Fig. 1: Structures and previously unsequenced regions of subtelomeres in S. pombe 972 strain.
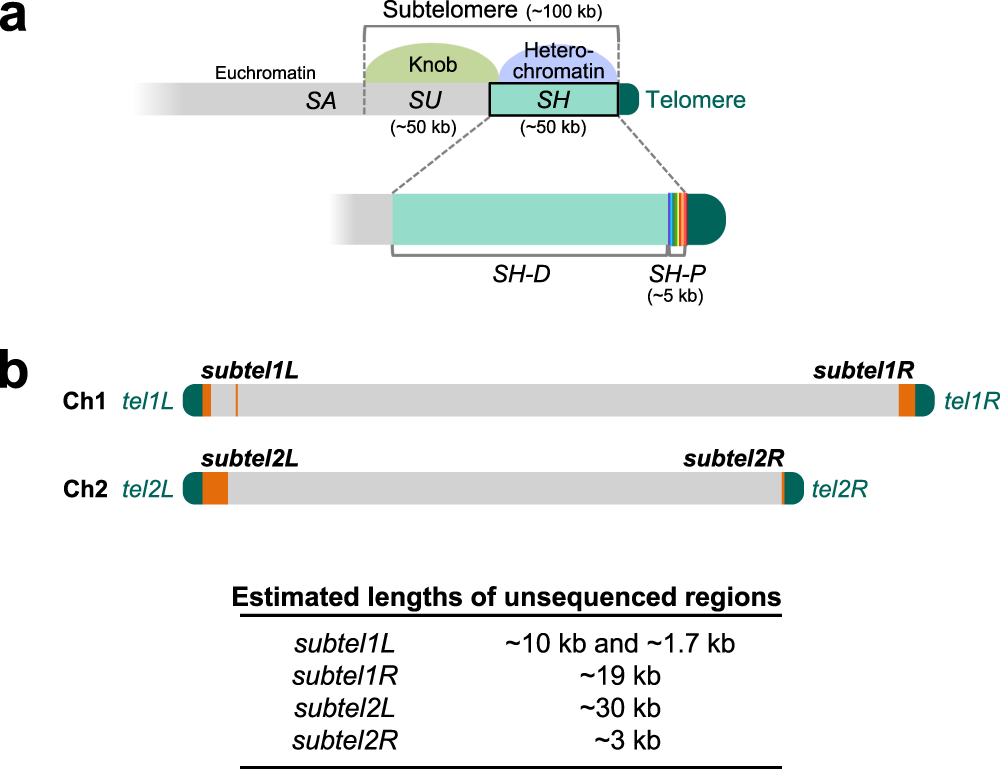
a Schematic illustration of the structures of subtelomeres (~100 kb) of Ch1 and Ch2 in strain 972. The SH region (~50 kb) shows high sequence identity (>90%) with other subtelomeres. Subtelomeric heterochromatin is formed around the SH region21. An SH sequence is composed of two characteristic regions, SH-P (~5 kb) and SH-D. In contrast, the SH-adjacent SU region (~50 kb) shows low sequence identities with other subtelomeres, but forms a highly condensed knob structure that is shared among them24. SA indicates a subtelomere-adjacent euchromatin region. b Schematic illustration of unsequenced regions of subtelomeres in Ch1 and Ch2 of strain 972 according to PomBase (indicated by orange boxes). Tel1L, tel1R, tel2L, and tel2R indicate telomeres at the left and right arms of Ch1 and those of Ch2, respectively. Subtel1L, subtel1R, subtel2L, and subtel2R indicate subtelomeres at the left and right arms of Ch1 and those of Ch2, respectively. Lengths of unsequenced regions are estimated based on the assumption that these SH sequences show high similarity with that of subtel2R of PomBase. Note that Ch3 is omitted in this panel (see Fig. 2a for the ends of Ch3 in strain 972).
