Fig. 1: Population associations between loneliness and brain structure.
From: The default network of the human brain is associated with perceived social isolation
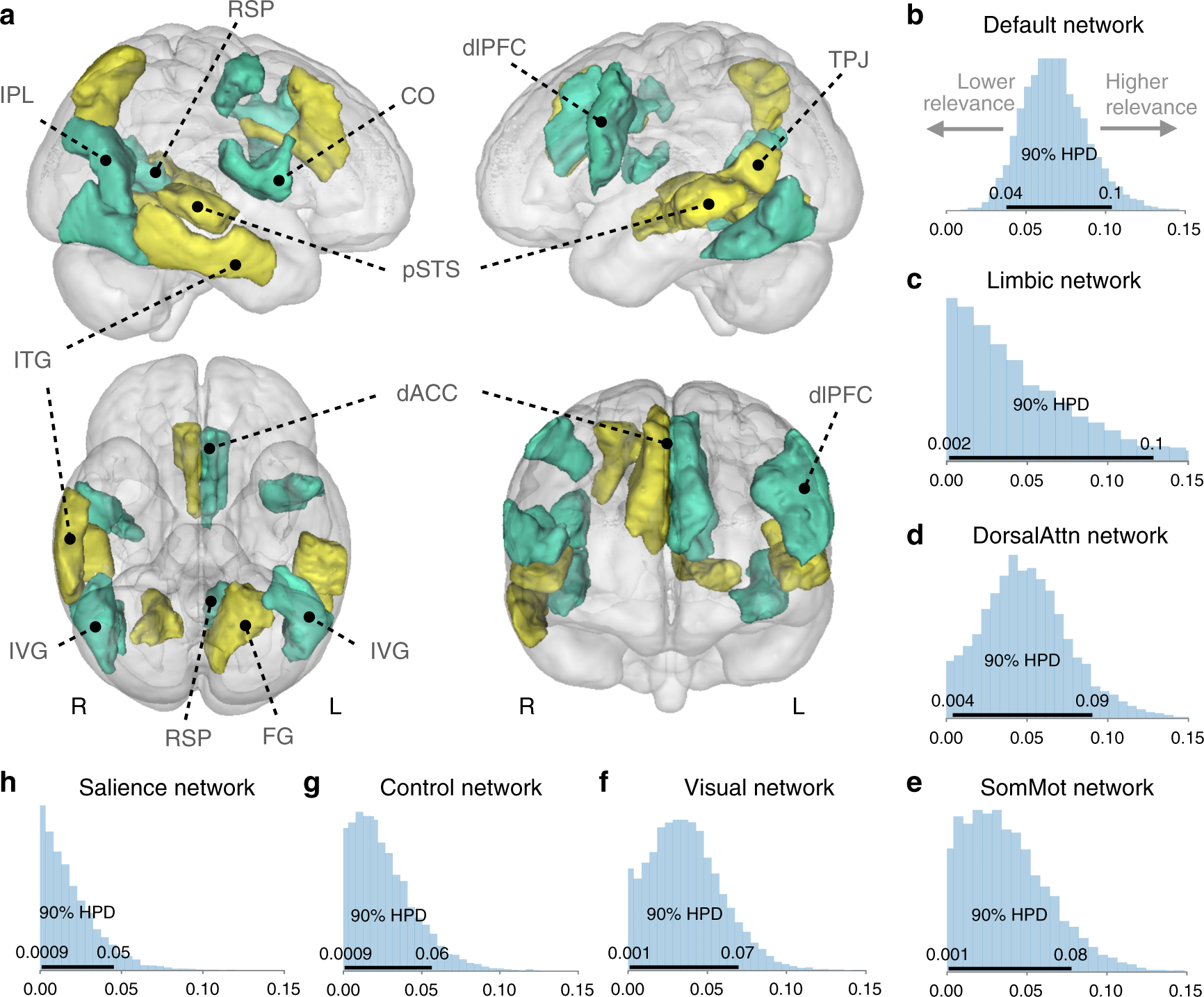
To provide a richer and more precise picture of variation, we purpose-designed a Bayesian hierarchical framework. The fully probabilistic modeling approach allowed jointly estimating varying effects in separate brain regions and spatially distributed networks of constituent brain regions. In rough analogy to ANOVA, the network definitions could be viewed as “factors” and the region definitions could be viewed as continuous factor “levels”. This analysis tactic enabled quantifying the extent to which spatially dispersed regional variation in gray matter volume can be better explained by coherent differences in major brain networks. a Contribution of each regional brain volume (thresholded according to 5–95% highest posterior density [HPD], black horizontal line in b–h) to explain the difference between lonely and non-lonely individuals. Yellow/green = positive/negative volume association. b–h Shows the degree to which volume variation in each canonical network of regions reliably relates to loneliness. Posterior distributions for the variance parameter (sigma) of each brain network are ordered from the most important (default network) to the least explanatory (salience network). CO central operculum, ITG inferior temporal gyrus, pSTS posterior superior temporal sulcus, TPJ temporoparietal junction, IPL inferior parietal lobe, dACC dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, dlPFC dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, RSP retrosplenial cortex, FG fusiform gyrus, IVG inferior visual gyrus, L/R denotes left/right hemisphere. The shown Bayesian model was fitted once to our whole UKB sample, but brain-loneliness associations held up to cross-validated out-of-sample testing in structural MRI (Supplementary Fig. 11). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
