evaluation of simple methods for the estimation of free testosterone in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84:3666–72. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.84.10.6079.
Rosen RC, Allen KR, Ni X, Araujo AB. Minimal clinically important differences in the erectile function domain of the international index of erectile function scale. Eur Urol. 2011;60:1010–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2011.07.053.
Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:1911–30. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2011-0385.
Portest S. A primer on model selection using the akaike information criterion. Infect Dis Model. 2020;5:111–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idm.2019.12.010.
Marrie RA, Dawson NV, Garland A. Quantile regression and restricted cubic splines are useful for exploring relationships between continuous variables. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:511–.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.05.015.
MacDonald SM, Burnett AL. Physiology of erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 2021;48:513–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ucl.2021.06.009.
Toda N, Ayajiki K, Okamura T. Nitric oxide and penile erectile function. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;106:233–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.11.011.
Andrukhova O, Slavic S, Zeitz U, Riesen SC, Heppelmann MS, Ambrisko TD, et al. Vitamin D is a regulator of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and arterial stiffness in mice. Mol Endocrinol. 2014;28:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2013-1252.
Molinari C, Uberti F, Grossini E, Vacca G, Carda S, Invernizzi M, et al. 1α,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol induces nitric oxide production in cultured endothelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;27:661–8. https://doi.org/10.1159/000330075.
Lin CS, Lin G, Xin ZC, Lue TF. Expression, distribution and regulation of phosphodiesterase 5. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12:3439–57. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161206778343064.
Grossman E. The role of tadalafil in treated hypertensive patients with erectile dysfunction. J Clin Hypertens. 2022;24:182–3. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.14434.
Taskiran M, Dogan K. The efficacy of systemic inflammatory response and oxidative stress in erectile dysfunction through multi-inflammatory index: a prospective cross-sectional analysis. J Sex Med. 2023;20:591–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/jsxmed/qdad037.
Querfeld U. Vitamin D and inflammation. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013;28:605–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2377-4.
De Vita F, Lauretani F, Bauer J, Bautmans I, Shardell M, Cherubini A, et al. Relationship between vitamin D and inflammatory markers in older individuals. Age. 2014;36:9694 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9694-4.
Defeudis G, Mazzilli R, Tenuta M, Rossini G, Zamponi V, Olana S, et al. Erectile dysfunction and diabetes: A melting pot of circumstances and treatments. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2021;38:e3494 https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3494.
Ma WJ, Qin M, Cui TW, Zhang XP, Ke ZH, Pan ZK, et al. Relationship between the risk factors of cardiovascular disease by testing biochemical markers and young men with erectile dysfunction: a case-control study. Transl Androl Urol. 2021;10:724 https://doi.org/10.21037/tau-20-1056.
Fujita N, Okamoto T, Yamamoto H, Yoneyama T, Hashimoto Y, Mikami T, et al. Association between sex hormones and erectile dysfunction in men without hypoandrogenism. Sci Rep. 2024;14:13433 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-64339-3.
Park CY, Shin S, Han SN. Multifaceted roles of vitamin D for diabetes: from immunomodulatory functions to metabolic regulations. Nutrients. 2024;16:3185 https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183185.
Radkhah N, Zarezadeh M, Jamilian P, Ostadrahimi A. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on lipid profiles: an umbrella review of meta-analyses. Adv Nutr. 2023;14:1479–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advnut.2023.08.012.
Wang XX, Jiang T, Shen Y, Santamaria H, Solis N, Arbeeny C, et al. Vitamin D receptor agonist doxercalciferol modulates dietary fat-induced renal disease and renal lipid metabolism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011;300:F801 https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00338.2010.
Hofer D, Münzker J, Schwetz V, Ulbing M, Hutz K, Stiegler P, et al. Testicular synthesis and vitamin D action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:3766–73. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-1690.
Wehr E, Pilz S, Boehm BO, März W, Obermayer-Pietsch B. Association of vitamin D status with serum androgen levels in men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010;73:243–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2009.03777.x.
Pilz S, Frisch S, Koertke H, Kuhn J, Dreier J, Obermayer-Pietsch B, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on testosterone levels in men. Horm Metab Res. 2010;43:223–5. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1269854.
Burnett AL, Nehra A, Breau RH, Culkin DJ, Faraday MM, Hakim LS, et al. Erectile dysfunction: AUA guideline. J Urol. 2018;200:633–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2018.05.004.
