Fig. 1: Characterization of the epiHSP70s probes through affinity purification techniques.
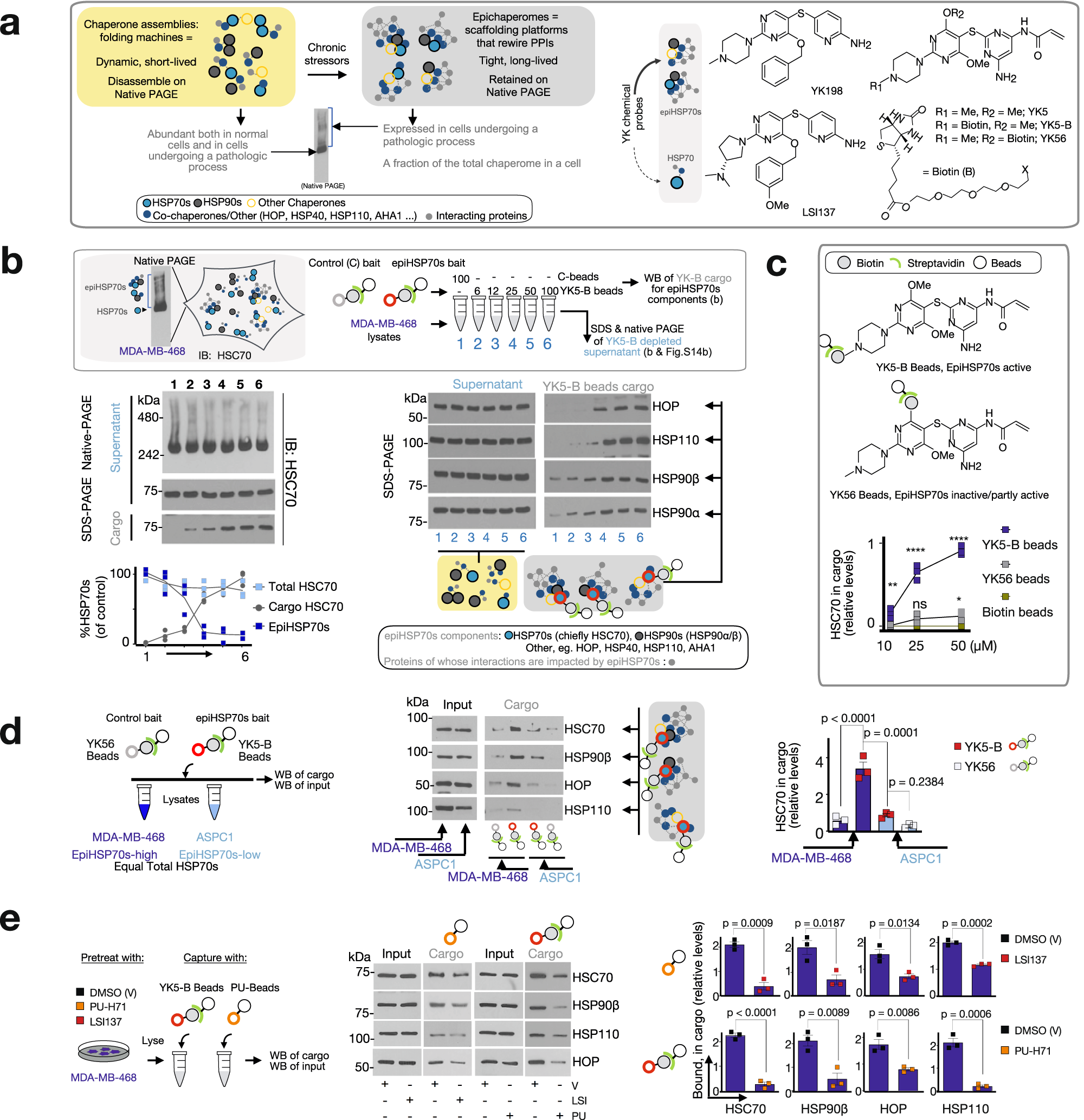
a Schematic showing the biochemical and functional distinctions between epiHSP70s and HSP70s (left). Chemical structure of several YK-type ligands (right). See also Supplementary Figs. 1–13. b, c Affinity purifications with indicated probe concentrations performed in MDA-MB-468 cell homogenates. Data are presented as mean, two-way ANOVA, n = 3, p < 0.0001, F (2, 36) = 80.18 (b) and two-way ANOVA, n = 3, p < 0.0001, F (2, 18) = 390.4 (c), with Dunnett’s post-hoc. YK5-B versus Control, p = 0.0013, p < 0.0001 and p < 0.0001 and YK56 versus Control, p = 0.9796, p = 0.0655 and p < 0.0116 at 10, 25 and 50 µM, respectively. See also Supplementary Fig. 14a–c. d Epichaperome components captured by the YK5-B probe and the control probe YK56 in epiHSP70s-high (MDA-MB-468) and -low (ASPC1) cancer cells, which have equal total chaperone levels, as indicated. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m., one-way ANOVA, n = 3, p < 0.0001, F (3, 8) = 49.61, with Tukey’s post-hoc. e EpiHSP70s components captured by the probes in cells pre-treated with vehicle, LSI137 (1 µM) or PU-H71 (1 µM), as indicated. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m., n = 3, unpaired two-tailed t-test; df = 4; PU-beads: t = 8.878, 3.823, 4.226, and 12.50 and YK5-B beads: t = 16.04, 4.759, 4.802 and 9.947 for HSC70, HSP90β, HOP and HSP110, respectively. d, e Protein amount loaded for Input represents 10% of the protein amount incubated with the beads. Abbreviations: HSP90, heat shock protein 90; HSC70, heat shock cognate 70; HOP, HSP-organizing protein; AHA1, activator of HSP90 ATPase activity 1. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