Zhou A, Selvanayagam JB, Hyppönen E. Non-linear Mendelian randomization analyses support a role for vitamin D deficiency in cardiovascular disease risk. Eur Heart J. 2022;43:1731–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab809.
Zhang JJ, Yu HC, Geng TT, Zhang JJ, Zhou XT, Wang YX, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations, vitamin D receptor polymorphisms, and risk of infections among individuals with type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2024;120:398–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.06.007.
Sofianopoulou E, Kaptoge SK, Afzal S, Jiang T, Gill D, Gundersen TE, et al. Estimating dose-response relationships for vitamin D with coronary heart disease, stroke, and all-cause mortality: observational and Mendelian randomisation analyses. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024;12:e2–e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(23)00287-5.
Ross AC, Manson JE, Abrams SA, Aloia JF, Brannon PM, Clinton SK, et al. The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the institute of medicine: what clinicians need to know. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-2704.
Kupelian V, Link CL, Rosen RC, McKinlay JB. Socioeconomic status, not race/ethnicity, contributes to variation in the prevalence of erectile dysfunction: results from the boston area community health (BACH) Survey. J Sex Med. 2008;5:1325–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2008.00822.x.
Irfan M, Hussain NHN, Noor NM, Mohamed M, Sidi H, Ismail SB. Epidemiology of male sexual dysfunction in asian and european regions: a systematic review. Am J Mens Health. 2020;14:1557988320937200 https://doi.org/10.1177/1557988320937200.
Cai Z, Li H. Developing a prediction model for the self-evaluation of erectile dysfunction in an adult male population. Andrologia. 2021;53:e13880 https://doi.org/10.1111/and.13880.
Zhao LM, Jiang H, Hong K, Liu DF, Ma LL, Zhu JC. Analysis of the benefits of tadalafil for patients with erectile dysfunction. Chin J Androl. 2011;17:89–92. https://doi.org/10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2011.01.021. Article in Chinese].
Jiang H, Zhao LM, Yan S, Liu JH, Zhu ZH, Luo JD, et al. Long-term tadalafil once daily in Chinese men with erectile dysfunction: a 2-year final analysis of a post-marketing, multicenter, randomized, open-label trial. Asian J Androl. 2024;26:282–7. https://doi.org/10.4103/aja202370.
Wang CM, Wu BR, Xiang P, Xiao J, Hu XC. Management of male erectile dysfunction: From the past to the future. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1148834 https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1148834.
Salonia, Capogrosso A, Boeri P, Cocci L, Corona G A, Dinkelman-Smit M, et al. European association of urology guidelines on male sexual and reproductive health: 2025 update on male hypogonadism, erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and peyronie’s disease. Eur Urol. 2025;S0302-2838:00211–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2025.04.010.
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their sincere gratitude to all individuals and organizations that have contributed to the successful completion of this study. Our deepest appreciation goes to the patients who participated in this research, acknowledging their patience and support throughout the study. We express our thanks to the staff at the Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine for their invaluable assistance in patient recruitment and data collection. We are also grateful to our colleagues in the Urology and Andrology departments of the same hospital for their insightful discussions and technical support throughout the course of this study. Special acknowledgment is due to our supervisor, Professor Cai Jian, for his significant contributions to the research ideas, data analysis, and manuscript preparation. His guidance was instrumental in shaping this work. Lastly, we extend our sincere thanks to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive feedback, which substantially enhanced the quality of our manuscript.
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hang Yang: Methodology, Data collection, Analysis, Writing – original draft. Hao Tan: Data collection, Writing - Review & Editing. Juan Zhao: Data collection, Writing - Review & Editing. Qing Li: Data collection, Writing & Editing. Jian Cai: Methodology, Data collection, Writing - Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Evaluation
The treatment methods used in our study are in accordance with clinical standards. All data collection was conducted with the informed consent of the patients. We did not collect any sensitive personal information, and all data were anonymized. After consulting with the local ethical review board, it was determined that our study does not require an ethical review. This decision was based on the minimal risk posed to participants and the absence of sensitive or personal data that could compromise their privacy.
Competing interests
The present study is an independent and original work, with no competing interests or conflicts with any organization or related publications.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Tan, H., Zhao, J. et al. Nonlinear association between vitamin D levels and response to tadalafil 5 mg daily treatment in erectile dysfunction patients: a prospective cohort study. Int J Impot Res (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-026-01242-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-026-01242-7